 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Field of Application | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
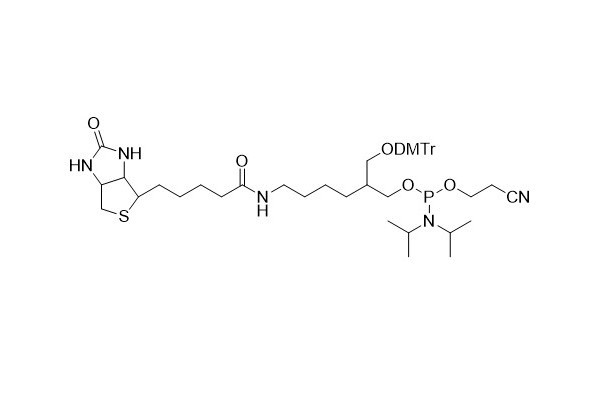
| DC67968 | Biotin CE Phosphoramidite Featured |
Biotin phosphoramidite stands as a vital instrument for incorporating biotin labels into oligonucleotide sequences, enabling the efficient labeling of oligonucleotides.
Biotin phosphoramidite features a spacer arm composed of 15 atoms. This spacer arm is designed to minimize potential hindrances associated with biotin binding. It complements the commonly used biotin phosphoramidite, which lacks the DMT group. The latter can only be added to the 5'- end of the oligonucleotide, and its addition effectively terminates the synthesis process.
More description
|
|
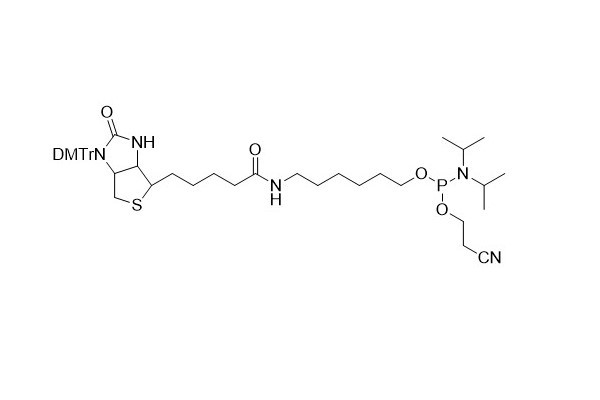
| DC67967 | 5'-Biotin CE Phosphoramidite Featured |
5'- Biotin phosphoramidite serves as a useful tool for incorporating biotin into oligonucleotides. However, it has a specific limitation in that it can only be added to the 5'- end of the oligonucleotide chain.
The DMTr (dimethoxytrityl) protecting group on the N1 position of biotin plays a crucial role during the coupling process. It effectively prevents the formation of branched structures, ensuring a more precise and controlled synthesis of the biotin - labeled oligonucleotides.
Biotin itself possesses sufficient hydrophobicity. This property allows for a relatively straightforward separation between biotin - labeled oligomers (in the DMT OFF state) and unlabeled oligomers. Nevertheless, the DMTr group still has its unique value. It can be utilized to facilitate the purification process when using reverse - phase cartridges and high - performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). This additional assistance from the DMTr group can lead to more efficient and accurate purification of the desired biotin - labeled oligonucleotides.
More description
|
|
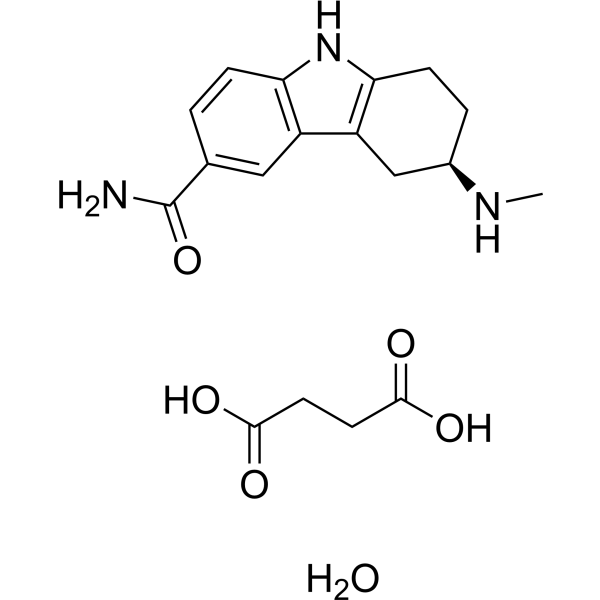
| DC22890 | Frovatriptan Featured |
A potent, long lasting 5-HT(1B/1D) receptor agonist as a antimigraine agent..
More description
|
|
| DC70589 | MC-GGFG-DX8951 Featured |
MC-GGFG-DX8951 is a drug-linker conjugate for ADC with antitumor activity by using DX8951 (DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor), linked via the protease cleavable MC-GGFG linker.
More description
|

|
| DC70526 | JP-11646 Featured |
JP-11646 is a novel potent, selective, non-ATP competitive Pim2 inhibitor with IC50 of 0.5/1/24 nM for Pim2/3/1, respectively; shows less potency for other kinases in a kinase selectivity panel; exhibits 4-760-fold greater suppression of MM proliferation and viability than ATP-competitive PIM inhibitors; significant reduces tumor burden and increases median survival in xenogeneic myeloma murine models.
