| Cas No.: | 183319-69-9 |
| Chemical Name: | Erlotinib hydrochloride |
| Synonyms: | N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-amine hydrochloride;ERLOTINIB;ERLOTINIB HCL SALT;TARCEVA;ERLOTINIB HCL SALT :TARCEVA;Erlotinib, Hydrochloride Salt;N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-;quinazolinamine, Hydrochloride Salt, OSI 774, Tarceva;N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis-(2-methoxyethoxy)-quinazolin-4-amine;[6,7-Bis-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-quinazolin-4yl]-(3-ethynyl-phenyl)-amine;Tarceva Hydrochloride See E625000;Erlotinib HCl;Erlotinib hydrochloride;Erlotinib HCl (OSI-744);[6,7-Bis-(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-quinazolin-4-yl]-(3-ethynyl-phenyl)-amine;Erlotinib Hydrochlorid;Erlotinib Hydrochloride (Tarceva);Erlotinib, Hydrochloride Salt (Tarceva®);N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-quinazolin-4-amine hydrochloride;Tarceva (Erlotinib Hydrochloride);(±)-Cloprostenol; 6,7-Bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-(3-ethynylanilino)quinazoline hydrochloride;CP-358774;Erlotinib (Hydrochloride);Erlotinib,OS-774;Erlotinib-d6 HCl;Erlotonid HCl;NSC 718781;OSI 774;OSI-774;774 hydrochloride;CP-358;N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine hydrochloride;OSI-744 hydrochloride;N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)[6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-yl]amine hydrochloride;RG-1415;CP 358774;RO-0508231;CP-358774-01;DA87705X9K;4-Quinazolinamine, N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-, hydrochloride (1:1);6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-(3-ethynylanilino)quinazoline hcl;(CP358774;N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7 |
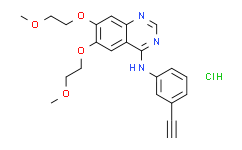
| SMILES: | Cl[H].O(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])OC([H])([H])[H])C1C([H])=C2C(=NC([H])=NC2=C([H])C=1OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])OC([H])([H])[H])N([H])C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C(C#C[H])=C1[H] |
| Formula: | C22H24ClN3O4 |
| M.Wt: | 429.8967 |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | Erlotinib hydrochloride inhibits purified EGFR kinase with an IC50 of 2 nM. |
| In Vivo: | There is a 1.49-fold statistically significant difference between AUC0-inf after p.o. administration of Erlotinib (5 mg/kg) comparing Bcrp1/Mdr1a/1b-/- and WT mice (7,419±1,720 versus 4,957±1,735 ng*h/mL respectively, P=0.01)[3]. The administration of Erlotinib (10 mg/kg/day, or 20 mg/kg/day) to Bleomycin (BLM)-treated rats shows no exacerbation of lung injuries in indices such as macroscopic findings, lung weights, histopathological scores (lung lesion density and lung fibrosis score), and pulmonary hydroxyproline (HyP) level. The result suggests that Erlotinib does not have any exacerbating effects on lung injuries induced by BLM in rats[4]. |
| In Vitro: | Erlotinib (CP-358,774) Hydrochloride is also a potent inhibitor of the recombinant intracellular (kinase) domain of the EGFR, with an IC50 of 1 nM. The proliferation of DiFi cells is strongly inhibited by Erlotinib with an IC50 of 100 nM for an 8-day proliferation assay[1]. The combination of B-DIM and Erlotinib (2 μM) results in a significant inhibition of colony formation in BxPC-3 cells when compared with either agent alone. The combination of B-DIM and Erlotinib (2 μM) results in a significant induction of apoptosis only in BxPC-3 cells when compare with the apoptotic effect of either agent alone[2]. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.