 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Field of Application | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC67664 | Allopole prodrug moiety Featured |
Allopole prodrug moiety is the prodrug form of Allopole.
More description
|

|
| DC7556 | VcMMAE (MC-Val-Cit-PAB-MMAE) Featured |
VcMMAE is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) with potent antitumor activity by using the anti-mitotic agent, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), linked via the lysosomally cleavable dipeptide, valine-citrulline (vc).
More description
|

|
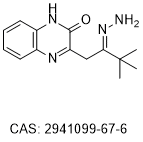
| DC74021 | IBS007125 Featured |
IBS007125 is a small molecule inhibitor of c-Maf, inhibits multiple myeloma proliferation by targeting cMaf transcriptional activity.
More description
|
|
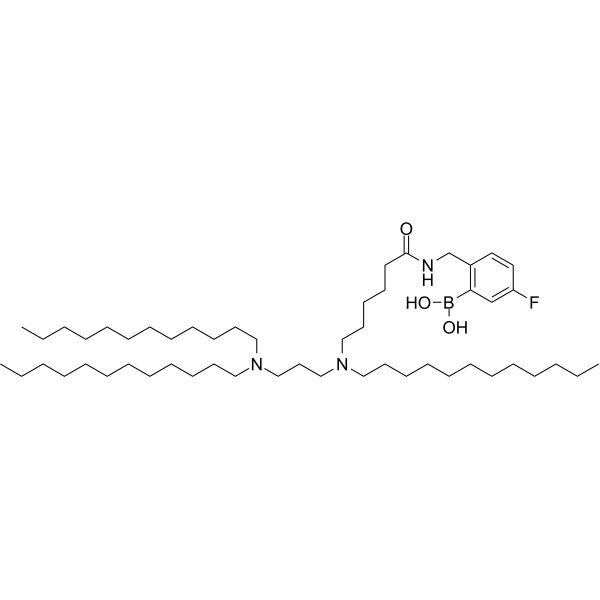
| DC67981 | Diamino lipid DAL4 Featured |
Diamino lipid DAL4 is diamino lipid for the preparation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) encapsulated with mRNAs encoding cytokines including IL-12, IL-27 and GM-CSF. Diamino lipid DAL4 delivers mRNA to tumor cells to exert anti-tumor activity.
More description
|
|
| DC67563 | S-Ac7-DOg Featured |
S-Ac7-DOg is an ionizable lipid engineered for optimized mRNA delivery to the retina, featuring a sulfur-based ester bond (S-Ac) and dual oleyl glyceride chains (DOg). Its pKa (~6.74) is finely tuned to enhance endosomal escape in acidic environments, enabling efficient cytosolic mRNA release. Unlike traditional lipids (e.g., C12-200, MC3), S-Ac7-DOg incorporates biodegradable ester linkages that hydrolyze intracellularly, minimizing lipid accumulation and reducing innate immune activation.
In vitro, S-Ac7-DOg LNPs achieved >80% transfection efficiency in retinal cells (ARPE-19, MIO-M1) with negligible cytokine secretion, outperforming MC3 and rivaling C12-200 while avoiding the latter’s high immunogenicity. In vivo, intravitreal delivery in mice showed robust protein expression in the optic nerve head (ONH) and Müller glia (75–100% of eyes), sustained for ≥7 days. Critically, it induced the lowest immunogenicity among tested lipids: minimal leukocyte infiltration (<1.5-fold vs. PBS), no microglial reactivity, and reduced GFAP upregulation.
More description
|

|
| DC33580 | DODMA Featured |
DODMA, also known as MBN 305A is a a cationic lipid containing the unsaturated long-chain (18:1) oleic acid inserted at both the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. It has been used in the composition of lipospomes formulated as stable nucleic acid lipid particles that can encapsulate siRNA or other small molecules to be used for drug delivery
More description
|

|
| DC86120 | EA-PIP(LIPID 10) Featured |
Lipid 10 is a novel ionizable cationic lipid be used for delivery of therapeutic RNA to the Bone Marrow in Multiple Myeloma Using CD38-Targeted with Lipid 10-LNP.