More description
|

|
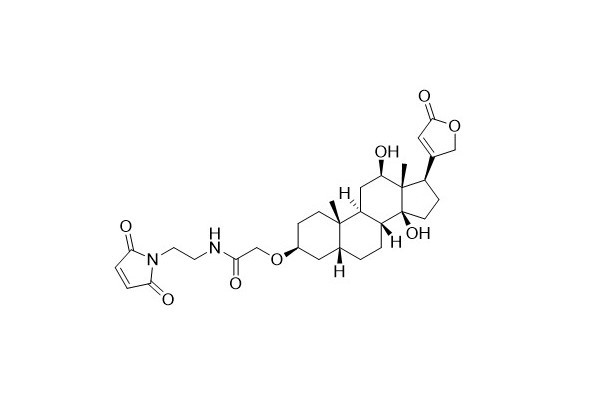
| DC67966 | Digoxigenin Maleimide Featured |
Digoxigenin (DIG) is a small molecule with high antigenicity. Similar to other commonly used haptens like 2,4 - Dinitrophenol (DNP) and biotin, it can be applied in a variety of biological detection methods. Generally, Digoxigenin is conjugated with large biomolecules to be detected, such as proteins and nucleic acids. Anti - Digoxigenin antibodies are directly or indirectly labeled with fluorescent dyes or enzymes for visualization and detection purposes. Under mild conditions, Digoxigenin maleimide can easily react with thiol groups, enabling the attachment of Digoxigenin molecules to proteins or thiol - substituted oligonucleotides.
More description
|
|
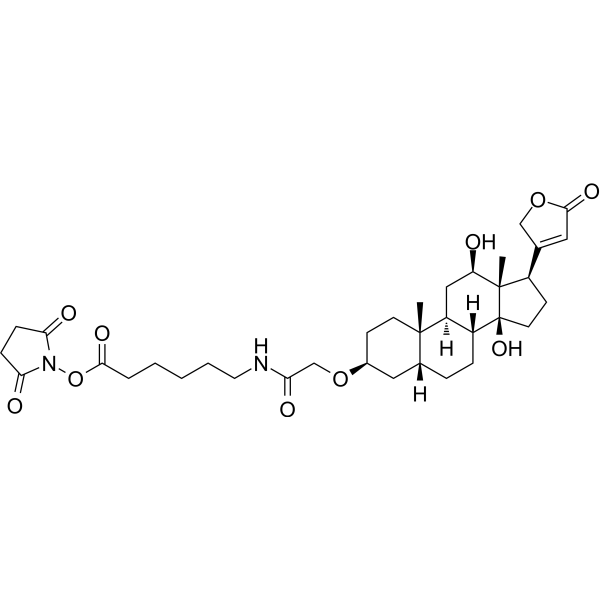
| DC67965 | Digoxigenin NHS Featured |
Digoxigenin NHS is an activated ester which readily reacts with amino groups under mild conditions, attaching the Digoxigenin (HY-B1025) moiety to proteins or amino-. Digoxigenin NHS ester can be used to label proteins and oligonucleotides.
More description
|
|
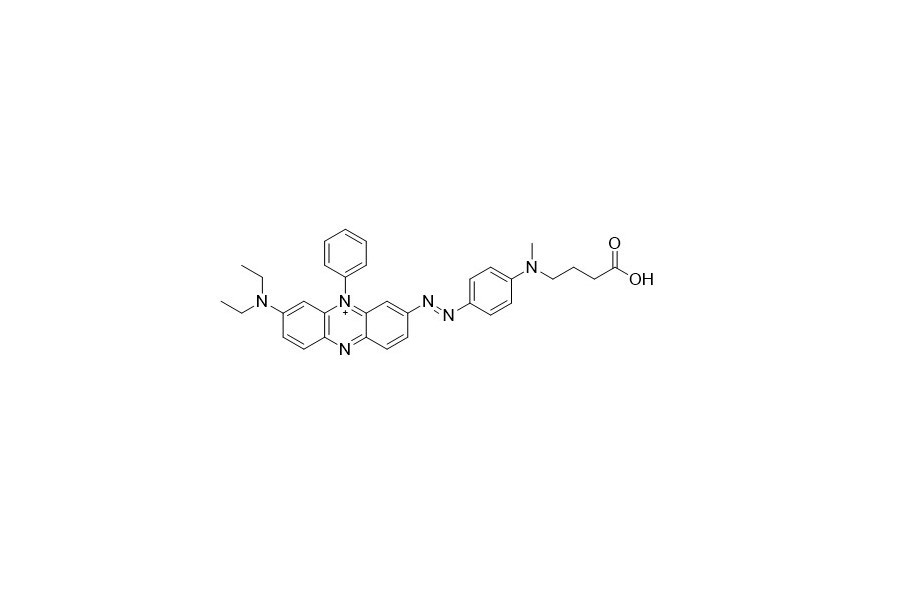
| DC67964 | HCQ-3 Acid Featured |
BHQ is a genuine dark quencher. Thanks to its polycyclic azo backbone, it has no natural emission. These quenchers can be paired with all common dyes to construct highly efficient quenching qPCR probes.
