 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Field of Application | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
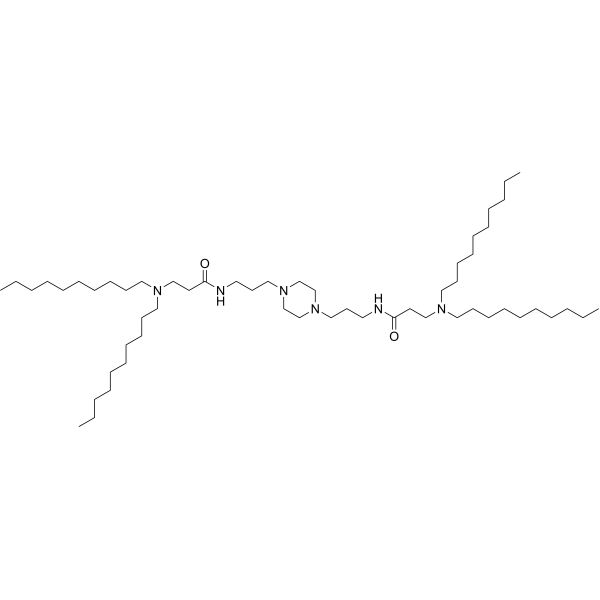
| DC82102 | PPZ-A10 Featured |
PPZ-A10 is an ionizable cationic lipid.It has been used in the generation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for the delivery of siRNA and mRNA in vitro and in vivo. Intraperitoneal administration of LNPs containing PPZ-A10 and encapsulating an mRNA reporter preferentially accumulates in hepatic Kupffer cells and splenic macrophages in mice.
More description
|
|
| DC77133 | AMG410 Featured |
AMG410 is a non-covalent and selective pan-KRAS inhibitor with IC50 values of 1-4 nM for KRAS G12D, KRAS G12V, and KRAS G13D. AMG410 shows greater than 100-fold selectivity against both HRAS and NRAS. AMG410 is a dual GTP(on)- and GDP(off)-state inhibitor (Kd(GDP-state) of 1 nM; Kd(GTP-state) of 22 nM). AMG410 blocks KRAS signaling in a cycling state-independent manner and also blocks proliferation in wildtype KRAS-amplified tumor cells. AMG410 can be used for the study of colorectal, pancreatic, and lung cancers.
More description
|
|
| DC82105 | 93-O17O Featured |
93-O17O is a chalcogen-containing ionizable cationic lipidoid. It has been used in the generation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). LNPs containing 93-O17O localize to the spleen after intravenous injection into mice.LNPs containing 93-O17O have been used for the delivery of Cre recombinase and ribonucleoproteins for genome editing in mice and for the intratumoral delivery of cGAMP to enhance cross-presentation of tumor antigens.
More description
|

|
| DC66219 | Lipid 88 Featured |
Lipid88 is a high-performance, novel ionizable lipid component engineered for advanced mRNA-LNP vaccine delivery. LNP88 formulation demonstrates superior biodistribution, achieving >10-fold higher transfection efficiency in spleen and lymph nodes compared to benchmark lipids like ALC-0315 via intramuscular delivery. When encapsulating antigen-encoding mRNA (e.g., optimized mCSA construct), Lipid-88 based LNPs drive robust humoral and cellular immunity, enabling complete protection against challenging SARS-CoV-2 variants (WA1/2020, Omicron BA.1, BQ.1) in preclinical models. Its design prioritizes potent immunogenicity with favorable safety profiles.
More description
|

|
| DC59010 | C14-4 Featured |
C14-4 (C14-494,Lipid B-4,Lipid B4) is a novel ionizable lipid with the highest T-cell transfection efficiency and low cytotoxicity.The C14-4 ionizable lipid has been explored for CAR-T therapy.To screen the excellent formulations for mRNA delivery, a
lipid library of 24 ionizable lipids was constructed to make
iLNPs, which were used to deliver luciferase mRNA into
Jurkat cells.[115] The optimal iLNPs formulation was C14-4
iLNPs (C14-4 ionizable lipid, DOPE, chol, and PEG at a molar
ratio of 35%, 16%, 46.5%, and 2.5%) (Figure 6c). The optimal
dose of luciferase mRNA for C14-4 iLNPs was 30 ng.
Compared with electroporated CAR T cells, the CAR T cells engineered
via C14-4 iLNPs showed potent cancer-killing activity
when they were cocultured with Nalm-6 acute lymphoblastic leukemia
cells. To obtain a safer and more effective CAR mRNA
delivery vehicle, the orthogonal design provided 256 potential
formulations, and 16 representative iLNPs formulations were
evaluated.Through evaluating the safety, delivery efficiency,
and transfection efficiency of 16 iLNPs, the formulation B10
(C14-4 ionizable lipid, DOPE, chol, PEG at a molar ratio of
40%, 30%, 25%, and 2.5%) was screened out as the optimal performing formulation. The luciferase expression based on B10
formulation was increased threefold than the initial formulation.
