| Cas No.: | 405169-16-6 |
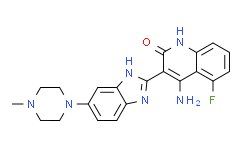
| Chemical Name: | 1-Amino-5-fluoro-3-[6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]quinolin-2-one |
| Synonyms: | 4-Amino-5-fluoro-3-[5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]quinolin-2(1H)-one;Dovitinib (TKI-258, CHIR-258);4-amino-5-fluoro-3- (6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl) quinolin-2(1H)-one;CHIR-258;Dovitinib;Dovitinib (CHIR-258,TKI-258);Dovitinib (TKI-258);Dovitinib-D8;TKI-258;4-amino-5-fluoro-3-(5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)quinolin-2(1H)-one;4-amino-5-fluoro-3-[6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]-1H-quinolin-2-one;4-amino-5-fluoro-3-[6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]quinolin-2(1H)-one;CHIR258;CHIR-258(Dovitinib);CHIR-258(Dovitinib,TKI258);TKI258;Unii-I35H55G906;Dovitinib (TKI258 CHIR258);1-Amino-5-fluoro-3-[6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]quinolin-2-one |
| SMILES: | FC1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C2=C1C([H])=C(C(N2N([H])[H])=O)C1=NC2C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=2N1[H])N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] |
| Formula: | C21H21FN6O |
| M.Wt: | 392.4294 |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | Dovitinib is a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor with IC50s of 1, 2, 8/9, 10/13/8, 27/210 nM for FLT3, c-Kit, FGFR1/3, VEGFR1/2/3 and PDGFRα/β, respectively. |
| In Vivo: | Dovitinib (10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, 60 mg/kg, p.o.) shows significant antitumor effect in the KMS11-bearing mice model, and the growth inhibition is 48%, 78.5%, and 94% in the 10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, and 60 mg/kg treatment arms, respectively, compared with the placebo-treated mice[1]. Dovitinib (50 and 75 mg/kg) results in 97% and 98% tumor growth inhibition, respectively, and the maximal efficacy is at 50 mg/kg[2]. |
| In Vitro: | Dovitinib potently inhibits the FGF-stimulated growth of WT and F384L-FGFR3-expressing B9 cells with IC50 values of 25 nM. B9-MINV cells are resistant to the inhibitory activity of Dovitinib at concentrations up to 1 μM. Dovitinib inhibits cell proliferation of KMS11 (FGFR3-Y373C), OPM2 (FGFR3-K650E), and KMS18 (FGFR3-G384D) cells with IC50 of values of 90 nM (KMS11 and OPM2) and 550 nM, respectively[1]. Dovitinib significantly reduces the basal phosphorylation levels of FGFR-1, FGFR substrate 2α (FRS2-α) and ERK1/2 but not Akt in both SK-HEP1 and 21-0208 cells[2]. Dovitinib enhances the BMP-2-induced alkaline phosphatase (ALP) induction, which is a representative marker of osteoblast differentiation. Dovitinib also stimulates the translocation of phosphorylated Smad1/5/8 into the nucleus and phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases, including ERK1/2 and p38[3]. Dovitinib strongly inhibits both the interaction of TNIK with ATP (Ki, 13 nM) and the activation of Wnt signaling effectors such as β-catenin and TCF4. Dovitinib also induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in IM-9 cells without significant cytotoxicity in PBMCs[4]. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.