More description
|
|
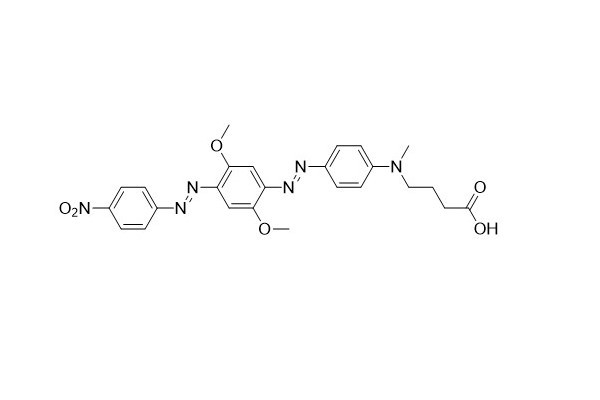
| DC67963 | HCQ-2 Acid Featured |
|
|
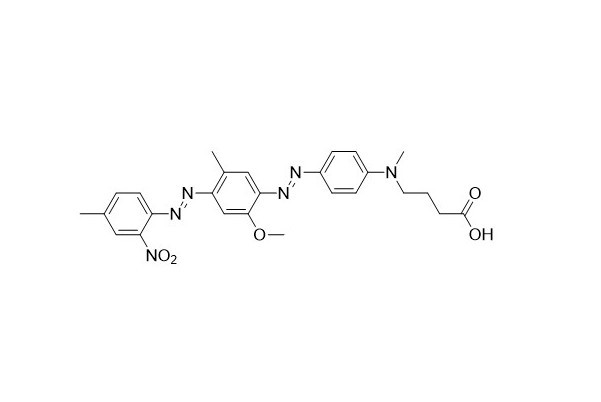
| DC67962 | HCQ-1 Acid Featured |
HCQ - 1 is equivalent to BHQ - 1. It can be positioned either at the end or within the oligonucleotide. Oligonucleotides labeled with BHQ - 1 have a wide range of applications, one of which is as dual - labeled fluorescent probes in real - time PCR. Regarding the synthesis and modification of BHQ - 1 quenched oligonucleotides, you can refer to the service link of biosynthesis.
More description
|
|
| DC67961 | Cyanine 5 Acid Featured |
Cyanine 5 Acid serves as an analog of the free carboxylic acid form of Cy5 and contains the Cyanine5 fluorophore. This particular dye has limited water - solubility. However, to obtain a solution material with an effective concentration, it can be dissolved in a mixture of water and organic phases such as DMF, DMSO, and alcohols.
More description
|
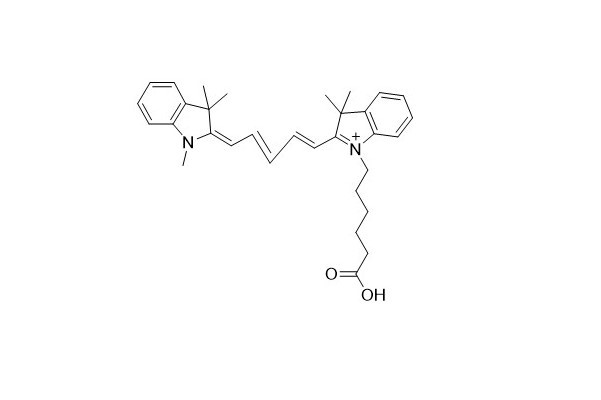
|
| DC67960 | Cyanine 3 Acid Featured |
Cyanine 3 Acid is a non-toxic red fluorescent dye with good solubility in organic solvents. Cyanine3 carboxylic acid chloride can be used as a non-reactive fluorophore for experimental control and calibration. Cyanine3 carboxylic acid chloride can also be synthesized with targeted agents as fluorescent probes for rapid detection of agent reactions.
More description
|
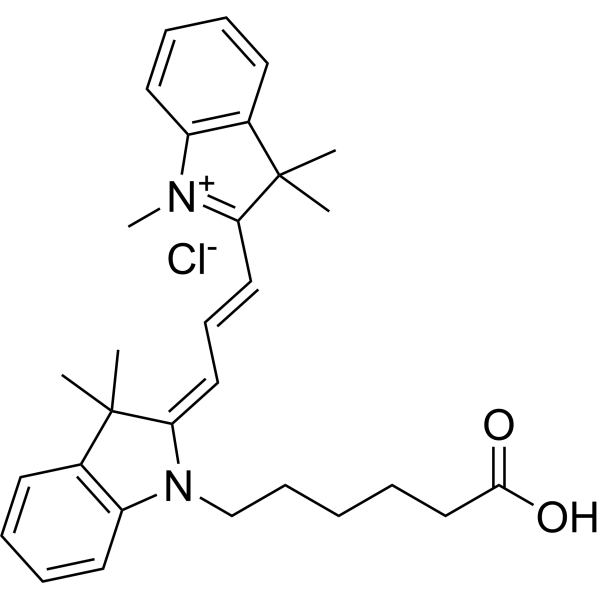
|
| DC67959 | Tex Red-X Acid Featured |
Tex Red-X dye is an innovative alternative to Tex Red. A key difference lies in its chemical structure - it features an additional seven - atom aminocaproyl spacer ("X") between the fluorophore and the carboxyl group. This spacer plays a crucial role in separating the fluorophore from its attachment point. By doing so, it effectively minimizes the interaction between the fluorophore and the conjugated biomolecule.
