| Cas No.: | |
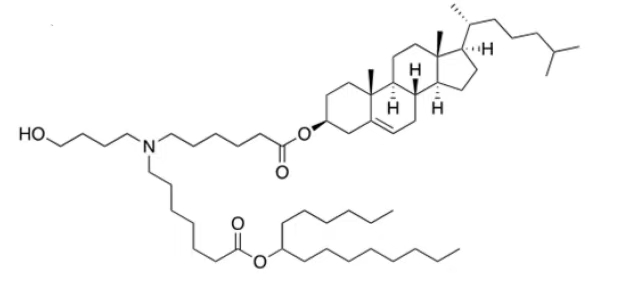
| Chemical Name: | ARV-T1 |
| Synonyms: | ARVT1, ARV T1 |
| Formula: | CsGH107NO5 |
| M.Wt: | 910.51 |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Publication: | Lipid Nanoparticles Formulated with a Novel Cholesterol-Tailed Ionizable Lipid Markedly Increase mRNA Delivery Both in vitro and in vivo-Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 28:20:9389-9405. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S527822. eCollection 2025. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.