| Cas No.: | 939375-07-2 |
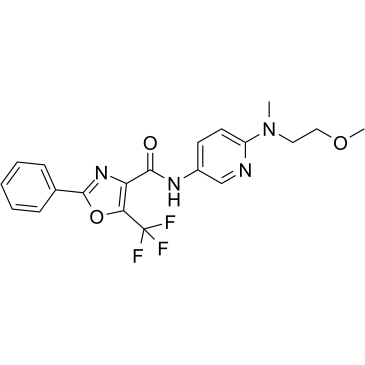
| SMILES: | O=C(C1=C(C(F)(F)F)OC(C2=CC=CC=C2)=N1)NC3=CC=C(N(CCOC)C)N=C3 |
| Formula: | C20H19F3N4O3 |
| M.Wt: | 420.39 |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | DGAT1-IN-3 is a potent, selective and orally bioavailable inhibitor of DGAT-1, with the IC50s of 38 nM for human DGAT-1 and 120 nM for rat DGAT-1. DGAT1-IN-3 could be used to research of obesity, dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome[1][2]. |
| Target: | IC50: 38 nM (human DGAT-1); 120 nM (rat DGAT-1)[2] |
| In Vivo: | DGAT1-IN-3 (5-50 mg/kg; p.o once daily for three weeks) reduces weight gain and plasma triglycerides, and improves lipid profile[2]. DGAT1-IN-3 (50 mg/kg; p.o) exhibits good oral bioavailability (77%) and the maximum exposure level in plasma (Cmax) is 24 μM[2]. DGAT1-IN-3 (5 mg/kg; i.v) exhibits terminal elimination half-lives (1.95 h) and low clearance (13.5 mL/min/kg)[2]. Animal Model: Three-month-old male Sprague Dawley DIO rats (fed with a high-fat diet)[2] Dosage: 0, 5, 25, 50 mg/kg; once daily for three weeks Administration: P.o. administration Result: Reduced cumulative body weight gain in a dose-dependent manner and was well tolerated in rats. Animal Model: Male Wistar rats[2] Dosage: 50 mg/kg for p.o. and 5 mg/kg for i.v. (Pharmacokinetic Analysis) Administration: P.o. and i.v. administration Result: Cmax (24 μM); T1/2 (1.95 h). |
| In Vitro: | DGAT1-IN-3 blocks the human ether-a-go-go-related gene (hERG) encoded potassium channel with an IC20 of 0.2 μM[1]. DGAT1-IN-3 inhibits human DGAT-1 in CHOK1 cells with an EC50 of 0.66 μM[1]. |
| References: | [1]. Yimin Q, et, al. Discovery of orally active carboxylic acid derivatives of 2-phenyl-5-trifluoromethyloxazole-4-carboxamide as potent diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1 inhibitors for the potential treatment of obesity and diabetes. J Med Chem. 2011 Apr 14; 54(7): 2433-46. [2]. Weiya Y, et, al. Discovery and optimization of 2-phenyloxazole derivatives as diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Dec 1; 21(23): 7205-9. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.