Reducing the accumulation and clearance of iLNPs in the liver
can increase the expression of CAR mRNA in T cells, further
improving the therapeutic effect of CAR-T. Studies have shown
that cholesterol analogs can alter the mechanisms of intracellular
circulation and enhance the delivery of mRNA, which may be
related to the reduced recognition of iLNPs by the Niemann
Pick C1 (NPC1) enzyme.The addition of a hydroxyl
group to various locations in the cholesterol molecule can alter
the binding kinetics between the modified cholesterol and NPC1,
and reduced NPC1 recognition of cholesterol. The results
showed that replacement of 25% and 50% 7 α-hydroxycholesterol
for cholesterol in iLNPs improved mRNA delivery to
primary human T cells in vitro by 1.8-fold and twofold,
respectively.C14-4 is one of the ionizable lipids to efficiently deliver mRNA
to Jurkat cells or primary human T cells. It will effectively promote
the development of mRNA delivery by iLNPs for CAR-T
therapy.
More description
|

|
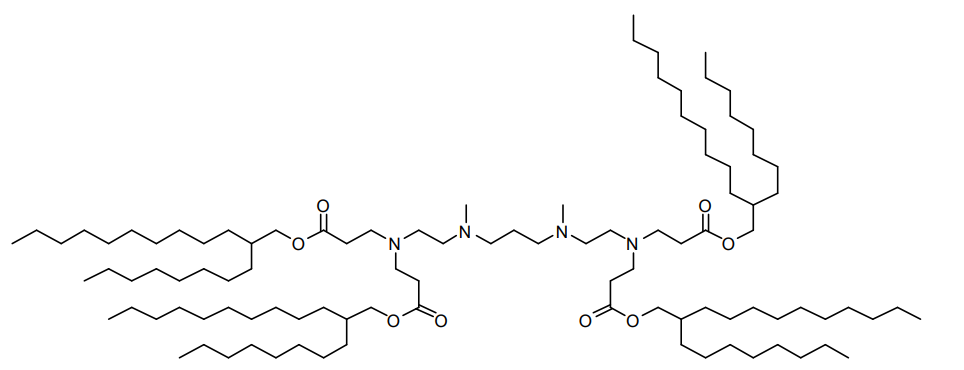
| DC60808 | 503O8,12 Featured |
503O8,12 is an ionizable lipidoid synthesized via Michael addition, combining a hydrophilic amine headgroup ("503" series) with two hydrophobic branched acrylate tails (C8 and C12 chains, likely with unsaturated bonds). Its design emphasizes organ-specific delivery, exhibiting spleen-tropic targeting in vivo.
More description
|
|
| DC67120 | YSK12-C4 (YSK12-MEND) Featured |
YSK 12C4 is an ionizable cationic lipid primarily used to enhance siRNA cellular delivery via multifunctional envelope-type nanodevices (MEND). YSK 12C4 promotes siRNA uptake and endosomal escape, effectively silencing genes in human immune cell lines.
More description
|

|
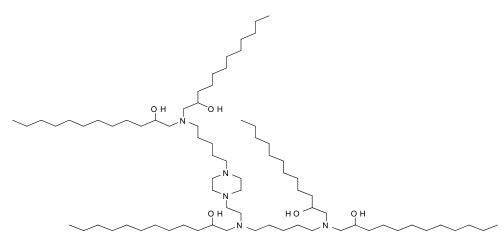
| DC60503 | C12-A1 Featured |
Lipid C12-A1 is an ionizable lipid. C12-A1-LPN is a potent and safe LNP platform to deliver Foxp3 mRNA to CD4+ T cells to engineer immunosuppressive FP3T cells. C12-A1 has a slightly lower average cell viability than C14-A1.
More description
|
|
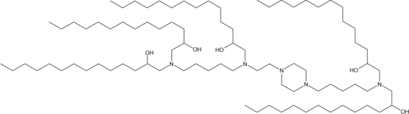
| DC60499 | C14-A1 Featured |
Lipid C14-A1 is an ionizable lipid. C14-A1-LPN is a potent and safe LNP platform to deliver Foxp3 mRNA to CD4+ T cells to engineer immunosuppressive FP3T cells.
More description
|
|
| DC67521 | Lipid TD5 Featured |
TD5 is a brain-targeting lipid nanoparticle (BLNP) engineered for efficient mRNA delivery to the central nervous system (CNS) via intrathecal injection. It incorporates a tryptamine-derived ionizable lipid headgroup, myristic acid hydrocarbon tails, and a biodegradable carbonate ester linker, enabling pH-dependent mRNA encapsulation (81.7% efficiency) and brain cell-specific targeting. With a hydrodynamic diameter of 107.5 nm, near-neutral pKa (7.30), and mild positive charge, TD 5 demonstrates superior CNS tropism through serotonin receptor (5-HT1A)-mediated endocytosis. In vitro, TD-5 achieved 80.8% GFP expression in SH-SY5Y neuronal cells, outperforming MC3 LNPs by 50-fold. Following intrathecal administration in mice, TD-5 mediated GFP expression in 29.6% of neurons and 38.1% of astrocytes brain-wide, with 10-fold higher CNS specificity than peripheral organs. Genome editing studies showed TD5-delivered Cas9/sgRNA induced tdTomato activation in ≈30% of neurons and 40% of astrocytes across key brain regions. Safety profiling revealed minimal systemic immune responses (lower IL-6, IL-12p40 vs MC3 LNPs), normal hepatic/renal biomarkers, and no histopathological toxicity. The optimized structure balances myristic chain hydrophobicity for membrane interaction, ionizable amines for mRNA complexation, and tryptamine-mediated targeting for enhanced CNS uptake, establishing TD5 as a promising platform for CNS gene therapies.
