| Cas No.: | 69075-42-9 |
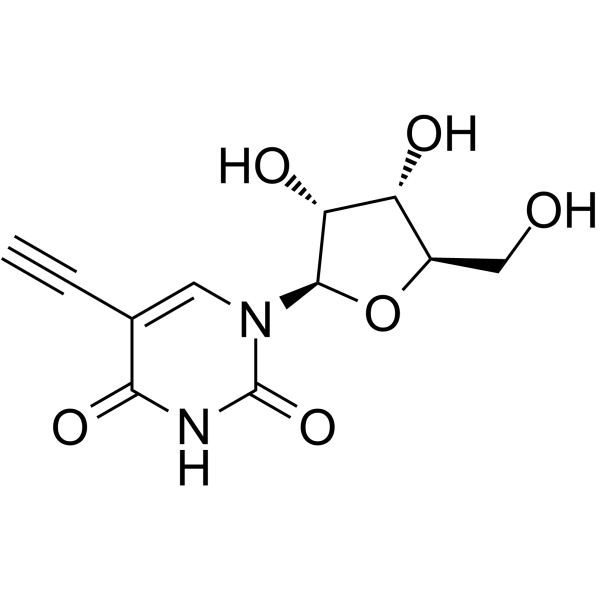
| Chemical Name: | 5-Ethynyluridine |
| Synonyms: | 5-Ethynyluridine;5-Ethynyl uridine;Uridine, 5-ethynyl-;AK163061;QCWBIPKYTBFWHH-FDDDBJFASA-N;AX8294829;1-((2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-5-ethynylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione;5-Ethynyl-uridine (5-EU);5-Ethynyluridine (5-EU) |
| SMILES: | O1[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])O[H])[C@]([H])([C@]([H])([C@]1([H])N1C(N([H])C(C(C#C[H])=C1[H])=O)=O)O[H])O[H] |
| Formula: | C11H12N2O6 |
| M.Wt: | 268.2228 |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | 5-Ethynyluridine (5-EU) is a potent cell-permeable nucleoside can be used to label newly synthesized RNA. 5-Ethynyluridine can be used for isolation and sequencing of nascent RNA from neuronal populations in vivo. 5-Ethynyluridine can be used to identify changes in transcription in vivo in nervous system disease models. |
| In Vivo: | 5-Ethynyluridine (75 mM in PBS for 1 µl; intracerebellar injection ) shows a labeling of central nervous system cells in mouse[1]. 5-Ethynyluridine (330-750 µMol/g; i.p.) results in in labelling of nascent RNA in cells of multiple organs and tissues, but not in the central nervous system in mouse[1]. |
| References: | [1]. Van't Sant LJ, et al. In vivo 5-ethynyluridine (EU) labelling detects reduced transcription in Purkinje cell degeneration mouse mutants, but can itself induce neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021 May 21;9(1):94. [2]. Jao CY, et al. Exploring RNA transcription and turnover in vivo by using click chemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Oct 14;105(41):15779-84. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.