| Cas No.: | 887375-67-9 |
| Chemical Name: | Ripasudil hydrochloride dihydrate |
| Synonyms: | K115;K-115 Hydrochloride Dihydrate;Ripasudil;K-115;Ripasudil hydrochloride dihydrate;016TTR32QF;Ripasudil hydrochloride hydrate [JAN];Ripasudil hydrochloride hydrate (JAN);Ripasudil hydrochloride hydrate;Glanatec (TN);Ripasudil hydrochloride dihydrate [WHO-DD];C15H18FN3O2S.ClH.2H2O;BCP11082;s7995;3757AH;1H-1,4-Diazepine, 1-((4-fluoro-5-is |
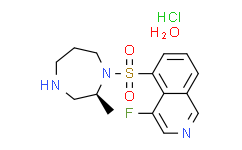
| SMILES: | Cl[H].S(C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C2=C([H])N=C([H])C(=C12)F)(N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])([H])[C@]1([H])C([H])([H])[H])(=O)=O.O([H])[H].O([H])[H] |
| Formula: | C15H23ClFN3O4S |
| M.Wt: | 395.8772 |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | Ripasudil (K-115) is a specific inhibitor of ROCK, with IC50s of 19 and 51 nM for ROCK2 and ROCK1, respectively. |
| In Vivo: | Ripasudil (K-115) reduces intraocular pressure (IOP) in a concentration-dependent manner at concentrations between 0.1% and 0.4% in monkey eyes and 0.0625% to 0.5% in rabbit eyes, respectively[1]. Ripasudil (K-115; 1 mg/kg, p.o. daily) shows a neuroprotective effect on retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) after nerve crush (NC). Ripasudil also inhibits the oxidative stress induced by axonal injury in mice. Ripasudil suppresses the time-dependent production of ROS in RGCs after NC injury[3]. |
| In Vitro: | Ripasudil (K-115) is a potent inhibitor of ROCK, with IC50s of 19 and 51 nM for ROCK2 and ROCK1, respectively. Ripasudil also shows less potent inhibitory activities against CaMKIIα, PKACα and PKC, with IC50s of 370 nM, 2.1 μM and 27 μM, respectively[1]. Ripasudil (K-115; 1, 10 μM) induces cytoskeletal changes, including retraction and cell rounding and reduced actin bundles of cultured trabecular meshwork (TM) cells. Ripasudil (5 μM) sifnificantly reduces transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER), and increases FITC-dextran permeability in Schlemm’s canal endothelial (SCE) cell monolayers[2]. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.