| Cas No.: | 353-09-3 |
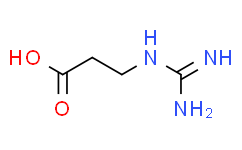
| Chemical Name: | 3-Guanidinopropionic acid |
| Synonyms: | 3-Guanidinopropanoic acid;3-guanidinopropionic acid;beta-guanidinopropionic acid;Guanidinopropionic Acid;3-Guanidinopropionic Acid;3-(diaminomethylideneamino)propanoic acid;GUANIDINOPROPIONIC ACID(P);3-carbamimidamidopropanoic acid;3-guanidinepropionic acid;3-Guanidinopropanoate;A-alanine;n-carbamimidoyl-;β-Guanidinopropionic acid;Guanidine propionate;beta-GPA;N-(Aminoiminomethyl)-beta-alanine;Beta-Guanadinopropionate;3-Guanidino-propionic acid;UL1984YRKA;KMXXSJLYVJEBHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N;b-Guanidinopropionate;PNU 10483;guanidinepropionic acid;Guanidinoprop |
| SMILES: | O([H])C(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])/N=C(\N([H])[H])/N([H])[H])=O |
| Formula: | C4N3O2H9 |
| M.Wt: | 131.1332 |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | RGX-202 is an oral small-molecule SLC6A8 transporter inhibitor. RGX-202 robustly inhibits creatine import in vitro and in vivo, reduces intracellular phosphocreatine and ATP levels, and induces tumor apoptosis. RGX-202 can be used for the research of cancer[1]. |
| In Vivo: | RGX-202 (800 mg/kg; p.o. for 35 days) reduces UN-KPC-961 pancreatic tumoral creatine levels in B6129SF1/J mice[1]. RGX-202 (approximately 650 mg/kg; i.p. daily for 14 days) treatment reduces Lvm3b cells liver metastatic colonization by eightfold in NOD-SCID mice[1]. Animal Model: UN-KPC-961 pancreatic tumor-bearing B6129SF1/J mice[1] Dosage: 800 mg/kg Administration: p.o. for 35 days Result: Suppressed tumoral d3-creatine import by 50% at 800 mg/kg. Animal Model: 6- to 9-week-old C57BL/6J male wild-type mice[1] Dosage: 100, 250, 500 mg/KG in sterile 0.9% NaCl Administration: p.o. for 35 days Result: Inhibited tissue uptake of d3-creatine in a dose-dependent manner by up to 75% at 500 mg/kg. |
| In Vitro: | RGX-202 (10 μM; 96 hours) reduces cell growth, and reveals a nearly complete depletion of phosphocreatine (>99%), greater than 79% reduction in cellular creatine and a substantial (46%) reduction in intracellular ATP levels relative to control cells in hypoxia[1]. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.