One of the standout features of Tex Red - X is that it exists as a single 5 - isomer. This characteristic significantly enhances the reproducibility of results, which is a highly desirable trait in scientific research and biological applications.
In terms of optical properties, Tex Red - X shares the same spectral characteristics as Texas Red. It can be utilized to create bright red fluorescent bioconjugates with excitation and emission maxima at approximately 595/615 nm. These bioconjugates are valuable tools in various biological and biochemical studies, enabling researchers to visualize and analyze biological processes with high precision.
More description
|
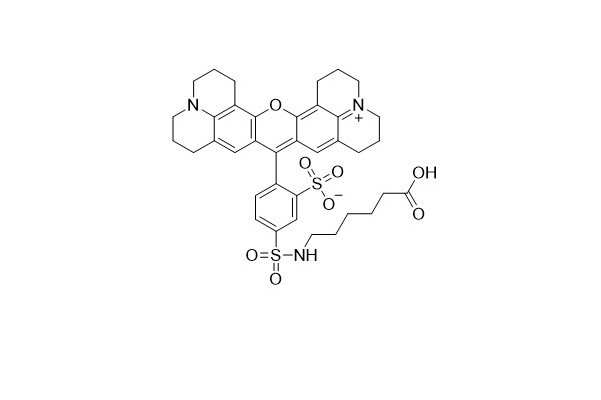
|
| DC32450 | Rhodamine 123 Featured |
Rhodamine 123 is a chemical compound and a dye.
More description
|
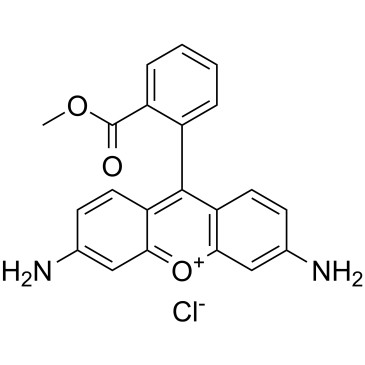
|
| DC60916 | 6-ROX Featured |
6-ROX is a selective fluorescent probe and potential inhibitor of COX-2. 6-ROX binds to the active site of COX-2 and inhibits its conversion of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins. 6-ROX is often used in the field of optical imaging related to tumors and inflammation, and helps detect diseased tissues with high expression of COX-2.
More description
|
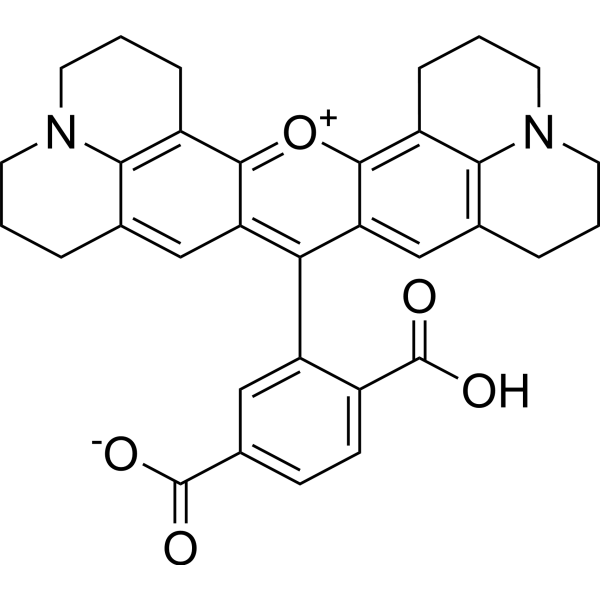
|
| DC70363 | DN200434 Featured |
DN200434 (DN-200434) is a highly potent (functional IC50=6 nM, binding IC50=40 nM), selective, biocompatible and orally available ERRγ inverse agonist.DN200434 binds to key ERRγ binding pocket residues through four-way interactions.DN200434 effectively upregulated iodide-handling genes and restored radioiodine avidity in ATC tumor lesions.DN200434 enhanced ATC tumor radioiodine therapy susceptibility, markedly inhibiting tumor growth.DN200434 shows higher potency than GSK5182.
More description
|
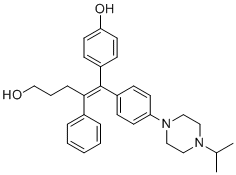
|
| DC67958 | 6-NED Acid Featured |
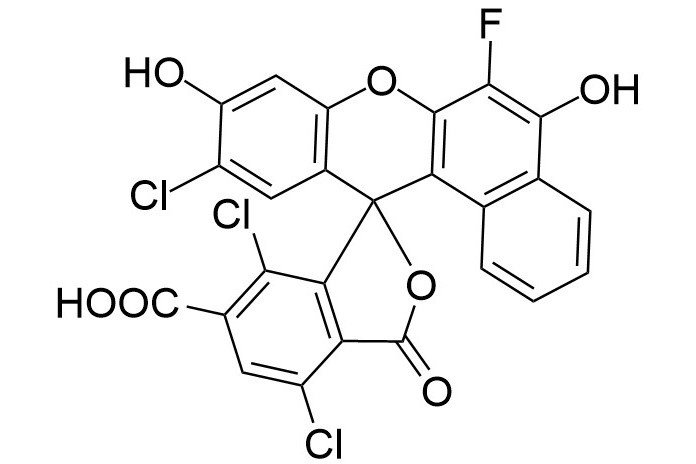
|
|
| DC47813 | OG 488, acid Featured |
OG 488, acid, a fluorescent pH indicator, has many applications in biochemistry and neurosciences.