More description
|

|
| DC71417 | YSK 05 Featured |
YSK 05 is a pH-sensitive cationic lipid. YSK 05 improves the intracellular trafficking of non-viral vectors. YSK 05-MEND shows significantly good gene silencing activity and hemolytic activity. YSK 05 overcomes the suppression of endosomal escape by PEGylation. YSK 05 effectively enhances siRNA delivery both in vitro and in vivo.
More description
|

|
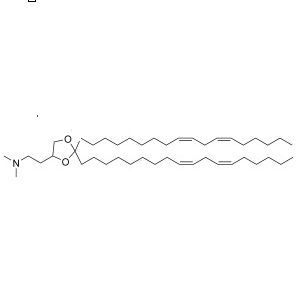
| DC12381 | DLin-KC2-DMA Featured |
DLin-KC2-DMA is a highly potent ionizable lipid used in the formulation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for the delivery of siRNA. It represents a significant advancement over earlier generations of lipids, such as DLin-DMA, due to its dramatically improved gene silencing efficiency.
More description
|
|
| DC67984 | L31(Lipid 31) Featured |
L31 is identified as a novel, proprietary ionizable cationic lipid that serves as the critical functional component within lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) engineered for CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). It was selected from a screened library of lipids for its superior performance. LNPs formulated with L31 exhibited excellent physicochemical properties, including a uniform size of 80-100 nm, low polydispersity, and high encapsulation efficiency (>85%) for both Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA. In vitro, L31-based LNPs demonstrated outstanding therapeutic efficacy, achieving approximately 68% gene editing of the oncogene SOX2 and an 88% reduction in cancer cell viability.For in vivo applications, L31-LNPs were further functionalized with anti-EGFR antibodies using the ASSET linker strategy to create targeted nanoparticles (tLNPs). This modification enhanced specific uptake by tumor cells. In a xenograft mouse model, intratumoral injection of these targeted L31-cLNPs co-encapsulating Cas9 mRNA and sgSOX2 led to potent tumor growth inhibition (90%) and a significant increase in survival, with tumor disappearance observed in half of the treated mice. In conclusion, L31 is a highly efficient ionizable lipid that forms the foundation of a potent targeted LNP platform for precise CRISPR-based cancer therapy against solid tumors.
More description
|
.png)
|
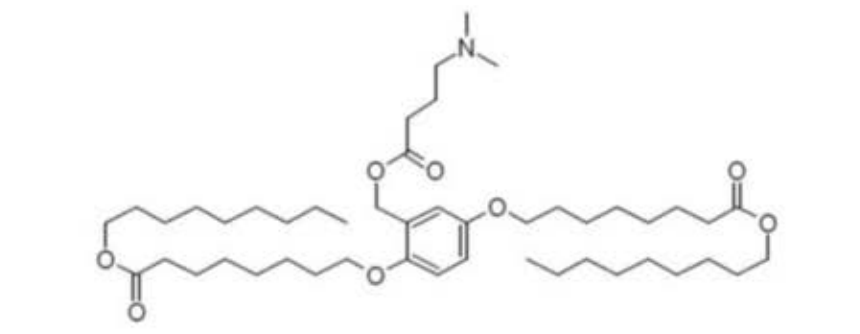
| DC67538 | XH-04 Featured |
XH-04 is an ionizable lipid engineered for advanced mRNA delivery developed by JiaChen West Lake Biotech. Its core structure features a central benzene ring with asymmetric hydrophobic tails (C9-C10 chains) and pH-responsive tertiary amines that enable efficient mRNA encapsulation and endosomal escape. As detailed in CN113993839A, XH04 outperforms industry benchmarks (e.g., MC3 lipid), boosting protein expression by >10-fold in BHK cells. In PCT/CN2024/121624, JiaChen further demonstrated its utility in lung-targeted LNPs (tLNP/tLCNP). When combined with cationic lipids (e.g., DOTMA at 2:1 molar ratio), XH 04 redirects >80% of mRNA delivery to murine lungs—overcoming liver tropism—while maintaining low toxicity. The lipid’s benzenic core and optimized alkyl chain geometry (patent claims 1-9) are credited for enhanced endosomal disruption and mRNA release kinetics. JiaChen’s innovations position XH-04 as a cornerstone for next-generation mRNA therapeutics.
