| Cas No.: | 739366-20-2 |
| Synonyms: | Suiny;SK-0403 |
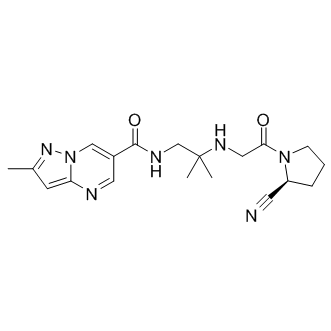
| SMILES: | O=C(C1=CN2C(N=C1)=CC(C)=N2)NCC(C)(NCC(N3[C@H](C#N)CCC3)=O)C |
| Formula: | C19H25N7O2 |
| M.Wt: | 383.4475 |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | Anagliptin is a potent and selective DPP-4 inhibitor(IC50= 3.8 nM); > 10 fold less potent for DPP-8 and DPP-9. in vitro: In THP-1 cells, anagliptin reduced lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α production with inhibiting ERK phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-κB . lipopolysaccharide (LPS)- or palmitate-induced elevations of inflammatory cytokine mRNA expressions in RAW264.7 macrophages were shown to be significantly suppressed by co-incubation with a DPP-4 inhibitor, anagliptin (10μM), despite low DPP-4 expression in the RAW264.7 cells. Anagliptin also acted on 3T3-L1 adipocytes, weakly suppressing the inflammatory cytokine expressions induced by LPS and TNF-α. When 3T3-L1 and RAW cells were co-cultured and stimulated with LPS, the effects of anagliptin on the suppression of cytokine expressions in 3T3-L1 adipocytes were more marked, and became evident at the 10μM concentration. in vivo: Treatment with anagliptin for 16 wk significantly reduced accumulation of monocytes and macrophages in the vascular wall, SMC content in plaque areas, and oil red O-stained area around the aortic valve without affecting glucose tolerance or body weight. Quantitative analysis also showed that anagliptin reduced the area of atherosclerotic lesion in apoE-deficient mice. Anti-inflammatory effects of anagliptin were also observed in vivo on the elevated hepatic and adipose expressions and serum concentrations of inflammatory cytokines in association with the suppression of hepatic NF-κB transcriptional activity, in LPS-infused mice. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.