More description
|

|
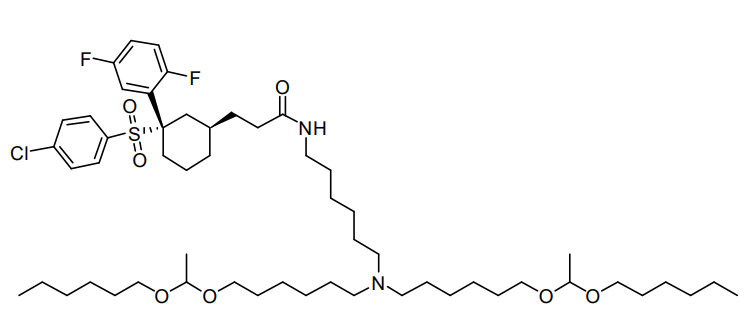
| DC67295 | Lipid MK16 Featured |
MK-16 is a specialized lipid designed to traverse the blood-brain barrier (BBB) for effective mRNA delivery. Its formulation, MK 16 BLNP, leverages dual mechanisms involving caveolae and γ-secretase to facilitate BBB penetration, ensuring the targeted and efficient transport of functional mRNA to diverse brain cell types. Demonstrating excellent tolerability across a range of dosing regimens, MK16 BLNP represents a promising platform for brain-targeted therapeutic applications.
More description
|
|
| DC65725 | POPC Featured |
1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-PC (POPC), a phospholipid, is a major component of biological membranes. 1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-PC is used for the preparation of liposomes and studying the properties of lipid bilayers.
More description
|

|
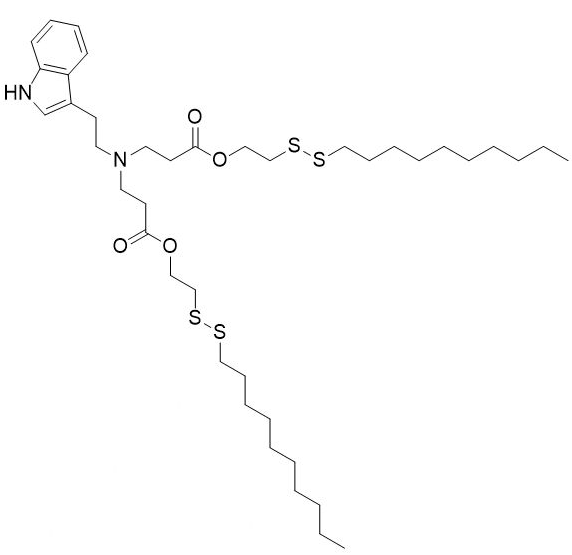
| DC60212 | NT1-O14B Featured |
NT1-O14B is a tryptamine-containing cationic lipidoid.1 It has been used in combination with other lipids in the formation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). Intravenous administration of LNPs containing NT1-O14B and encapsulating antisense nucleotides against tau decreases tau brain levels in mice.
More description
|
|
| DC41043 | NT1-O12B Featured |
NT1-O12B, an endogenous chemical and a neurotransmitter-derived lipidoid (NT-lipidoid), is an effective carrier for enhanced brain delivery of several blood-brain barrier (BBB)-impermeable cargos. Doping NT1-O12B into BBB-impermeable lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) gives the LNPs the ability to cross the BBB. NT-lipidoids formulation not only facilitate cargo crossing of the BBB, but also delivery of the cargo into neuronal cells for functional gene silencing or gene recombination.
More description
|

|
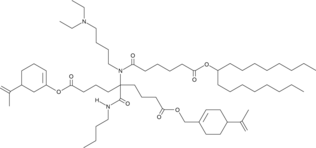
| DC60706 | FO-35 Featured |
FO35 is an artificial intelligence-guided designed ionizable lipid for RNA delivery to the muscle, lung and nose. FO-35 LNPs enable potent transfection throughout the whole ferret lung epithelium, from trachea to alveoli.
More description
|
|
| DC60705 | FO-32 Featured |
FO-32 is an artificial intelligence-guided designed ionizable lipid for RNA delivery to the muscle, lung and nose. FO-32 LNPs enable potent transfection throughout the whole ferret lung epithelium, from trachea to alveoli.