More description
|
|
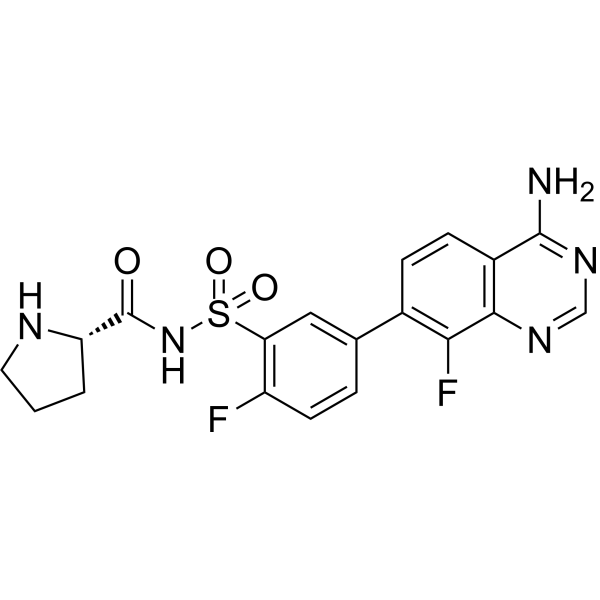
| DC76017 | PAA-38 Featured |
PAA-38 is a highly potent selective inhibitor targeting bacterial prolyl-tRNA synthetase (ProRS). PAA-38 againsts Pseudomonas aeruginosa ProRS (PaProRS) with a Kd value of 0.399 nM and an IC50 value of 4.97 nM. PAA-38 againsts human cytoplasmic ProRSs (HsProRS) with an IC50 value of 35.5 nM. PAA-38 demonstrates an in vitro antibacterial activity of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) = 4-8 μg/mL.
More description
|
|
| DC74356 | ACA22 Featured |
ACA22 is a small molecule KRAS inhibitor, inhibits KRAS-mediated signal transduction in cells expressing wild type (WT) and G12D mutant KRAS.
More description
|
|
| DC11041 | QCA276 Featured |
QCA276 is a novel potent BET proteins inhibitor with IC50/Ki of 10/.3 nM, QCA276 is the BET ligand for PROTAC QCA570.
More description
|

|
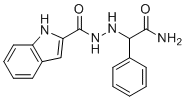
| DC49305 | Nangibotide Featured |
Nangibotide is a TREM-1 receptor inhibitor that can modulate innate immune response. Nangibotide can reduce systemic and in situ inflammatory reaction in rodent models of myocardial ischaemia‐reperfusion.
