 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Field of Application | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
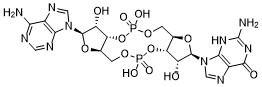
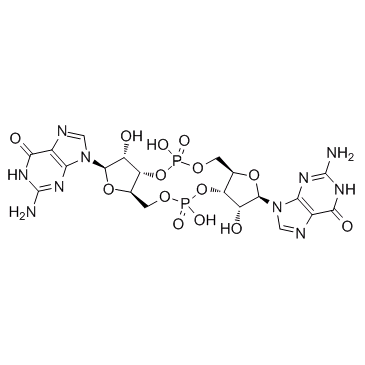
| DC50039 | 3'3'-cGAMP (sodium salt) Featured |
3’3’-cGAMP Fluorinated (c-[2'FdGMP]-[2'FdAMP]) is a synthetic analog of cyclic guanosine monophosphate- adenosine monophosphate (cyclic GMP-AMP, cGAMP) with a fluorine atom at 2’ position of the nucleosides. 3’3’-cGAMP is a cyclic di-nucleotide produced by bacteria. It is also referred to as "canonical" cGAMP due the presence of the classical 3’-5’ phosphodiester linkages between the guanosine and the adenosine. It has been reported that cGAMP binds STING (stimulator of IFN genes) and subsequently induces TBK1-IRF3-dependent production of IFN-β [1].
The incorporation of fluorine into biologically active molecules is commonly used in medicinal chemistry to improve their metabolic stability or to modulate physicochemical properties such as lipophilicity [2, 3]. Moreover, the introduction of a fluorine atom can change the biological activities of a molecule. Interestingly, when used at low concentrations in various cellular assays, 3’3’-cGAMP Fluorinated induces higher levels of type I IFNs than does cGAMP.
STING ligands such as cGAMP induce type I IFNs and activate interferon stimulated genes (ISG) through IRFs. To facilitate their study, InvivoGen has developed stable reporter cells in two well established immune cell models: THP-1 human monocytes and RAW 264.7 murine macrophages. These cells express a reporter gene (SEAP or Lucia luciferase), under control of an IRF-inducible promoter.
More description
|
|
| DC73558 | SHR1032 |
SHR1032 is a novel small molecule non-cyclic di-nucleotide STING agonist, exhibits significantly high affinity binding to STING and cellular reporter assay (EC50=30 nM).
More description
|

|
| DC73557 | SB24011 |
SB24011 (SB 24011) is a selective small molecule inhibitor of the STING-TRIM29 interaction with IC50 of 3.85 uM in luciferase complementation assays, enhances cGAMP-mediated STING immunity.
More description
|

|
| DC73556 | MK-1454 |
MK-1454 (Ulevostinag) is a novel cyclic dinucleotide STING agonist with robust tumor cytokine upregulation and effective antitumor activity.
More description
|

|
| DC73555 | LB244 |
LB244 (LB-244) is a highly potent, selective and irreversible STING antagonist, blocks STING oligomerization and inhibits STING signaling THP1 dual cells with IC50 of 0.8 uM.
More description
|

|
| DC73553 | DWL-4-140 |
DWL-4-140 is a small molecule inhibitor of cyclized nucleotide-binding domain (CBD) of STING, selectively inhibits DNA-mediated IFNβ responses with IC50 of 617 nM.
More description
|

|
| DC73552 | ChX0306710 |
ChX710 (ChX0306710) is a small molecule that primes the type I interferon response to cytosolic DNA, which is dependent on the adaptor MAVS and IRF1, but not the IRF3.
More description
|

|
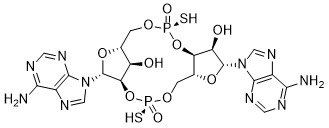
| DC10908 | ML RR-S2 CDA Featured |
ML RR-S2 CDA is a synthetic cyclic dinucleotide (CDN) that contains non-canonical 2'5'-phosphodiester bonds and is an activator of stimulator of interferon genes (STING).
More description
|
|
| DC12367 | Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate Featured |
2'3'-cGAMP has been used to identify small compounds capable of binding human stimulator of interferon genes (STING). It is also used to study type I interferon response to cytosolic DNA.
More description
|