More description
|

|
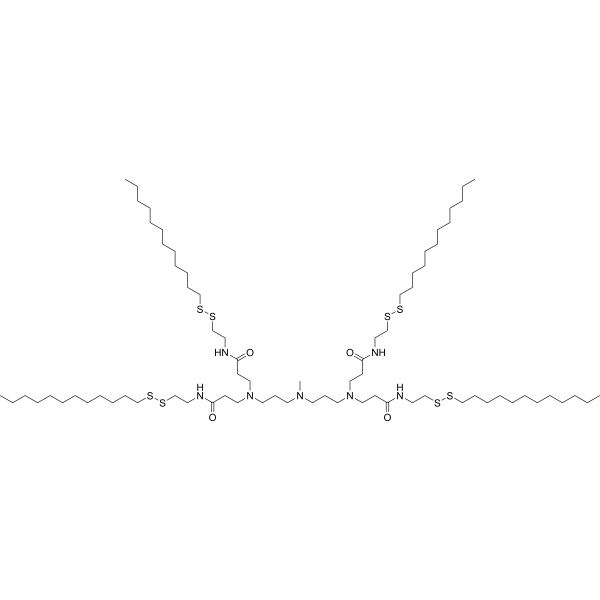
| DC65327 | 306-N16B Featured |
306-N16B is a lipidnanoparticle, and allows systemic codelivery of Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA. 306-N16B can transport mRNA to the pulmonaryendothelial cell. 306-N16B can be used for research of genome editing-based therapies. Based on the same lipid libraries with 306-O12B, the researchers also found that N-series ionizable lipids were able to selectively deliver mRNA to the lungs of mice. Compared with the liver-targeted O-series ionizable lipids which contained ester bond in lipid tail found in previous work, such as 306-O12B, the N-series ionizable lipids with
the lipid tail containing amide bond prefer to deliver mRNA to the lung. As a N-series ionizable lipid, the chemical structure of the 306-N16B is shown in Figure 4a,b. The difference of organ targeting may be due to their adsorption
of different protein coronas during blood circulation caused
by their different structures mentioned earlier.It has
shown that the second major protein of the protein
corona adsorbed by liver-targeting 306-O12B iLNPs was apolipoprotein
E (ApoE), while the three dominant proteins in the
protein corona adsorbed by lung-targeting 306-N16B iLNPs
were serum albumin, fibrinogen beta chain, and fibrinogen
gamma chain. However, the 306-N16B iLNPs showed less
organ selectivity when systematically codelivered Cas9
mRNA and sgRNA in vivo, which could simultaneously
activate tdTomato expression in the liver and lung of Ai14
mice, whereas single mRNA delivery could almost
exclusively deliver mRNA to the lungs. This surprising phenomenon
requires further investigation. Both the change of
iLNPs charge and the change of lipids functional group
can influence the distribution of iLNPs in vivo due to
the altering of protein corona composition. Therefore,
it is possible to control the organ targeting of iLNPs by
controlling the composition of the outer protein corona of
iLNPs.
More description
|
|
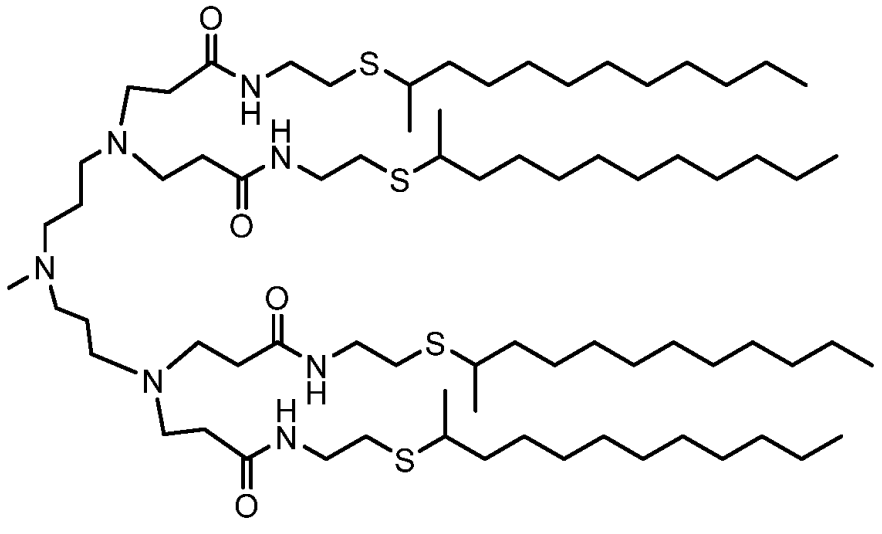
| DC67525 | Hopewell Lipid 649 Featured |
L649 is a next-generation, lung-targeting ionizable lipid specifically designed for systemic mRNA delivery developed by Hopewell. Belonging to the novel "N-series" lipid class, it features a unique structure with an amine-containing head group and hydrophobic tails incorporating amide bonds. This design enables L649 to form highly stable lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) that exhibit exceptional tropism for the lower respiratory tract (lungs, bronchi, trachea) following intravenous administration. It demonstrates superior efficiency in delivering therapeutic payloads (like mRNA) specifically to key lung cell types, including alveolar epithelial cells (AT1 and AT2) and bronchial cells, while minimizing off-target accumulation in organs like the liver. L649-based LNPs, particularly when formulated with helper lipids like POPE, combine high potency with significantly improved tolerability, allowing for effective dosing in vivo. This makes L649 a promising candidate for developing treatments for various lung diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis, COPD, lung cancer, and infectious diseases like COVID-19.
