| Cas No.: | 4727-31-5 |
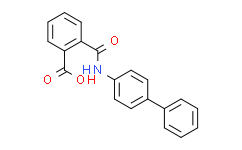
| Chemical Name: | 2-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-ylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid |
| Synonyms: | 2-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-ylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid;Kartogenin;2-?[(Biphenyl-?4-?yl)?carbamoyl]?benzoic acid;2-[([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-ylaMino)carbonyl]benzoic Acid;KGN;2-(biphenyl-4-ylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid;AC1MCUNV;CBDivE_009769;Maybridge3_004725;Oprea1_848730;SureCN1336628;2-[(Biphenyl-4-yl)carbamoyl]benzoic acid;4′-Phenyl-phthalanilic acid (8CI) |
| SMILES: | O=C(O)C1=CC=CC=C1C(NC2=CC=C(C3=CC=CC=C3)C=C2)=O |
| Formula: | C20H15NO3 |
| M.Wt: | 317.338 |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | Kartogenin is an inducer of differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes. |
| In Vivo: | hen injected into intact rat patellar tendons, kartogenin induces cartilage-like tissue formation in the injected area. When injected into experimentally injured rat Achilles TBJs, wound healing in the TBJs is enhanced, as evidenced by the formation of extensive cartilage-like tissues[1]. Kartogenin stimulates collagen synthesis in the mouse dermis. Dermis in the kartogenin (100 nM)-treated group exhibits increased dermal thickness and intense blue staining, which represents more collagen composition in the dermis[2]. |
| In Vitro: | Kartogenin enhances cell proliferation in both cell types in a concentration-dependent manner and induces chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells, as demonstrated by high expression levels of chondrogenic markers aggrecan, collagen II and Sox-9. Besides, kartogenin induces the formation of cartilage-like tissues in cell cultures, as observed through the staining of abundant proteoglycans, collagen II and osteocalcin[1]. Kartogenin stimulates type-I collagen synthesis of fibroblasts at the mRNA and protein levels in a time-dependent manner without obvious influence on fibroblasts’ apoptosis and viability. Smad4/smad5 of the TGF-β signaling pathway is activated by kartogenin while MAPK signaling pathway remains unchanged[2]. Kartogenin treatment enhances chondrocyte pericellular matrix assembly and retention in the presence of IL-1β. Kartogenin partially blocks the IL-1β-induced increased expression of ADAMTS-5. Additionally, kartogenin-treated articular chondrocytes exhibits a decrease in CD44 proteolytic fragmentation[3]. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.