| Cas No.: | 214358-33-5 |
| Chemical Name: | 1400W HCl |
| Synonyms: | 1400 W Dihydrochloride;1400W (Dihydrochloride);1400W (hydrochloride);N-(3-(Aminomethyl)benzyl)acetamidine Dihydrochloride;NULL;1400W dihydrochloride;1400 W;1400W 2HCl;N-(3-(Aminomethyl)Benzyl)Acetimidamide Dihydrochloride;N-(3-Aminomethyl)benzylacetamidine, 2HCl;N-[[3-(AMINOMETHYL)PHENYL]METHYL]-ETHANIMIDAMIDE DIHYDROCHLORIDE;WDJHSQZCZGPGAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N;BS0225;1204AH;s8337;TRA0076918;1400W dihydrochloride, & |
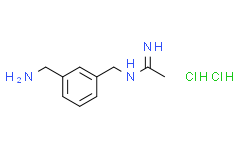
| SMILES: | Cl[H].Cl[H].N(=C(/C([H])([H])[H])\N([H])[H])/C([H])([H])C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C(C([H])([H])N([H])[H])=C1[H] |
| Formula: | C10H17Cl2N3 |
| M.Wt: | 250.167 |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Sotrage: | 4°C for 1 year, -20°C for more than 2 years |
| Description: | 1400W dihydrochloride is a potent and selective inhibitor of human inducible NO synthase with Ki values of 7 nM. |
| Target: | Ki: 7 nM (iNOS), 2 µM (nNOS), 50 µM (eNOS)[1] |
| In Vivo: | 1400W potently (ED50=0.3 mg/kg) reduces the delayed vascular injury in rats attributable to LPS-induced iNOS but fails to exacerbate acute vascular leakage when given concurrently with LPS[1]. Administration of 1400W lowers NOx levels in all the experimental groups. In addition, lipid peroxidation, the percentage of apoptotic cells, and nitrated protein expression fall in the late post-hypoxia period (48 h and 5 days)[3]. |
| In Vitro: | 1400W is a slow, tight binding inhibitor of human inducible nitric- oxide synthase (iNOS). The slow onset of inhibition by 1400W shows saturation kinetics with a maximal rate constant of 0.028 s-1 and a binding constant of 2.0 μM. Inhibition is dependent on the cofactor NADPH. 1400W is at least 5000-fold selective for iNOS versus eNOS. In contrast, inhibition of human neuronal NOS and endothelial NOS (eNOS) is relatively weaker, rapidly reversible, and competitive with L-arginine, with Ki values of 2 μM and 50 μM, respectively[1]. 1400W treatment inhibits iNOS expression without affecting nNOS or eNOS. 1400W also reduces NO, 3-NT and MDA production, and prevents neuronal cell apoptosis in cerebral cortex[2]. |
| Animal Administration: | Rats: The effects of 1400W on plasma leakage are assessed in rats by determining the leakage of [125I]human serum albumin from plasma into organs. 1400W (0.1-10 mg/kg, subcutaneous) is dissolved in isotonic saline and administered either concurrently with endotoxin or 3 h following LPS administration (E. coli LPS, 3 mg/kg intravenously). Plasma leakage is then assessed 1 or 5 h after delivery of 1400W[1]. |
| References: | [1]. Garvey EP, et al. 1400W is a slow, tight binding, and highly selective inhibitor of inducible nitric-oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1997 Feb 21;272(8):4959-63. [2]. Shi Q, et al. 1400W ameliorates acute hypobaric hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cognitive deficits by suppressing the induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat cerebral cortex microglia. Behav Brain Res. 2017 Feb 15;319:188-199. [3]. Rus A, et al. Inducible NOS inhibitor 1400W reduces hypoxia/re-oxygenation injury in rat lung. Redox Rep. 2010;15(4):169-78. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.