More description
|
|
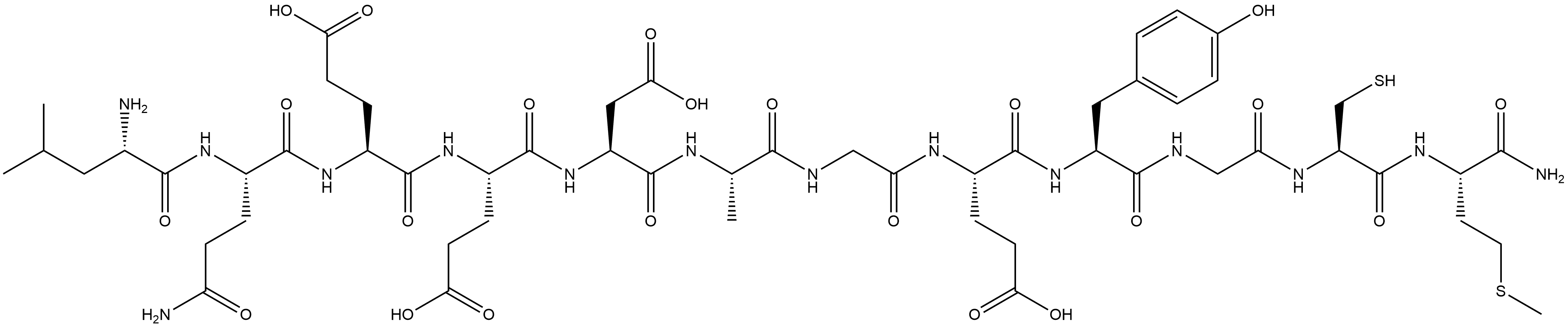
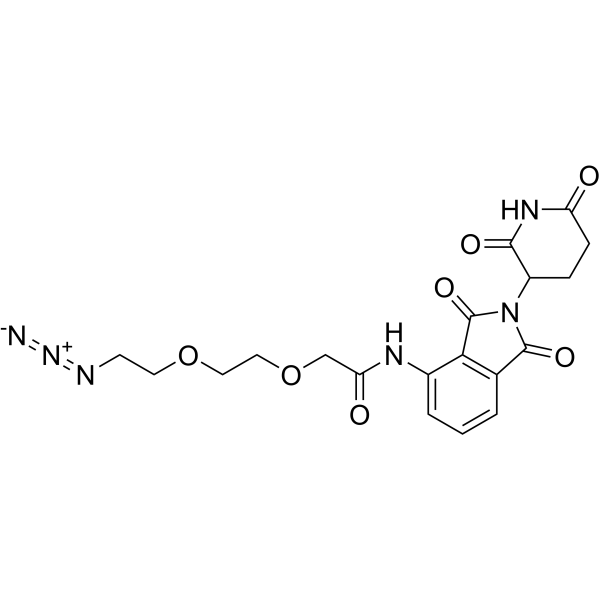
| DC67980 | Pomalidomide-PEG2-azide Featured |
Pomalidomide-PEG2-azide is a synthesized E3 ligase ligand-linker conjugate that incorporates the Pomalidomide based cereblon ligand and 2-unit PEG linker used in PROTAC technology[1]. Pomalidomide-PEG2-azide is a click chemistry reagent, it contains an Azide group and can undergo copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition reaction (CuAAc) with molecules containing Alkyne groups. It can also undergo strain-promoted alkyne-azide cycloaddition (SPAAC) reactions with molecules containing DBCO or BCN groups.
More description
|
|
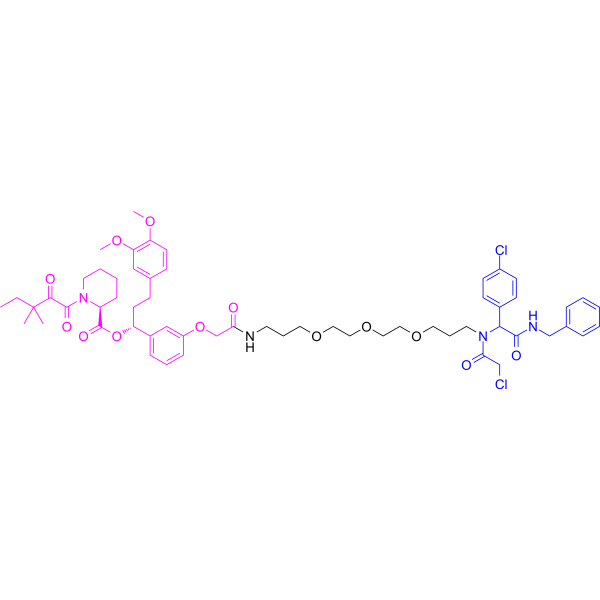
| DC77218 | 10-SLF Featured |
10-SLF is a PROTAC FKBP12 degrader. 10-SLF induces a ternary complex between FKBP12 and FBXW7-R465C, and promotes FBXW7-R465C-dependent proteasomal degradation of FKBP12. 10-SLF selectively reduces FKBP12 levels in cells expressing FBXW7-R465C.