More description
|
|
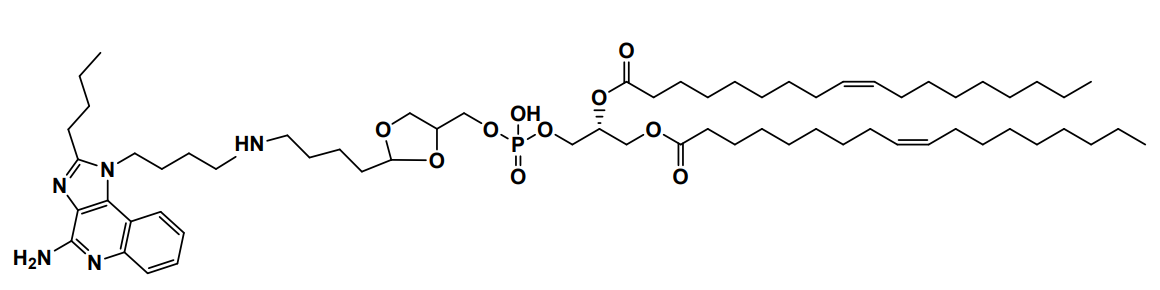
| DC60828 | YK-TLR-001 Featured |
YK-TLR-001 is a cyclic acetal-based ionizable lipid for mRNA delivery. YK-TLR-001 LNPs are demonstrated to enhance mRNA expression in the spleens and to induce exceptional maturation of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and to promote antigen presentation.
More description
|
|
| DC67568 | ORNA Lipid AX-6 Featured |
AX6 is an ionizable lipid in the F32 LNP formulation, engineered by ReNAgade/Orna Therapeutics for targeted mRNA delivery to T cells. AX-6's unique bridged bicyclic/polycyclic core with a tertiary amine group enables pH-dependent protonation and endosomal escape, while C14-C18 hydrophobic tails (optionally branched/fluorinated) enhance bilayer stability and mRNA encapsulation. Demonstrating exceptional T-cell tropism, AX6 achieves high transfection efficiency in CD4+/CD8+ T cells (validated in NHP/humanized models) with minimal toxicity. Compared to clinical benchmarks (SM-102, ALC-0315), its rigid core offers superior serum stability and immune-cell specificity, positioning it as an ideal candidate for CAR-T/NK therapies and next-gen vaccines. The F32 LNP system's proven efficacy (e.g., in vivo B-cell depletion) underscores AX 6's transformative potential for cell engineering and immunotherapies.
More description
|
|
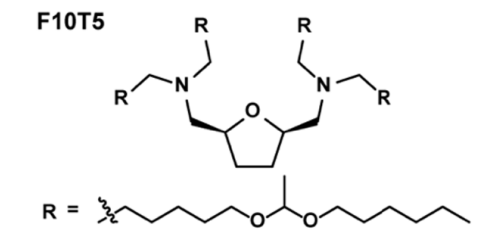
| DC60840 | Lipid F10T5 Featured |
F10T5 is a tetrahedral tetrahydrofuran (THF)-derived lipid nanoparticle (LNP) engineered with four acid-labile acetal tails, designed for efficient mRNA delivery to the central nervous system. This lipid features a mono-THF core conjugated with branched hydrophobic chains that balance lipophilicity (LogD ≈11) and endosomal escape capability. Preclinical studies demonstrated F10T5 LNPs bypass the blood-brain barrier via meningeal lymphatic vessels (MLVs) after subcutaneous neck injection, showing 40-fold higher brain luciferase expression than FDA-approved SM102 LNPs. Cryo-EM revealed spherical nanoparticles (~170 nm diameter) with 91.9% mRNA encapsulation. In Neuro-2a cells, F10T5 exhibited superior cytoplasmic mRNA release through enhanced endosomal membrane disruption, evidenced by diffuse calcein fluorescence. Flow cytometry confirmed neuron-predicted delivery (8.8% GFP+ neurons vs 1.28% with SM102) in mice, with functional validation in Ai14 transgenic models where Cre mRNA-loaded F10T5 induced tdTomato expression in neurons and glial cells. Safety assessments showed normal hepatic/renal biomarkers and no histopathological abnormalities. The THF core and acetal tail design synergistically optimize lymphatic trafficking, brain penetration, and biodegradability, positioning F10T5 as a transformative platform for mRNA-based therapies targeting neurodegenerative diseases.
