| Cas No.: | 132465-11-3 |
| Chemical Name: | CDC |
| Synonyms: | CDC;CINNAMYL-3,4-DIHYDROXY-ALPHA-CYANOCINNAMATE;1-CYCLOHEXYL-3-(3-DIMETHYLAMINOPROPYL)CARBODIIMIDE METHIODIDE(CDC);(E,Z)-2-Cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoic acid 3-phenyl-2-propenyl ester;CINNAMYL-3,4-DIHYDROXY-α-CYANOCINNAMATE;Cinnamyl 3,4-dihydroxy-alpha-cyanocinnamate CDC;1-Cyclohexy1-3-(3-dimethylamino proply)carbodilimide methiodide |
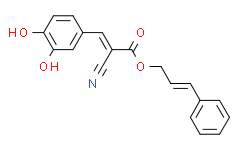
| SMILES: | C1=CC=C(/C=C/COC(/C(/C#N)=C/C2=CC(O)=C(O)C=C2)=O)C=C1 |
| Formula: | C19H15NO4 |
| M.Wt: | 321.326705217361 |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | Cinnamyl-3,4-dihydroxy-α-cyanocinnamate (CDC) is a potent 12/15-Lipoxygenases (LO) inhibitor. Cinnamyl-3,4-dihydroxy-α-cyanocinnamate has the potential for the research of type 1 diabetes mellitus[1]. |
| In Vivo: | The high glucose and 12(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (HETE) could alter vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin and β‐catenin phosphorylation levels, but did not alter total protein expression. However, the 12/15-LO inhibitor, Cinnamyl-3,4-dihydroxy-α-cyanocinnamate (CDC), antagonized the effect of high glucose on protein phosphorylation to mitigate destruction of the endothelial cell barrier, and the mouse diabetes mellitus model further confirmed these conclusions[1]. |
| In Vitro: | High glucose or 12(S)-HETE remarkably increased transendothelial dextran transport, and in combination it was increased further. Addition of the 12/15-LO inhibitor, CDC, partially suppressed dextran transport[1]. |
| References: | [1]. Wang X, et al. 12(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid impairs vascular endothelial permeability by altering adherens junction phosphorylation levels and affecting the binding and dissociation of its components in high glucose-induced vascular injury. J Diabetes Investig. 2019;10(3):639-649. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.