| Cas No.: | 53882-12-5 |
| Chemical Name: | Lodoxamide |
| Synonyms: | Lodoxamide;2-[2-chloro-5-cyano-3-(oxaloamino)anilino]-2-oxoacetic acid;Acetic acid,2,2'-((2-chloro-5-cyano-1,3-phenylene)diimino)bis(2-oxo;Alomide (TN);diesters of N,N'-(2-chloro-5-cyano-m-phenylene)dioxamic acid;Lodoxamida;Lodoxamida [INN-Spanish];Lodoxamidum;Lodoxamidum [INN-Latin];N,N'-(2-Chlor-5-cyan-3-phenylen)dioxamsaeure;N,N'-(2-Chlor-5-cyan-m-phenylen)-dioxamsaeure;N-N'-(2-chloro-5-cyano-m-phenylene)dioxamic acid;UNII-SPU695OD73;2,2′-[(2-Chloro-5-cyano-1,3-phenylene)diimino]bis-2-oxoacetic acid |
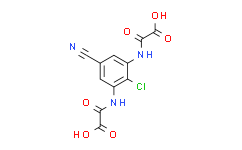
| SMILES: | OC(C(NC1=C(Cl)C(NC(C(O)=O)=O)=CC(C#N)=C1)=O)=O |
| Formula: | C11N3O6ClH6 |
| M.Wt: | 311.6348 |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | Lodoxamide is an antiallergic compound acting as a mast-cell stabilizer for the treatment of asthma and allergic conjunctivitis. |
| In Vivo: | Lodoxamide has been demonstrated to have cromolyn-like activity when studied in the rat peritoneal mast cell assay (PCA) model3 and in Ascaris antigen-sensitized rhesus monkeys. When given intravenously, orally, or intrabronchially by aerosol, lodoxamide significantly inhibits the increased respiratory frequency and decreased tidal volume induced by antigen challenge in Ascaris-sensitized. anesthetized rhesus monkeys[1]. Addition of lodoxamide tromethamine to Euro-Collins or University of Wisconsin solution results in a marked decrease in lung reperfusion injury as demonstrated by increased oxygenation, decreased microvascular permeability, and increased compliance[3]. Patients treated with lodoxamide tromethamine demonstrate an improvement in daytime breathing difficulty, cough, sputum production, and sleep[4]. |
| In Vitro: | Lodoxamide inhibits compound 48/80-induced histamine release and ionophore-induced 45Ca influx with associated histamine release in purified rat peritoneal mast cells[1]. The chemotactic response of eosinophils to fMLP as well as to IL-5 is significant and dose-dependent inhibited by Lodoxamide. Lodoxamide is also able to strongly inhibit the release of eosinophil peroxidase after IgA-dependent activation and, to a lesser extent, the release of eosinophil cationic protein and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin[2]. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.