| Cas No.: | 1936529-65-5 |
| Synonyms: | YKL 05-099 |
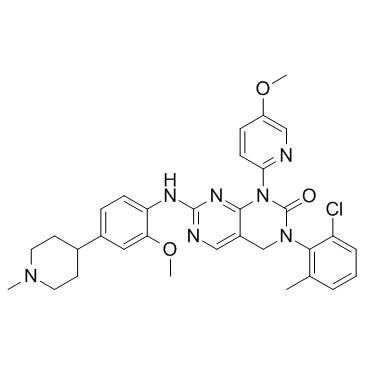
| SMILES: | O=C1N(C2=NC=C(OC)C=C2)C3=NC(NC4=CC=C(C5CCN(C)CC5)C=C4OC)=NC=C3CN1C6=C(C)C=CC=C6Cl |
| Formula: | C32H34ClN7O3 |
| M.Wt: | 600.11 |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks4°C in DMSO,6 months-80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | YKL-05-099 is a salt-inducible kinase (SIK) probe; inhibits SIK2 with an IC50 of 40 nM. |
| Target: | IC50: 40 nM (SIK2)[1] |
| In Vivo: | YKL-05-099 is non-toxic at concentrations less than 10 μM and stable in mouse liver microsomes for more than 2 hours. YKL-05-099 is highly soluble (PBS solubility=428 μM) and present in an unbound state at appreciable levels in mouse plasma. YKL-05-099 dose dependently decreases phosphorylation of HDAC5 at the SIK-regulated site Ser259; reduced phosphorylation is observed at the lowest dose (5 mg/Kg) and is below the limit of detection by immunoblotting beginning at the 20 mg/Kg dose. YKL-05-099 dose-dependently reduces abundance of TNFα in serum beginning at 5 mg/Kg, and increases IL-10 levels at the 20 mg/Kg dose by more than 2-fold[1]. |
| In Vitro: | YKL-05-099 has slightly less potent SIK2-inhibitory (IC50=40 nM) and IL-10-enhancing activities (EC50=460 nM). YKL-05-099 binds to SIK1 and SIK3 with IC50s of 10 and 30 nM, respectively, in a competitive binding assay. Preincubating bone marrow-derived macrophages with YKL-05-099 reduces LPS stimulated phosphorylation of HDAC5 at the SIK-specific phosphorylation site Ser259. YKL-05-099 suppresses production of the inflammatory cytokines TNFα, IL-6 and IL-12p40, and only modestly enhances IL-1β release in BMDCs stimulated with the yeast cell wall extract Zymosan A[1]. |
| Animal Administration: | Mice: YKL-05-099 is diluted in 5% N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone, 5% Solutol HS15 and 90% normal saline and administered IP to male 8–10 week-old C57BL/6 mice. Serum and tissue samples are collected after euthanizing mice by CO2 inhalation overdose followed by cervical dislocation[1]. |
| References: | [1]. Sundberg TB, et al. Development of Chemical Probes for Investigation of Salt-Inducible Kinase Function in Vivo. ACS Chem Biol. 2016 Aug 19;11(8):2105-11. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.