| Cas No.: | 733750-99-7 |
| Chemical Name: | N-(2-Fluoro-4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-6-(4-(3-isopropyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)piperidin-1-yl)-5-nitropyrimidin-4-amine |
| Synonyms: | N-(2-Fluoro-4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-6-(4-(3-isopropyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)piperidin-1-yl)-5-nitropyrimidin-4-amine;AR 231453;N-(2-FLUORO-4-METHANESULFONYLPHENYL)-(6-[4-(3-ISOPROPYL-[1,2,4]OXADIAZOL-5-YL)-PIPERIDIN-1-YL]-5-NITRO-PYRIMIDIN-4-YL)A...;(2-fluoro-4-methanesulfonyl-phenyl)-{6-[4-(3-isopropyl-[1,2,4]oxadiazol-5-yl)-piperidin-1-yl]-5-nitropyrimidin-4-yl}-amine;(2-fluoro-4-methanesulfonyl-phenyl)-{6-[4-(3-isopropyl-[1,2,4]oxadiazol-5-yl)-piperidin-1-yl]-5-nitro-pyrimidin-4-yl}-amine;AK120688;AR-231453;CHEBI:550644;CHEMBL461384;KB-145984;SureCN114213;UNII-07Z1P4981I;(2-Fluoro-4-methanesulfonylphenyl)-(6-[4-(3-isopropyl-[1,2,4]oxadiazol-5-yl)-piperidin-1-yl]-5-nitropyrimidin-4-yl)amine |
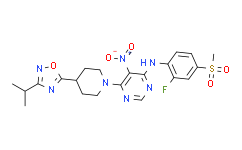
| SMILES: | CC(C)C1=NOC(C2CCN(C3=NC=NC(NC4=CC=C(S(=O)(C)=O)C=C4F)=C3[N+]([O-])=O)CC2)=N1 |
| Formula: | C21H24N7O5FS |
| M.Wt: | 505.52256 |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | AR231453 is a potent and selective small molecule agonist of GPR119 that enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) release; Antidiabetic agent. |
| In Vivo: | AR231453 also enhanced glucose-dependent insulin release in vivo and improved oral glucose tolerance in wild-type mice but not in GPR119-deficient mice. Diabetic KK/A(y) mice were also highly responsive to AR231453. Orally active GPR119 agonists may offer significant promise as novel antihyperglycemic agents acting in a glucose-dependent fashion [1]. When administered in mice, AR231453 increased active GLP-1 levels within 2 min after oral glucose delivery and substantially enhanced total glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide levels. Blockade of GLP-1 receptor signaling with exendin(9-39) reduced the ability of AR231453 to improve glucose tolerance in mice [2]. |
| In Vitro: | The GPR119-specific agonist AR231453 significantly increased cAMP accumulation and insulin release in both HIT-T15 cells and rodent islets. In both cases, loss of GPR119 rendered AR231453 inactive [1]. In GLUTag cells, a well-established model of intestinal L-cell function, the potent GPR119 agonist AR231453 stimulated cAMP accumulation and GLP-1 release [2]. |
| References: | [1]. Chu ZL, et al. A role for beta-cell-expressed G protein-coupled receptor 119 in glycemic control by enhancing glucose-dependent insulin release. Endocrinology. 2007 Jun;148(6):2601-9. [2]. Chu ZL, et al. A role for intestinal endocrine cell-expressed g protein-coupled receptor 119 in glycemic control by enhancing glucagon-like Peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic Peptide release. Endocrinology. 2008 May;149(5):2038-47. [3]. Semple G, et al. Discovery of the first potent and orally efficacious agonist of the orphan G-protein coupled receptor 119. J Med Chem. 2008 Sep 11;51(17):5172-5. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.