More description
|

|
| DC67957 | QCY 21 NHS Featured |
QSY 21 has a wide - ranging and intense absorption with a peak at 661 nanometers. It emits no detectable fluorescence, which makes it highly useful as an acceptor in Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) applications. As a commonly - used long - wavelength quencher, it can be optimally paired with fluorescent dyes such as Cy5, Alexa Fluor 647, iFluor 647, or other dyes with similar spectra.
More description
|
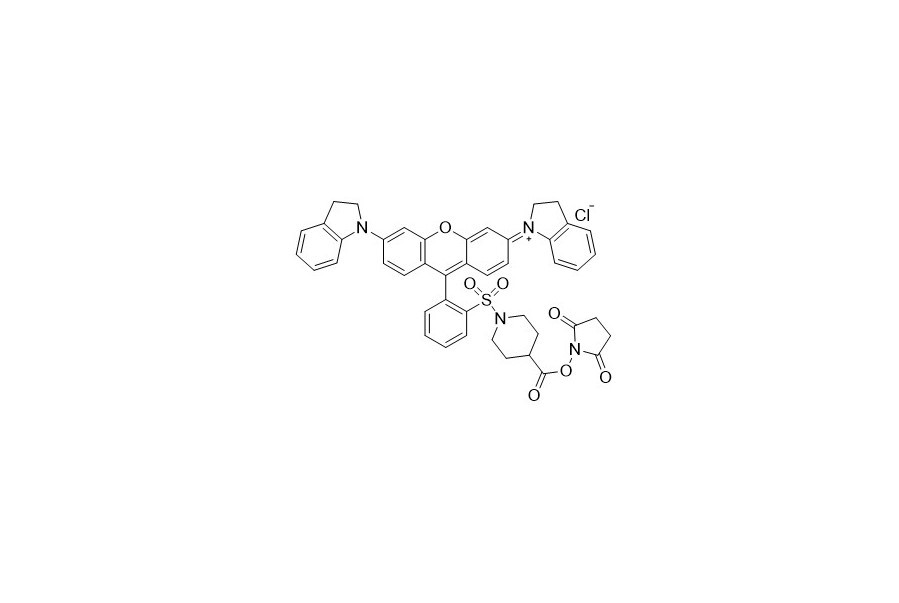
|
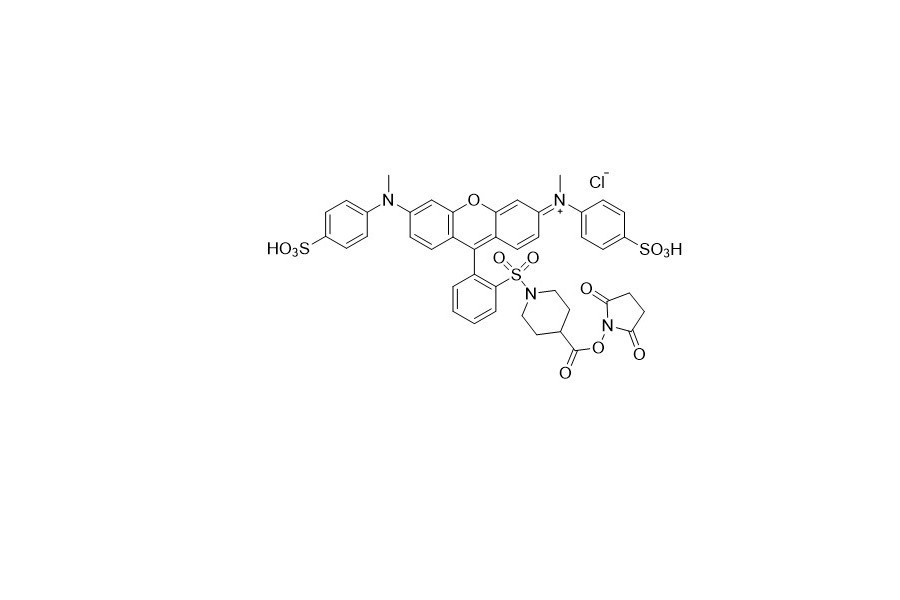
| DC67956 | QCY 9 NHS Featured |
The amine - reactive quencher, QCY9 NHS, shows a broad and intense absorption in the visible light range with a peak at approximately 560 nm. Moreover, it lacks fluorescence, which disqualifies it from being used as an acceptor in Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) applications.
