| Cas No.: | 160162-42-5 |
| Chemical Name: | SR 11302 |
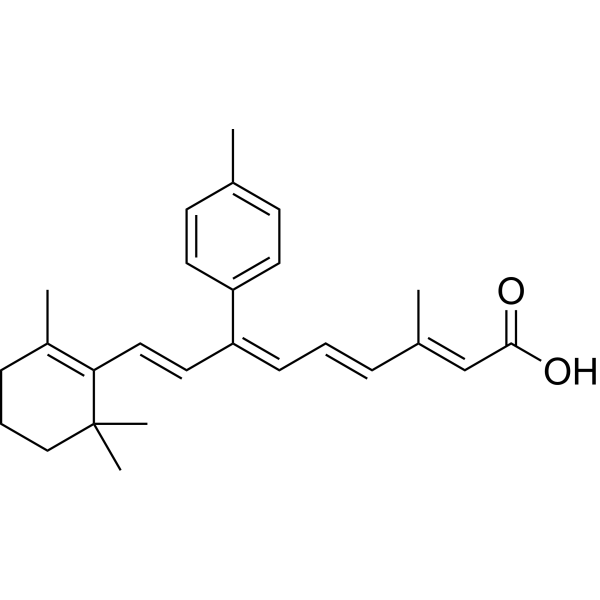
| SMILES: | OC(=O)C=C(C)C=CC=C(C=CC1C(C)(C)CCCC=1C)C2=CC=C(C)C=C2 |
| Formula: | C26H32O2 |
| M.Wt: | 376.53108 |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Sotrage: | Powder-20°C3 yearsIn solvent-80°C6 months-20°C1 month |
| Description: | SR 11302 is an activator protein-1 (AP-1) transcription factor inhibitor. SR 11302 is a retinoid that specifically inhibits AP-1 activity without activating the transcription of retinoic acid response element (RARE)[1]. |
| Target: | AP-1[1] |
| In Vivo: | SR 11302 (SR11302; low dose 0.5 mg/kg and high dose 1 mg/kg body weight; orally gavaged daily) treatment reduces the total vascular lesion number and lesion size in Vldlr-/- mice in a dose-dependent manner[4]. Animal Model: Vldlr-/- mice[4] Dosage: Low dose 0.5 mg/kg and high dose 1 mg/kg body weight Administration: Orally gavaged daily from P5 to P15 Result: High-dose from P5 to P15 reduced the total vascular lesion number by 48% and decreased the lesion size by 40%, without detectable signs of toxicity in mice, including no change in body weight. |
| In Vitro: | SR 11302 (SR11302) show strong anti-AP-1 activity with selective binding with RARα and RARγ, but not with RARβ and RXRα[1]. SR 11302 (SR-11302; 1 μM) inhibits AP-1 transcription factor activity and decreases aldosterone levels by 61.9% in hypoxia-treated cells[2]. SR 11302 (SR-11302; 2 µM; 48 hours) inhibits Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-induced cell proliferation in adenocarcinoma gastric (AGS) cells[3]. SR 11302 (2 µM; 24 hours) inhibits H. pylori-induced expression of β-catenin and c-myc in AGS cells[3]. |
| References: | [1]. C Huang, et al. Blocking activator protein-1 activity, but not activating retinoic acid response element, is required for the antitumor promotion effect of retinoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 May 27;94(11):5826-30. [2]. Bradley A Maron, et al. Upregulation of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein by hypoxia stimulates aldosterone synthesis in pulmonary artery endothelial cells to promote pulmonary vascular fibrosis. Circulation. 2014 Jul 8;130(2):168-79. [3]. Eunyoung Byun, et al. Activation of NF-κB and AP-1 Mediates Hyperproliferation by Inducing β-Catenin and c-Myc in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Epithelial Cells. Yonsei Med J. 2016 May;57(3):647-51. [4]. Ye Sun, et al. Inflammatory signals from photoreceptor modulate pathological retinal angiogenesis via c-Fos. J Exp Med. 2017 Jun 5;214(6):1753-1767. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.