More description
|
|
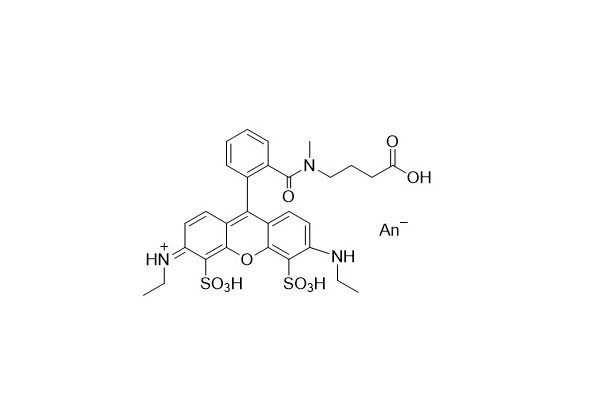
| DC67979 | ATO 532 Featured |
ATO 532 Acid has an identical molecular structure to ATTO 532 Acid. It is a fluorescent label related to the well - known dye Rhodamine 6G.
This dye is characterized by strong absorption, a high fluorescence quantum yield, excellent thermal and photostability, and good water solubility. Thanks to these features, ATO 532 is highly appropriate for single - molecule detection applications and high - resolution microscopy techniques, including Photoactivated Localization Microscopy (PALM), direct Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (dSTORM), Structured Illumination Microscopy (SIM), and Stimulated Emission Depletion Microscopy (STED).
In addition, it is also very suitable for use in Fluorescence - Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) and Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH). The fluorescence of ATO 532 Acid can be most efficiently excited within the range of 515 - 545 nanometers.
More description
|
|
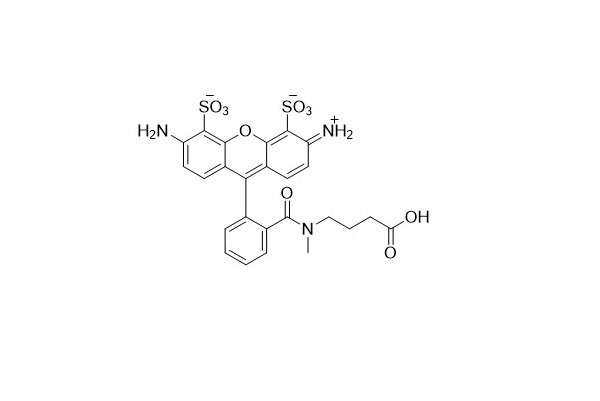
| DC67978 | ATO 488 Acid Featured |
ATO 488 has the same molecular structure as ATTO 488. It is a new type of hydrophilic fluorescent dye that offers excellent water - solubility, strong absorption capacity, a high fluorescence quantum yield, as well as outstanding thermal and photostability.
Due to these remarkable properties, ATO 488 is highly suitable for single - molecule detection applications and high - resolution microscopy techniques such as Structured Illumination Microscopy (SIM) and Stimulated Emission Depletion Microscopy (STED). Moreover, this dye is also well - suited for use in Fluorescence - Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) and Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH).
More description
|
|
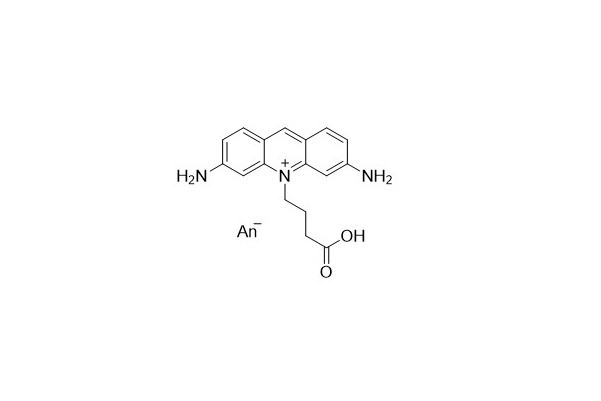
| DC67977 | ATO 465 NHS Featured |
The ATO 465 molecule shares the same structure as ATTO 465. It is a fluorescent dye derived from the well - known acridone dye.
