| Cas No.: | 20153-98-4 |
| Chemical Name: | DILAZEP DIHYDROCHLORIDE |
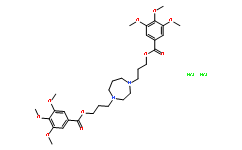
| SMILES: | Cl.Cl.COC1=C(OC)C(OC)=CC(C(=O)OCCCN2CCN(CCCOC(=O)C3=CC(OC)=C(OC)C(OC)=C3)CCC2)=C1 |
| Formula: | C31H44N2O10.2[HCl] |
| M.Wt: | 677.61034 |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | Dilazep dihydrochloride is an inhibitor of adenosine uptake. Dilazep dihydrochloride has cerebral and coronary vasodilating action through enhancement of effect of adenosine. Dilazep dihydrochloride also inhibits the ischemic damage, platelet aggregation, and membrane transport of nucleosides[1][2]. |
| Target: | Adenosine uptake |
| In Vivo: | After administration of Dilazep, even low doses (0.04-0.1 mg/kg/min) of exogenous adenosine significantly increases superior mesenteric arterial conductance (SMAC) and elevates arterial plasma adenosine concentration. The increased adenosine levels were highly correlated with the increased percentage of change of SMAC and values for Rmax and EC50 were 193.4% change of SMAC and 2.8 μM, respectively. Administration of bolus doses of 8-phenyltheophylline abolishes the ability of Dilazep to potentiate vasodilation, but did not affect isoproterenol-induced relaxation[1]. Dilazep inhibits the phospholipase activation in reperfused heart mitochondria and also inhibits the lipid peroxidation caused by cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Dilazep may prevent ischemic cerebral injury due to an increase in cerebral blood flow and/or its protective effects on vascular endothelial cell membrane[1]. |
| In Vitro: | The uptake mechanism has been studied extensively in vitro and Dilazep, NBI and Dipyridamole have been reported to inhibit the uptake of adenosine into different cells. Of these compounds, Dilazep and NBI are almost 10 times more potent than Dipyridamole. In addition, only Dilazep is water soluble and no solubility aiding organic solvent is needed for preparing an aqueous solution[1]. |
| References: | [1]. Zhang Y, et al. Dilazep potentiation of adenosine-mediated superior mesenteric arterial vasodilation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Sep;258(3):767-71. [2]. Kawagoe J, et al. Effect of dilazep dihydrochloride against ischemia and reperfusion-induced disruption of blood-brain barrier in rats: a quantitative study. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;345(4):485-8. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.