| Cas No.: | 212844-53-6 |
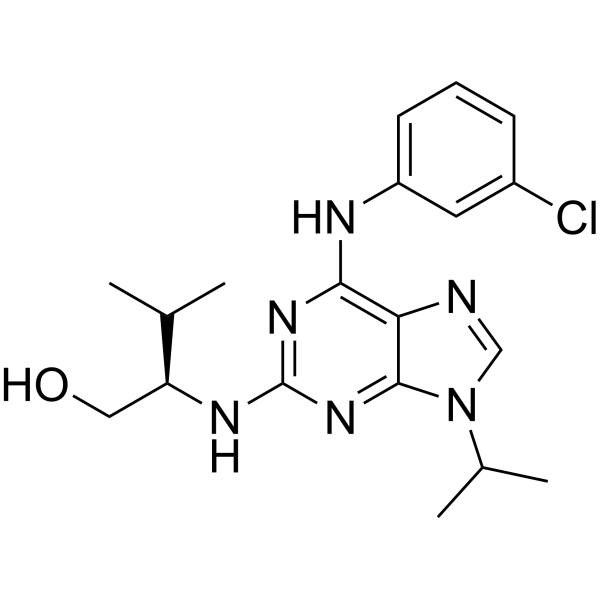
| Chemical Name: | (2R)-2-[[6-[(3-Chlorophenyl)amino]-9-(1-methylethyl)-9H-purin-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-butanol |
| Synonyms: | NG 60,NG60,NG-60 |
| SMILES: | CC(C)[C@H](CO)NC1=NC2=C(C(=N1)NC3=CC(=CC=C3)Cl)N=CN2C(C)C |
| Formula: | C19H25ClN6O |
| M.Wt: | 388.89 |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | Purvalanol A is a potent CDK inhibitor, which inhibits cdc2-cyclin B, cdk2-cyclin A, cdk2-cyclin E, cdk4-cyclin D1, and cdk5-p35 with IC50s of 4, 70, 35, 850, 75 nM, resepctively. |
| Target: | cdc2-cyclin B:4 nM (IC50) cdk2-cyclin E:35 nM (IC50) cdk2-cyclin A:70 nM (IC50) cdk4-cyclin D1:850 nM (IC50) cdk5-p35:75 nM (IC50) erk1:9000 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro: | Purvalanol A inhibits cdc28 (S. cerevisiae) and erk1 with IC50s of 80 and 9000 nM. Purvalanol A shows inhibitory activities against the NCI panel of 60 human tumor cell lines, with average GI50 of 2 μM; two cell lines show an ∼20-fold increase in sensitivity to purvalanol A: the KM12 colon cancer cell line with a GI50 of 76 nM and the NCI-H522 non–small cell lung cancer cell line with a GI50 of 347 nM[1]. Purvalanol A is a 2.5-fold more potent inhibitor of CDK2, but also inhibits DYRK1A potently and a number of other protein kinases in the low micromolar range. Purvalanol A inhibits MKK1, MAPK2/ERK2, JNK/SAPK1c with IC50s of 80, 26, 84 μM[2]. Purvalanol A selectively inhibits the phosphorylation of cellular proteins. Purvalanol A prevents the increases of the contents of cyclins D and E during serum-induced G1 phase progression. Purvalanol A does not inhibit transcription under cell-free conditions[3]. |
| References: | [1]. Gray NS, et al. Exploiting chemical libraries, structure, and genomics in the search for kinase inhibitors. Science. 1998 Jul 24;281(5376):533-8. [2]. Bain J, et al. The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors: an update. Biochem J. 2003 Apr 1;371(Pt 1):199-204. [3]. Villerbu N, et al. Cellular effects of purvalanol A: a specific inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase activities. Int J Cancer. 2002 Feb 20;97(6):761-9. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.