ATO 465 has moderate hydrophilicity. Its fluorescence can be effectively excited within the range of 420 - 465 nm. This dye has remarkable features such as strong absorption, a high fluorescence quantum yield, excellent thermal stability, and high photostability.
In an aqueous solution, this dye exhibits an astonishingly large Stokes shift of 55 nm. When it comes to a solid matrix, especially under low - temperature conditions, the dye emits intense and long - lasting phosphorescence.
More description
|
|
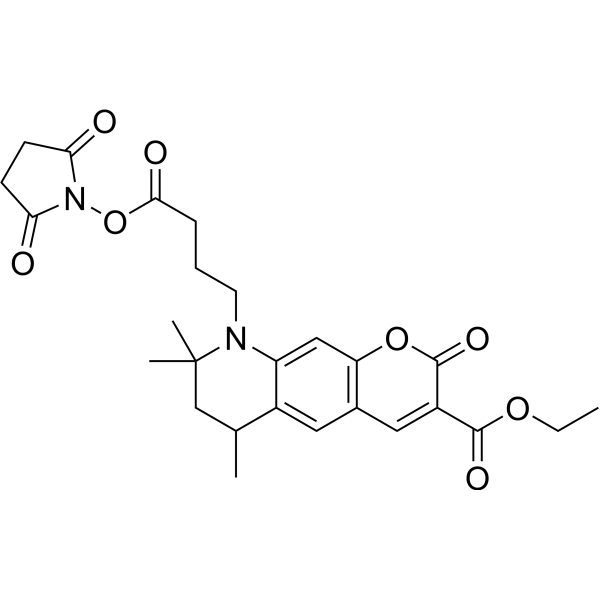
| DC67976 | ATO 425 NHS Featured |
ATTO 425 NHS ester is a new fluorescent marker based on the Rhodamine structure. It has strong absorption, high fluorescence quantum yield, high thermal stability and photochemical stability, and is suitable for single molecule detection and high-resolution microscopy. ATTO 425 NHS ester is an NHS ester derivative of ATTO 425 that can be used to label proteins or antibodies.
More description
|
|
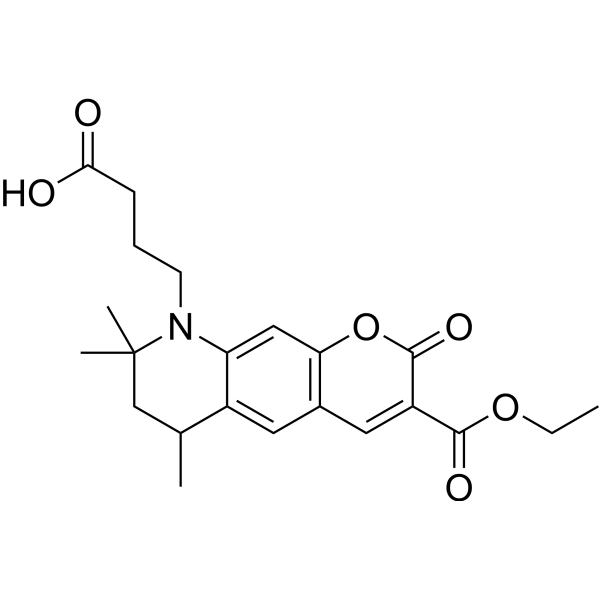
| DC67975 | ATTO 425 Acid Featured |
The ATO 425 Acid molecule is equivalent to ATTO 425. It is a novel fluorescent marker with a coumarin structure. This marker boasts several notable characteristics, including a high fluorescence quantum yield, excellent photostability, and a relatively low molecular weight.