More description
|
|
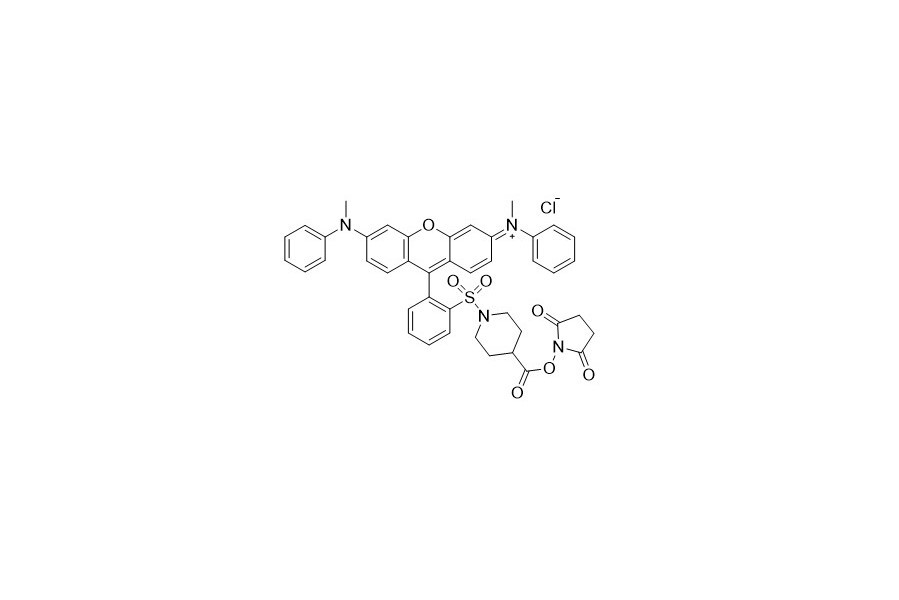
| DC67955 | QCY 7 NHS Featured |
QCY 7 NHS and QSY 7 NHS refer to the same molecule. QCY 7 features a broad and intense absorption with a peak at around 550 nanometers and has no detectable fluorescence. These characteristics make it highly useful as an acceptor in Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) applications when paired with fluorescent dyes such as Cy3, TAMRA, Alexa Fluor 555, iFluor 647, or other dyes with similar spectra.
More description
|
|
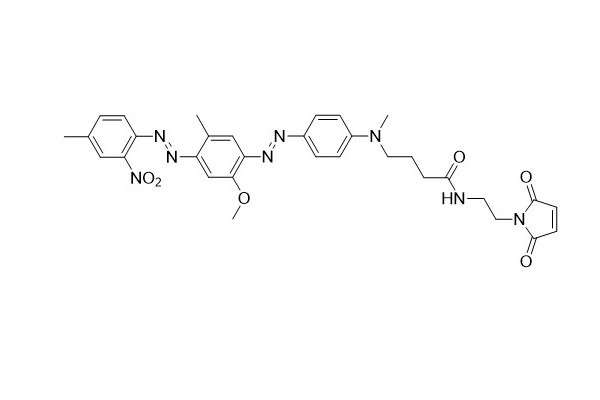
| DC67954 | HCQ-1 Maleimide Featured |
HCQ - 1 maleimide serves as an excellent building block for labeling thiol - containing molecules. The HCQ - 1 dye exhibits almost no fluorescence and has a moderate extinction coefficient. These dark quenchers are commonly utilized in molecular beacon probes. In such probes, the contribution of FRET to fluorescence quenching is extremely small. As a result, compared with other FRET probes like FRET peptides, the dependence on donor - acceptor spectral overlap is not as prominent. The HCQ - 1 dye is capable of quenching a variety of fluorophores, especially fluorescein derivatives such as FAM, HEX, TET, NED, and JOE.
More description
|
|
| DC67953 | HCQ-3 NHS Featured |
HCQ-3 NHS has a maximum absorbance at 672 nm and can be placed at either the 5' or 3' end of an oligonucleotide or within its interior. Oligonucleotides labeled with BHQ-3 are employed in numerous applications, such as dual-labeled fluorescent probes for real-time PCR. This dark quencher has a strong absorption range from 620 to 730 nm, enabling it to quench fluorophores that emit fluorescence within this range, like Quasar 670 and Quasar 705 dyes.
More description
|
|
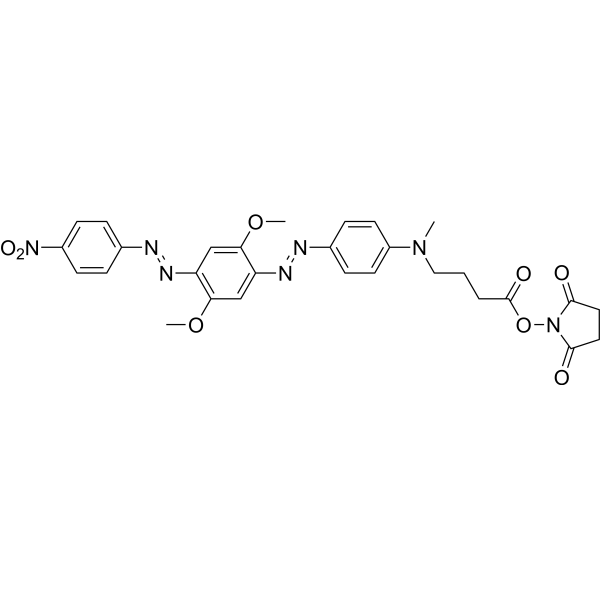
| DCC0967 | HCQ-2 NHS Featured |
HCQ-2 NHS is a dark quencher with no native emission due to the polyaromatic-azo backbone and a terminal NHS ester. UBHQ-2 NHS has a wide and intense quenching range from 560-670 nm, which makes it useful as an acceptor in fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) applications in conjunction with orange to far-red emitting dyes. The NHS ester can be applied to label the primary amines (-NH2) of proteins, amine-modified oligonucleotides, and other amine-containing molecules.
