| Cas No.: | 1198300-79-6 |
| Chemical Name: | Cerdulatinib free base |
| Synonyms: | PRT062070; PRT2070; PRT-062070; PRT-2070; PRT 062070; PRT 2070 |
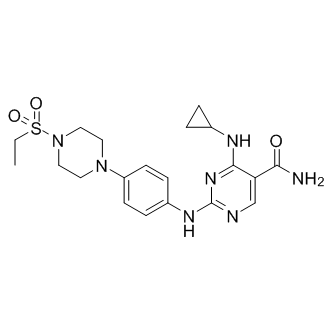
| SMILES: | O=S(N(CC1)CCN1C2=CC=C(NC3=NC=C(C(N)=O)C(NC4CC4)=N3)C=C2)(CC)=O.Cl |
| Formula: | C20H27N7O3S |
| M.Wt: | 445.54 |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | Cerdulatinib (PRT062070) is a dual JAK and SYK inhibitor with IC50s of 12, 6, 8 and 32 for JAK1, 2, 3 and SYK, respectively. |
| In Vivo: | PRT062070 (0.5 mg/kg) results in a nonstatistically significant trend toward reduced ankle inflammation, whereas significant reductions in inflammation are achieved with the 1.5, 3, and 5 mg/kg doses. PRT062070 also affects anticollagen antibody formation. PRT062070 (15 mg/kg) suppresses upregulation of splenic B-cell surface CD80/86 and CD69, and inhibits BCR signaling and activation in the spleen after oral dosing in mice[2]. |
| In Vitro: | Cerdulatinib shows inhibitory effect on 60 CLL with IC50 ranging from 0.37 to 10.02 µM. Cerdulatinib induces apoptosis in CLL in association with MCL-1 down-regulation and PARP cleavage. Cerdulatinib (2μM) is able to overcome the support of the microenvironment and induces CLL cell death. Cerdulatinib (250-500 nM) blocks proliferation of ibrutinib-sensitive and ibrutinib-resistant primary CLL cells. Cerdulatinib also blocks proliferation of both ibrutinib-sensitive and ibrutinib-resistant primary CLL cells as well as BTKC481S-transfected cell lines, and blocks BCR and JAK-STAT signaling pathways. Furthermore, inhibition of SYK and JAK by cerdulatinib translates to downstream inhibition of AKT and ERK. Cerdulatinib inhibits the activity of NF-kB pathway[1]. PRT062070 reduces the ability of stimulated B cells to upregulate cell-surface expression of the early activation marker CD69 (IC50=0.11 µM). PRT062070 exhibits differential potency against cytokine JAK/STAT signaling pathways. PRT062070 (1 or 3 µM) induces apoptosis in BCR-signaling competent NHL cell lines[2]. Cerdulatinib demonstrates inhibitory activity against both ABC and GCB subtypes of DLBCL cells. Cerdulatinib also induces apoptosis in both GCB and ABC subtypes of DLBCL cell lines via caspase 3 and PARP cleavage. And cerdulatinib blocks cell cycle in both ABC and GCB subtypes of DLBCL via inhibition of RB phosphorylation and down-regulation of cyclin E. Cerdulatinib induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis under the condition of BCR stimulation in all DLBCL cell lines. Besides, cerdulatinib blocks JAK/STAT and BCR signaling in both ABC and GCB DLBCL cell lines. Cerdulatinib induces cell death in primary human DLBCL samples[3]. Cerdulatinib inhibits BCR-induced signals in a dose-dependent manner and most strongly between 0.3 to 1 μM. and particularly in IGHV-unmutated samples with greater BCR signaling capacity and response to IL4, or samples expressing higher levels of sIgM, CD49d+, or ZAP70+. Cerdulatinib overcomes anti-IgM, IL4/CD40L, or NLC-mediated protection by preventing upregulation of MCL-1 and BCL-XL; however, BCL-2 expression is unaffected. Furthermore, in samples treated with IL4/CD40L, cerdulatinib synergizes with venetoclax in vitro to induce greater apoptosis than either drug alone[4]. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.