| Cas No.: | 1279037-95-4 |
| Chemical Name: | Topiramate D12 |
| Synonyms: | Topiramate-d12?(di-iso-propylidene-d12);Topiramate-d12;Topiramate-D12 solution;Topiramate D12 |
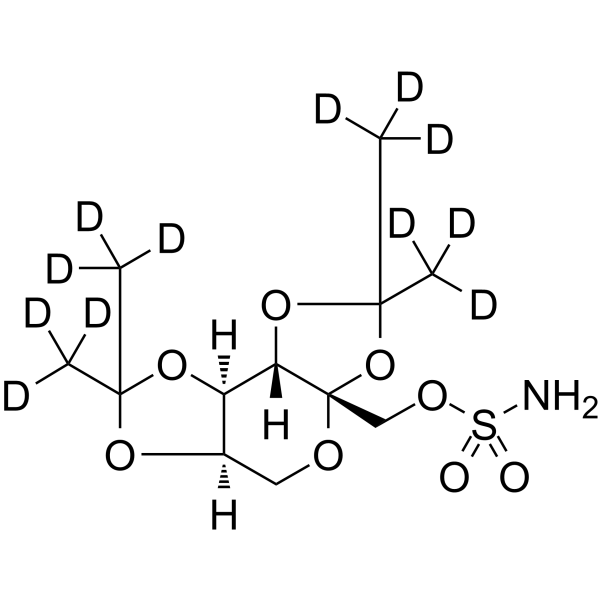
| SMILES: | O1[C@@]2(COS(=O)(=O)N)OC(C([2H])([2H])[2H])(C([2H])([2H])[2H])O[C@H]2[C@@H]2OC(C([2H])([2H])[2H])(C([2H])([2H])[2H])O[C@@H]2C1 |
| Formula: | C12H9D12NO8S |
| M.Wt: | 351.436 |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | Topiramate D12 (McN 4853 D12) is a deuterium labeled Topiramate. Topiramate is a broad-spectrum antiepileptic agent. Topiramate is a GluR5 receptor antagonist. Topiramate produces its antiepileptic effects through enhancement of GABAergic activity, inhibition of kainate/AMPA receptors, inhibition of voltage-sensitive sodium and calcium channels, increases in potassium conductance, and inhibition of carbonic anhydrase[1][2][3]. |
| Target: | GluR5 receptor[1]; GABAergic[2]; Kainate/AMPA[2]; Sodium channel[2]; Calcium channel[2]; Potassium channel[2]; Carbonic anhydrase[2] |
| References: | [1]. Kaminski RM, et al. Topiramate selectively protects against seizures induced by ATPA, a GluR5 kainate receptor agonist. Neuropharmacology. 2004 Jun;46(8):1097-104. [2]. Lyseng-Williamson KA, et al. Topiramate: a review of its use in the treatment of epilepsy. Drugs. 2007;67(15):2231-56. [3]. Nakamura J, et al. Target pharmacology of topiramate, a new antiepileptic drug. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2000 Jan;115(1):53-7. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.