More description
|
|
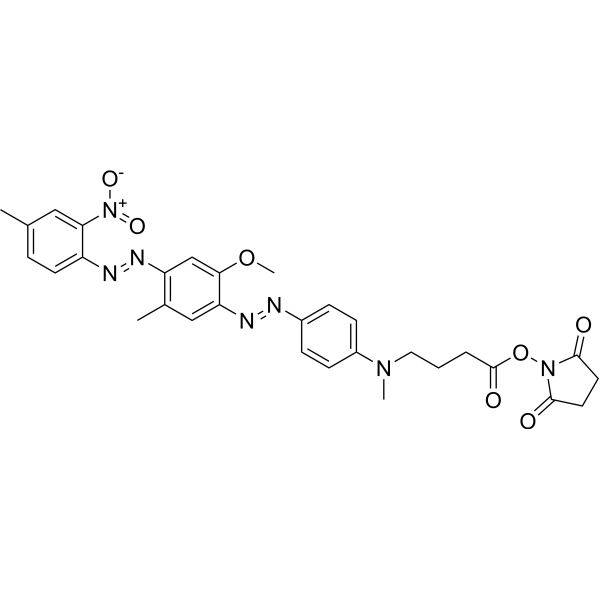
| DC67952 | HCQ-1 NHS Featured |
HCQ-1 NHS directly labeled by fluorescently labeled nucleotide.
More description
|
|
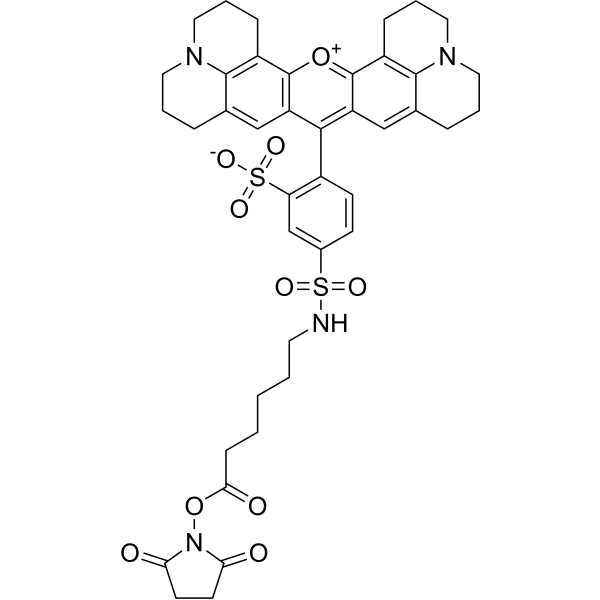
| DC67951 | Tex Red-X NHS Featured |
Tex Red-X NHS is a derivative of Texas Red (HY-101878), an amphoteric rhodamine red fluorescent dye. Texas Red is widely used to study neuronal morphology and as a cell type-selective fluorescent marker for astrocytes, both in vivo and in slice preparations.
More description
|
|
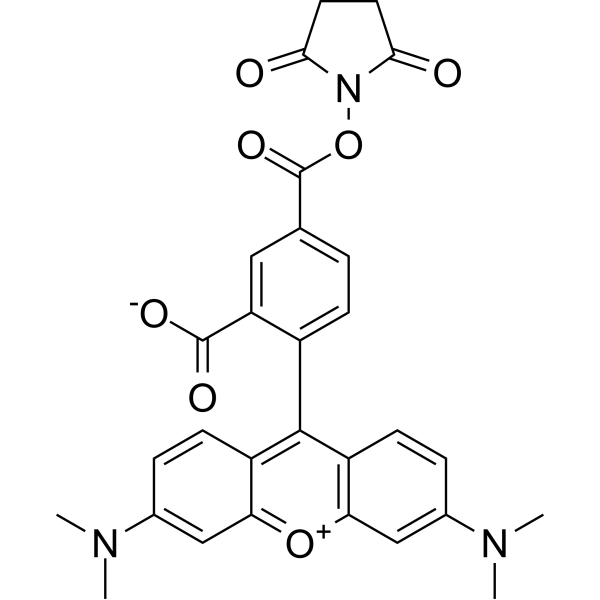
| DC67950 | 5-TAMRA NHS Featured |
5-TAMRA NHS is an amine-reactive fluorescent agent, and its conjugate produces bright, pH-insensitive orange-red fluorescence with good photostability (Ex/Em = 565/580 nm).