|
| DC60034 | STING inhibitor-1 Featured |
STING inhbiitor, which inhibited the activation of the STING signal pathway and to prevent or treat a STING-mediated disease.
More description
|
.jpg)
|
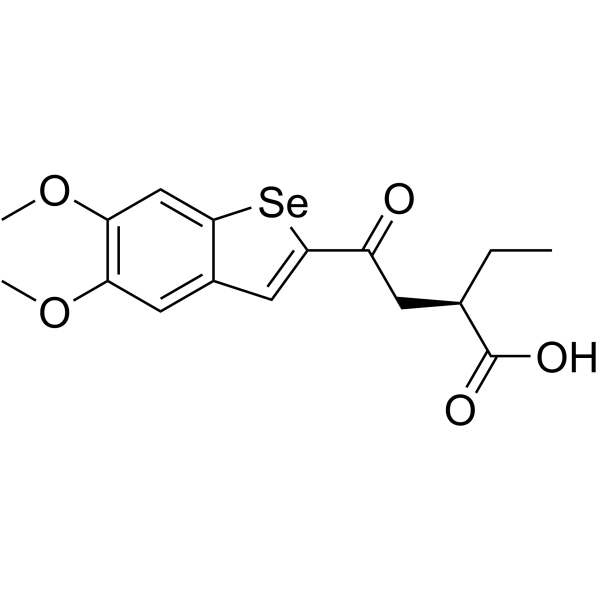
| DC72041 | BSP16 Featured |
BSP16 is a potent, orally active stimulator of interferon genes (STING) agonist. BSP16 can selectively stimulate the STING pathway. BSP16 can be used for the research of cancer.
More description
|
|
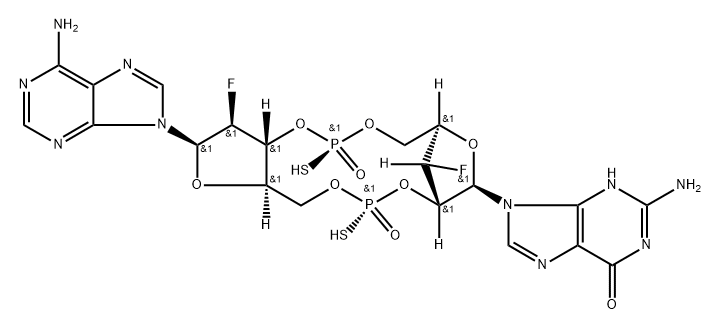
| DC47077 | Ulevostinag |
Ulevostinag (MK-1454) is a STING agonist.
More description
|
|
| DC72849 | STING agonist-22 |
STING agonist-22 (CF501) is a potent non-nucleotide STING agonist. STING agonist-22 is a adjuvant by activating STING to induce the type I interferon (IFN-I) response and proinflammatory cytokine production. STING agonist-22 can be used as an adjuvant to boost the original protein vaccine, producing potent, broad, and long-term immune protection. STING agonist-22 can be used for SARS-CoV-2 variants and sarbecovirus diseases research.
More description
|

|
| DC72646 | CL845 |
CL845 is an analog of the STING agonist CL656. CL845 can be used to synthesize conjugatable PRR ligands that target STING (stimulator of interferon genes). CL845 can be usexd for the research of cancers, immunological disorders or infections.
More description
|

|
| DC72645 | C-di-IMP |
C-di-IMP (Cyclic-di-IMP) is a STING agonist. C-di-IMP can be used for the research of tumor.
More description
|

|
| DC72644 | CL845-PAB-Ala-Val-C5-MC |
CL845-PAB-Ala-Val-C5-MC is a conjugatable STING ligand, it is synthesized from the proprietary cyclic dinuleotide CL845. CL845-PAB-Ala-Val-C5-MC can be used for bioconjugation.
More description
|

|
| DC72643 | CL845-PAB-Ala-Val-PEG4-Azide |
CL845-PAB-Ala-Val-PEG4-Azide is a conjugatable STING ligand, it is synthesized from the proprietary cyclic dinuleotide CL845. CL845-PAB-Ala-Val-PEG4-Azide can be used for bioconjugation.
More description
|

|
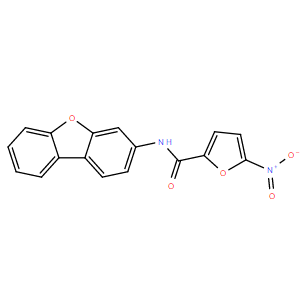
| DC10959 | STING inhibitor C-178 Featured |
STING inhibitor C-178 is a covalent, small-molecule inhibitor of STING, blocks palmitoylation (PMA)-induced clustering of STING; covalently binds to Cys91, directly targets mouse STING (mmSTING) but not human STING (hsSTING).
More description
|
|
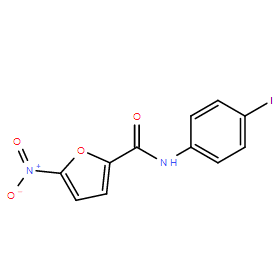
| DC10960 | STING inhibitor C-176 Featured |
STING inhibitor C-178 is a covalent, in vivo-active, small-molecule inhibitor of STING
More description
|
|
| DC39031 | MSA-2 Featured |
MSA-2 is an orally available human STING agonist.MSA-2 is bound to STING as a noncovalent dimer. Extensive experimental analysis indicates that MSA-2 predimerization is required for binding. Acidic tumor microenvironments favor permeable, uncharged MSA-2.
More description
|
|
| DC7404 | DMXAA Featured |
DMXAA (Vadimezan) is a vascular disrupting agents (VDA) and competitive inhibitor of DT-diaphorase with Ki of 20 μM and IC50 of 62.5 μM, respectively. Phase 3.
More description
|