More description
|
|
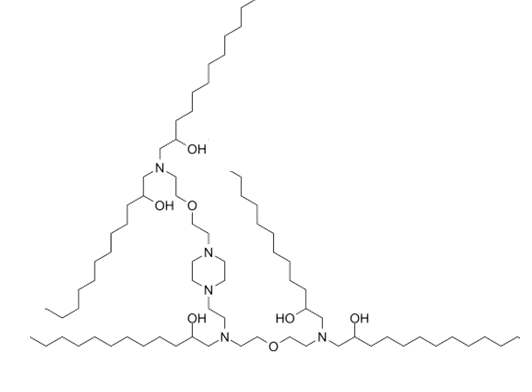
| DC89101 | C12-4 (Lipid A-4) Featured |
C12-4 (C12-494,Lipid A-4) is a branched-chain ionizable cationic lipidoid that has been used in the formation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for the delivery of mRNA. LNPs containing lipid A4 and encapsulating an mRNA reporter accumulate in the uterus, placenta, and ovaries, as well as to the spleen and liver, in pregnant mouse dams unlike LNPs containing the branched-chain ionizable cationic lipidoid C12-200, which primarily accumulate in the liver. Intravenous administration of LNPs containing lipid A4 and encapsulating mRNA encoding VEGF increase placental VEGFR1 levels and mean fetal blood vessel area without inducing liver damage in pregnant mouse dams.
More description
|
|
| DC11303 | CT7001(Samuraciclib hydrochloride) Featured |
ICEC0942 is a selective CDK7 inhibitor, with IC50s of 41 nM and 578 nM for CDK7/CycH/MAT1 and CDK2/cycE1, respectively.
More description
|

|
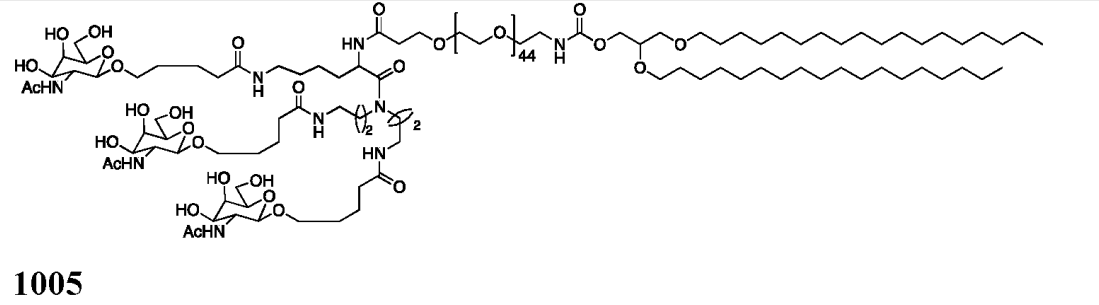
| DC67444 | GalNAc Lipid 1005 Featured |
GalNAc Lipid 1005 is a trivalent GalNAc-lipid conjugate designed for ASGPR-mediated hepatic delivery. It features a lysine-based scaffold covalently linked to three GalNAc moieties via a 44-unit PEG spacer, anchored by a 1,2-O-dioctadecyl-sn-glyceryl (DSG) lipid tail.
More description
|
|
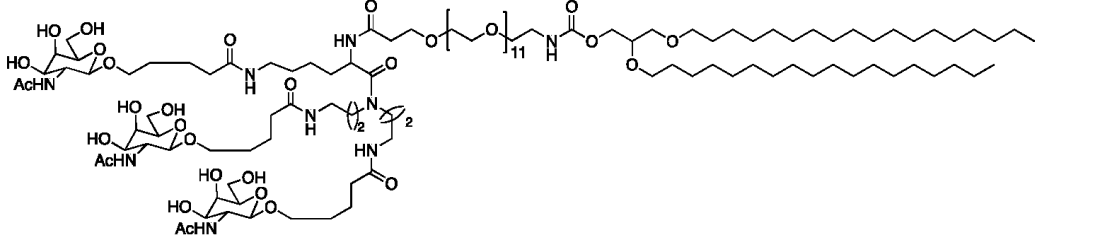
| DC67443 | GalNAc Lipid 1002 Featured |
GalNAc Lipid 1002 is a trivalent GalNAc-lipid conjugate designed for ASGPR-mediated hepatic delivery. It features a lysine-based scaffold covalently linked to three GalNAc moieties via a 12-unit PEG spacer, anchored by a 1,2-O-dioctadecyl-sn-glyceryl (DSG) lipid tail.
More description
|
|
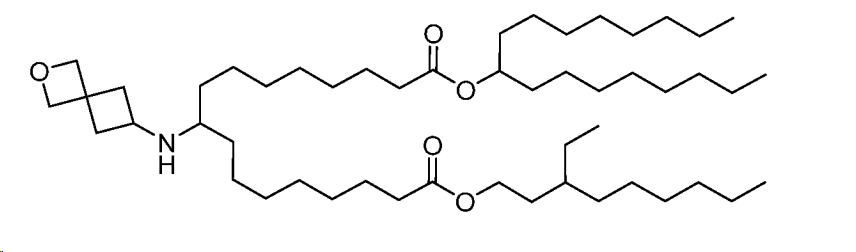
| DC67522 | AZD Lipid 17 Featured |
Lipid 17 is a novel, highly potent ionizable lipid designed for mRNA delivery within lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) developed by AstraZeneca . Its structure features a secondary amine head group attached to a cyclic ether moiety (specifically, the 2-oxaspiro[3.3]heptan-6-amine head group). It possesses an asymmetric tail architecture: one tail is derived from heptadecan-9-ol (a branched C17 secondary alcohol), while the other tail is a modified nonyl chain (C9) with a key ethyl branch at the 3-position. The linker connecting the head group to the tails has a length equivalent to n=3 (three methylene units) as defined in the study. This specific combination of the secondary amine cyclic ether head group, asymmetric tails, and the ethyl branch at the 3-position of the nonyl chain proved critical for its exceptional performance. When formulated into LNPs and administered intravenously in mice, Lipid 17 demonstrated a remarkable 6-fold increase in functional protein (eGFP) expression in the liver compared to the benchmark lipid MC3, with high statistical significance (P < 0.0001). This makes Lipid 17 one of the most active lipids identified in the study and a promising candidate for liver-targeted mRNA therapeutics.