More description
|
|
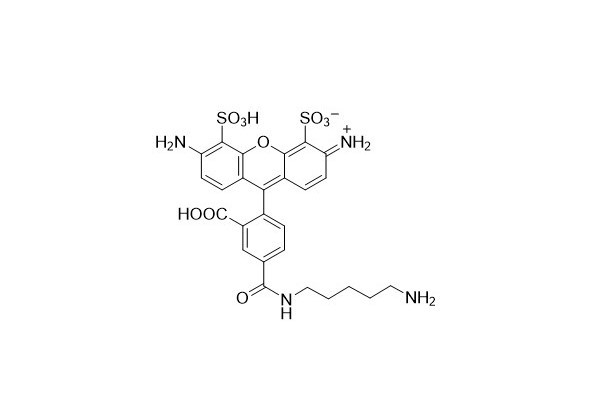
| DC67974 | AF488 Cadaverine Featured |
AF 488 Cadaverine is a carbonyl - reactive structural unit. In the presence of activators like EDC or DCC, or activated esters such as NHS esters, it can be used to modify carboxyl groups through the formation of stable amide bonds. Additionally, it can serve as a polar tracer and an active dye for labeling proteins via carboxylic acid molecules.
More description
|
|
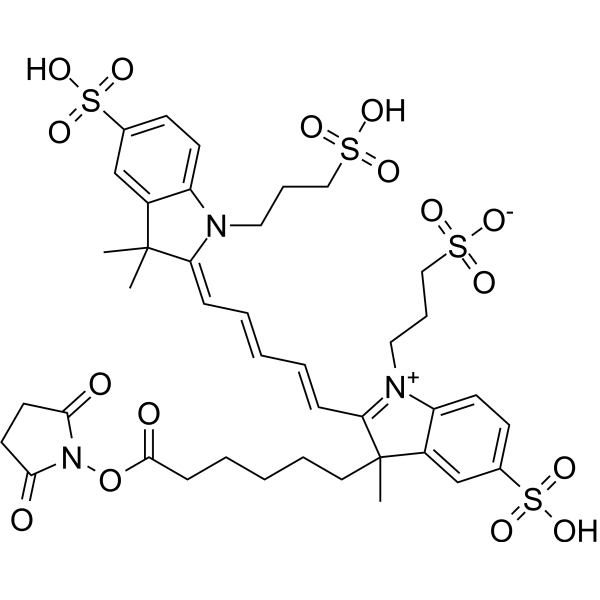
| DC67973 | AF 647 NHS Featured |
AF647-NHS ester is an analog of Alexa Fluor 647 (AF647). NHS ester can covalently bind to molecules with amino groups (such as proteins, antibodies, etc.). AF647 is a far-red fluorescent dye with an excitation wavelength (λex) of 635 nm (conventional fluorescence detection)/620 nm (instantaneous detection). Storage: Protect from light.
More description
|
|
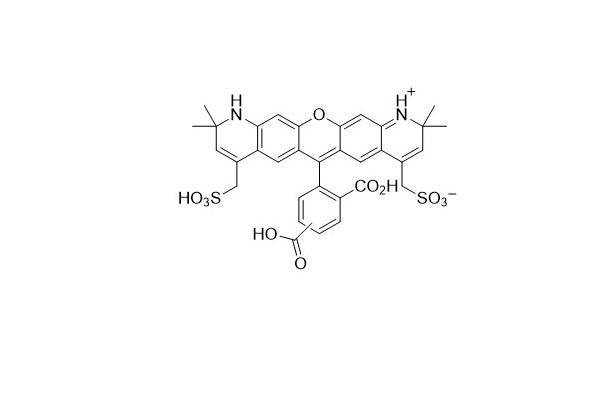
| DC67972 | AF 568 Acid Featured |
AF 568 Acid shares the same chemical structure as Alexa Fluor 568 Acid. It is a bright red fluorescent dye that is optimally suited for use with the 568 - nanometer laser line. The AF 568 dye is soluble in water and is insensitive to pH values ranging from 4 to 10.
AF 568 Acid represents the most cost - effective amine - reactive form for conjugating the Alexa Fluor 568 fluorophore with polypeptides.