|
| DC11641 | Cridanimod Featured |
A potent type I interferon (IFN) inducer that directly binds to STING and triggers a strong antiviral response through the TBK1/IRF3 route.
More description
|

|
| DC72351 | CDN-A |
CDN-A is a cyclic di-nucleotide, it can be used to synthesis antibody-drug conjugate (ADC). Cyclic di-nucleotides are potent stimulators of innate and adaptive immune responses. In humans, cyclic di-nucleotide, which are either produced endogenously in response to foreign DNA or by invading bacterial pathogens, trigger the innate immune system by activating the expression of interferon genes.
More description
|

|
| DC72040 | TAK-676 |
TAK-676 is an agonist of STING, triggering the activation of STING signaling pathway and type I interferons. TAK-676 is also a modulator of immune system, resulting complete regressions and durable memory T-cell immunity. TAK-676 promotes durable IFN-dependent antitumor immunity.
More description
|

|
| DC71134 | Ulevostinag (isomer 1) |
Ulevostinag isomer 1 (MK-1454 isomer 1) is the isomer of Ulevostinag. Ulevostinag is a STING agonist.
More description
|

|
| DC70810 | STING agonist 22 |
STING agonist 22 is a novel, non-nucleotide specific small-molecule STING agonist with IC50 of 28, 11 uM for human STING isoforms WT and HAQ, respectively.STING agonist 22 did not show any cytotoxicity in an immune cell proliferation panel across a variety of immune cell types and also did not show any activity in a kinome panel.STING agonist 22 introduced higher levels of iFIT3 and MX1 mRNA across three different donors possessing different STING genotypes: WT/WT, WT/HAQ, and WT/R232H in human PBMCs (IC50=5-35 uM).STING agonist 22 demonstrated in vivo antitumor effect in an MC38 mice model, with STING pathway activation and production of type I IFNs and proinflammatory cytokines, serum levels of IL-6, G-SCF, and MIP-1β.
More description
|

|
| DC49672 | STING agonist-8 |
STING agonist-8 is a potent STING agonist with an EC50 of 27 nM in THP1-Dual KI-hSTING-R232 cells (WO2021239068A1, compound 5-AB).
More description
|

|
| DC49671 | IACS-8779 disodium |
IACS-8779 disodium is a highly potent stimulator of interferon genes (STING) agonist with robust systemic antitumor efficacy. IACS-8779 disodium shows robust activation of the STING pathway in vitro and a superior systemic anti-tumor response in the B16 murine model of melanoma.
More description
|

|
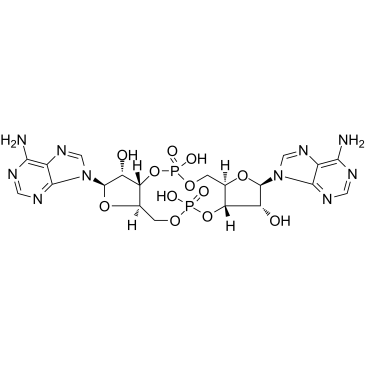
| DC28012 | c-Di-AMP(Cyclic-Di-AMP) ammonium salt Featured |
Bis-(3'-5')-cyclic dimeric adenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) is a bacterial second messenger implicated in the control of cell wall metabolism, osmotic stress responses and sporulation.
Detection of c-di-AMP by the host cytoplasmic surveillance pathway (CSP) is known to elicit type I IFN responses through a signaling axis that involves STING, TBK1 and IRF3 [1, 2].
Involvement of the helicase DDX41 in the recognition of c-di-AMP has been suggested [3].
Recent studies have also demonstrated that c-di-AMP exerts strong adjuvant activities when delivered by the mucosal route [4, 5].
More description
|
|
| DC28013 | Cyclic-di-GMP(c-di-GMP) Featured |
Cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP) is one of the most important and common bacterial second messenger. It is involved in numerous prokaryotic processes, including biofilm formation, motility, virulence, and cell cycling. c-di-GMP also has functions in eukaryotic cells. It is detected by the transmembrane protein stimulator of interferon genes (STING), leading to activation of the innate immune system.
More description
|
|