More description
|
|
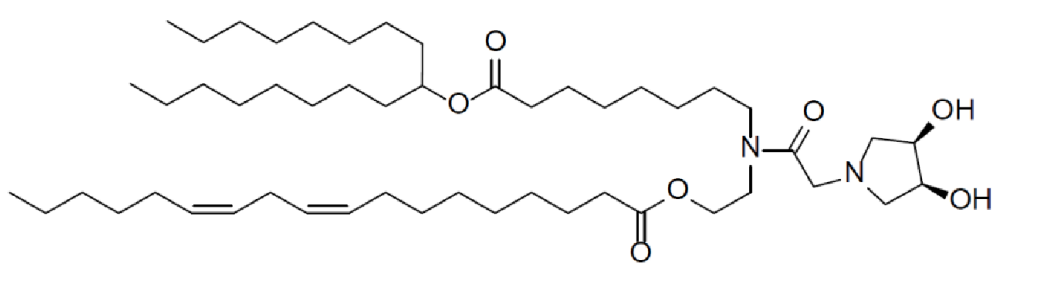
| DC67524 | Nitto Lipid 19 Featured |
Lipid 19 is an engineered cationic lipid designed to optimize the delivery of RNA within lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) developed by Nitto. Its unique structure—featuring a dual-hydroxyl headgroup and tailored hydrophobic chains—enables highly efficient encapsulation of these fragile genetic payloads, protecting them from degradation. The resulting LNPs exhibit exceptional stability (<100 nm size), target the liver specifically for enhanced therapeutic impact, and support applications ranging from mRNA vaccines to gene-silencing therapies. This makes lipid 19 a pivotal advancement in precision nanomedicine for liver-related disorders.
More description
|
|
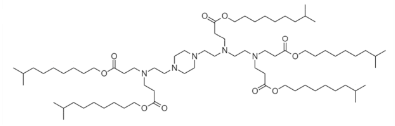
| DC60545 | 200Oi10 Featured |
200Oi10 is an ionizable lipidoid used in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for RNA delivery. Structurally, it features ester-conjugated cleavable lipid tails, enhancing biodegradability and reducing toxicity compared to non-cleavable analogs. Preclinical studies show that 200Oi10-based LNPs primarily accumulate in the liver (97.7%) after intravenous administration. However, intraperitoneal injection redirects biodistribution, achieving 46.4% pancreatic uptake, which can be further amplified by incorporating cationic lipids like DOTAP. This unique tropism enables pancreas-targeted mRNA delivery. 200Oi10's ester linkages promote rapid clearance, improving biocompatibility while maintaining siRNA/mRNA delivery efficiency. Its design exemplifies the use of degradable lipidoids to balance organ specificity, efficacy, and safety in RNA therapeutics.
More description
|
|
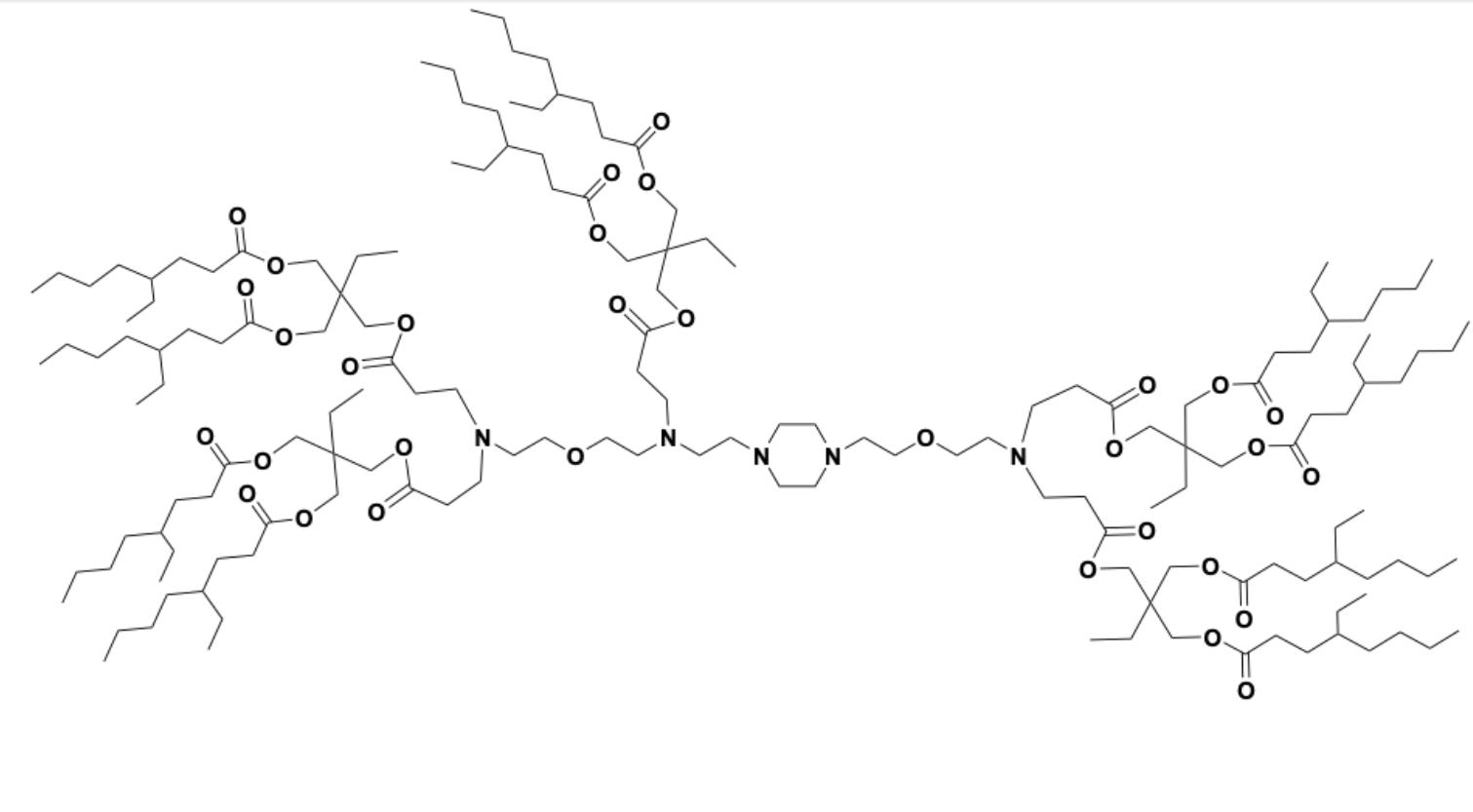
| DC60800 | 18-2-9b2 Featured |