More description
|
|
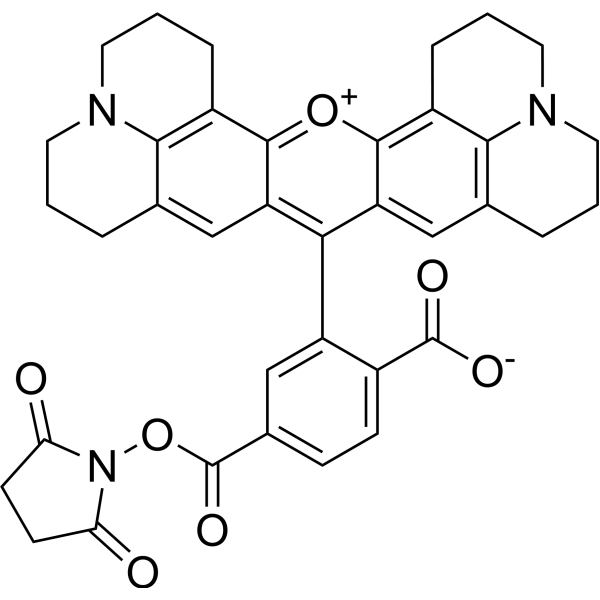
| DC67949 | 6-ROX NHS Featured |
6-Carboxy-X-rhodamine, succinimidyl ester (6-ROX, SE) is a fluorescent dye for oligonucleotide labeling and automated DNA sequencing.
More description
|
|
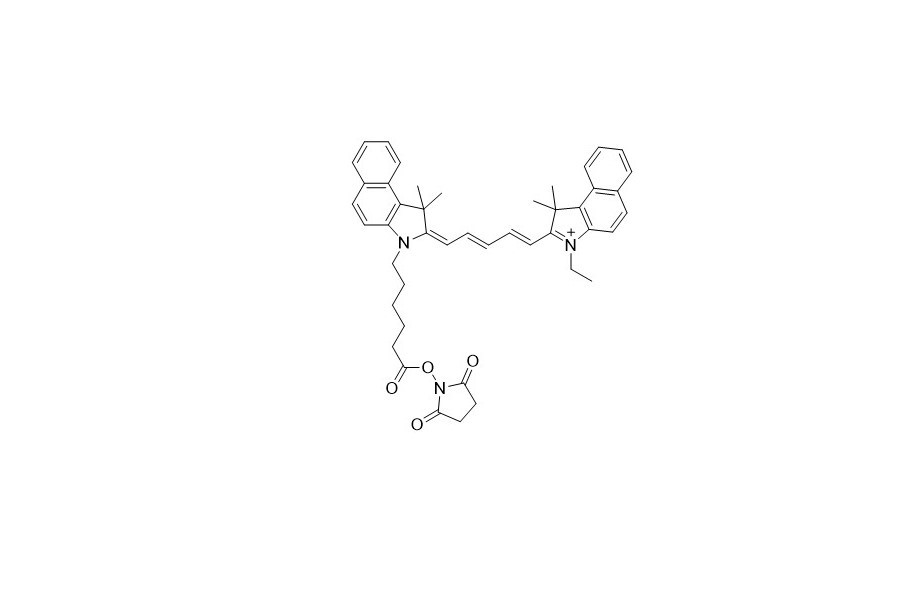
| DC67948 | Quassar 705 NHS Featured |
Quasar 705 fluorophore is an indocarbocyanine dye. It emits fluorescence in the deep - red region of the visible spectrum. This fluorescence can be effectively quenched by BHQ - 2 or BHQ - 3 dyes. The excitation wavelength of Quasar 705 is 690 nm, and its emission wavelength is 705 nm.
More description
|
|
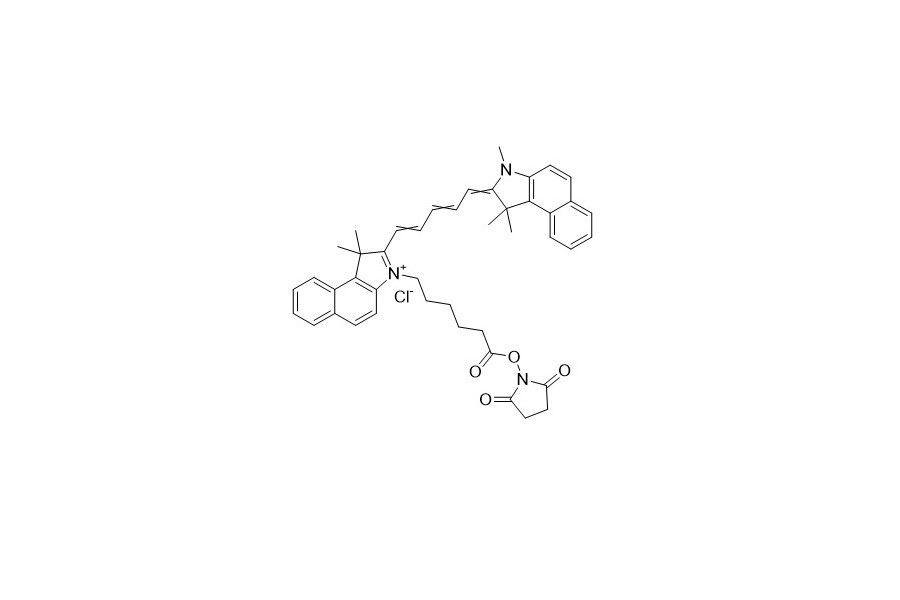
| DC67947 | Quasar 670 NHS Featured |
Quassar 670 NHS emits red fluorescence. It has an excitation wavelength of 670 nm and an emission wavelength of 644 nm.
More description
|
|