| Cas No.: | 133550-35-3 |
| Chemical Name: | Tyrphostin B48 |
| Synonyms: | 2-Propenamide,2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-N-phenyl-, (2E)-;Tyrphostin AG 494;(E)-2-Cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-N-phenyl-2-propenamide;2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-N-phenylprop-2-enamide;AG 494;AG-494;TYRPHOSTIN B48;HMS3266B19;Tyrphostin 48;(E)-2-Cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-N-phenylacrylamide;AG 494 (Tyrphostin AG 494);-2-Cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl);A-CYANO-(3,4-DIHYDROXY)-N-PHENYLCINNAMIDE;A-CYANO-(3,4-DIHYDROXY)-N-PHENYLCINNAMAMIDE;ALPHA-CYANO-(3,4-DIHYDROXY)-N-PHENYLCINNAMIDE;N-PHENYL-3,4-DIHYDROXYBENZYLIDENECYANOACETAMIDE;Lopac0_001147;MLS002172496;BDBM4304;cid_5328771;HMS3678I07;HMS3263F15;HMS2232N04 |
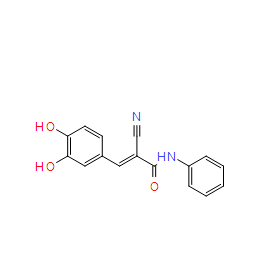
| SMILES: | O([H])C1=C(C([H])=C([H])C(/C(/[H])=C(\C#N)/C(N([H])C2C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=2[H])=O)=C1[H])O[H] |
| Formula: | C16H12N2O3 |
| M.Wt: | 280.2781 |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | AG-494 (Tyrphostin AG 494) is a potent and selective EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (IC50=0.7 μM). AG-494 inhibits the autophosphorylation of EGFR, ErbB2, HER1-2 and PDGF-R with IC50s 1.1, 39, 45 and 6 μM, respectively. AG-494 blocks Cdk2 activation and inhibits EGF-dependent DNA synthesis[1][2][3]. |
| Target: | EGFR:0.7 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro: | In DHER-14 cells, AG 494 inhibits Cdk2 activation and EGF-dependent DNA synthesis[2]. AG-494 significantly prevents NF-kB activation in silica-stimulated cells, and also reduces NF-kB activation in H2O2-treated cells[4]. AG-494 (3-9 μM; 5-7 days) inhibits BMP9-induced ALP activity in a dose-dependent manner[5]. |
| References: | [1]. Gazit A, et al. Tyrphostins. 2. Heterocyclic and alpha-substituted benzylidenemalononitrile tyrphostins as potent inhibitors of EGF receptor and ErbB2/neu tyrosine kinases. J Med Chem. 1991;34(6):1896-1907. [2]. Osherov N, et al. Tyrphostin AG 494 blocks Cdk2 activation. FEBS Lett. 1997;410(2-3):187-190. [3]. Osherov N, et al. Selective inhibition of the epidermal growth factor and HER2/neu receptors by tyrphostins. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11134-42. [4]. Liu X, Qin J, et al. Cross-talk between EGF and BMP9 signalling pathways regulates the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2013;17(9):1160-1172. [5]. Jihee Lee Kang, et al. SILICA-INDUCED NUCLEAR FACTOR- k B ACTIVATION: INVOLVEMENT OF REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES AND PROTEIN TYROSINE KINASE ACTIVATION. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part A. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.