18-2-9b2 is a dendron-like degradable ionizable lipid which facilitates mRNA delivery to splenic macrophages. 18-2-9b2 LNP encapsulating therapeutic BTB domain and CNC homologue 1 (BACH1) mRNA exhibited proficient BACH1 expression and subsequent Spic downregulation in splenic red pulp macrophages (RPM) in a Spic-GFP transgene model.
More description
|
|
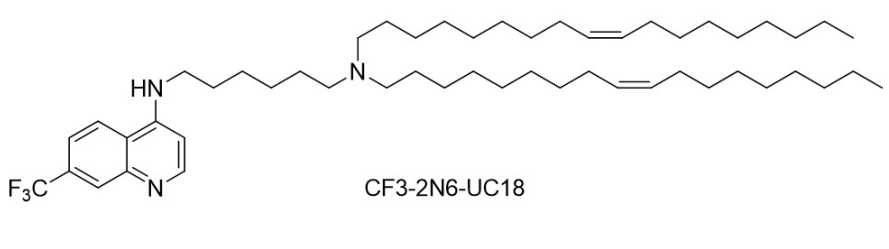
| DC60843 | CF3-2N6-UC18 Featured |
CF3-2N6-UC18 is a rationally designed chloroquine-inspired ionizable lipid that enables robust mRNA delivery and genome editing. It integrates three modular components: a 7-trifluoromethyl-substituted quinoline scaffold (mimicking chloroquine’s endosomolytic properties), a hexamethylenediamine linker with two ionizable nitrogen atoms (pH-responsive protonation), and two unsaturated oleyl (C18:1) hydrophobic tails (enhancing membrane fusion and nanoparticle stability). This lipid self-assembles into ecoLNPs (endosomolytic chloroquine-like lipid nanoparticles) with spherical morphology (~200 nm diameter, 98% mRNA encapsulation). Its pH-sensitive activity triggers endosomal escape through dual mechanisms: proton sponge effect (buffering endo-lysosomal pH) and saposin B-mediated membrane disruption (molecular docking confirms chloroquine-like binding to lysosomal saposin B). In vitro, ecoLNPs outperform commercial reagents (18.9-fold higher mRNA delivery than Lipofectamine 2000) and penetrate 3D cell models. They resist serum/RNase degradation and retain >90% activity after 7-day storage at 4°C. In vivo, ecoLNPs achieve tissue-specific mRNA expression via multiple routes (intravenous, intramuscular, etc.), with strong lymph node tropism (90.2% after intramuscular injection) comparable to SM-102 LNPs (Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccine carrier). They mediate efficient Cre mRNA-driven recombination and CRISPR-Cas9 editing in transgenic mice. CF3-2N6-UC18’s modular design, stability, and dual endosomal escape strategies position it as a versatile platform for mRNA vaccines, gene therapy, and genome editing applications.
More description
|
|