| Cas No.: | 5352-53-4 |
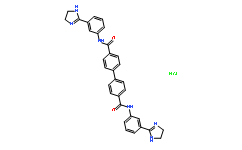
| Chemical Name: | [1,1'-Biphenyl]-4,4'-dicarboxamide,N4,N4'-bis[3-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)phenyl]-, hydrochloride (1:2) |
| Synonyms: | BPH-1358;BPH 1358;BPH1358 |
| SMILES: | Cl.O=C(NC1C=C(C=CC=1)C2=NCCN2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(=O)NC5C=C(C=CC=5)C6=NCCN6 |
| Formula: | C32H28N6O2.HCl |
| M.Wt: | 565.06466 |
| Sotrage: | Please store the product under the recommended conditions in the Certificate of Analysis. |
| Publication: | [1]. Zhu W, et al. Antibacterial drug leads: DNA and enzyme multitargeting. J Med Chem. 2015 Feb 12;58(3):1215-27. [2]. Liu YL, et al. Farnesyl diphosphate synthase inhibitors with unique ligand-binding geometries. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015 Jan 29;6(3):349 |
| Description: | BPH-1358 (NSC50460) is a potent human farnesyl diphosphate synthase (FPPS) and undecaprenyl diphosphate synthase (UPPS) inhibitor with IC50s of 1.8 μM and 110 nM, respectively, and is active against S. aureus in vitro (MIC ~250 ng/mL)[1][2]. |
| In Vivo: | BPH-1358 is active against S. aureus in vivo (20/20 mice survived in an i.p. infection model with a MRSA strain)[1]. |
| In Vitro: | BPH-1358 is the most potent inhibitor of both E. coli UPPS (EcUPPS) as well as S. aureus UPPS (SaUPPS) with an IC50 of 110 nM. BPH-1358 against E. coli and S. aureus with EC50 of 300 nM and 290 nM, respectively[1]. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.