More description
|
|
| DC41285 | TFAX 488,SE dilithium Featured |
TFAX 488,SE dilithium, an amine reactive green fluorescent dye, is insensitive to pH in the range 4-10. TFAX 488,SE dilithium forms bright and photostable conjugates with proteins and antibodies. TFAX 488,SE dilithium is suitable for use in flow cytometry, two-photon excitation microscopy (TPE), and super resolution microscopy techniques, such as dSTORM, SIM and STED. Excitation maximum=495 nm; emission maximum=515 nm; extinction coefficient=73,000 M-1cm-1; quantum yield=0.92.
More description
|

|
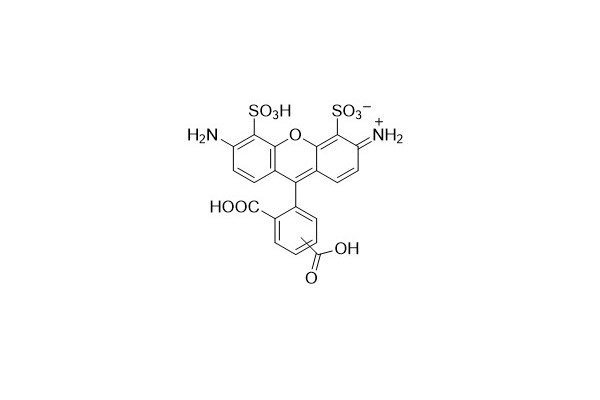
| DC67971 | AF 488 Acid Featured |
AF 488 is a vivid green fluorescent dye. Owing to its excellent photostability, it is frequently utilized in microscopy and cell detection. AF 488 can be used in conjunction with DAPI and is highly suitable for multiplex detection. It exhibits a high quantum yield and stable fluorescence within a pH range of 4 to 10.
More description
|
|
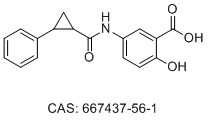
| DC74355 | ACA-14 Featured |
ACA-14 is a small molecule direct inhibitor of KRAS, impedes the interaction of KRAS with its effector Raf and reduces both intrinsic and SOS-mediated nucleotide exchange rates.
More description
|
|
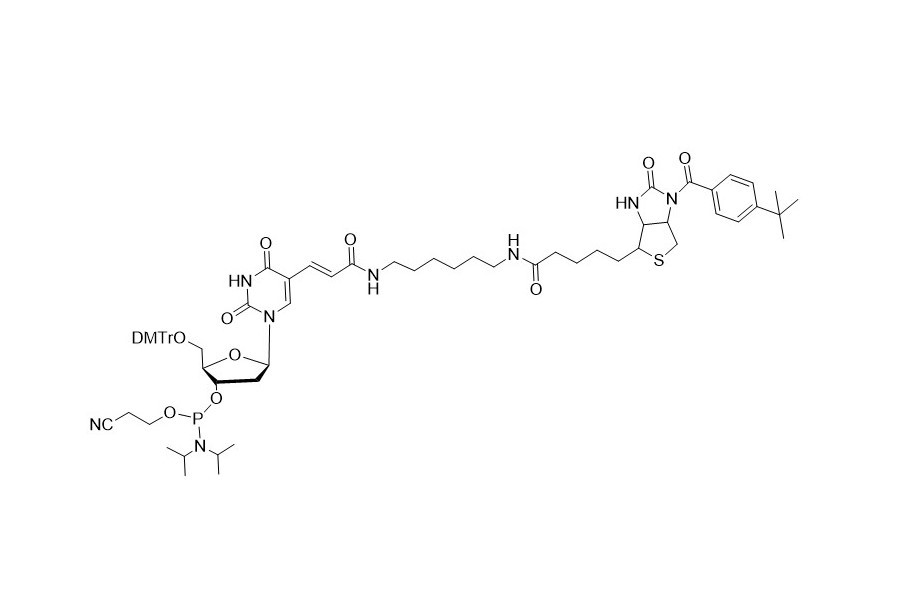
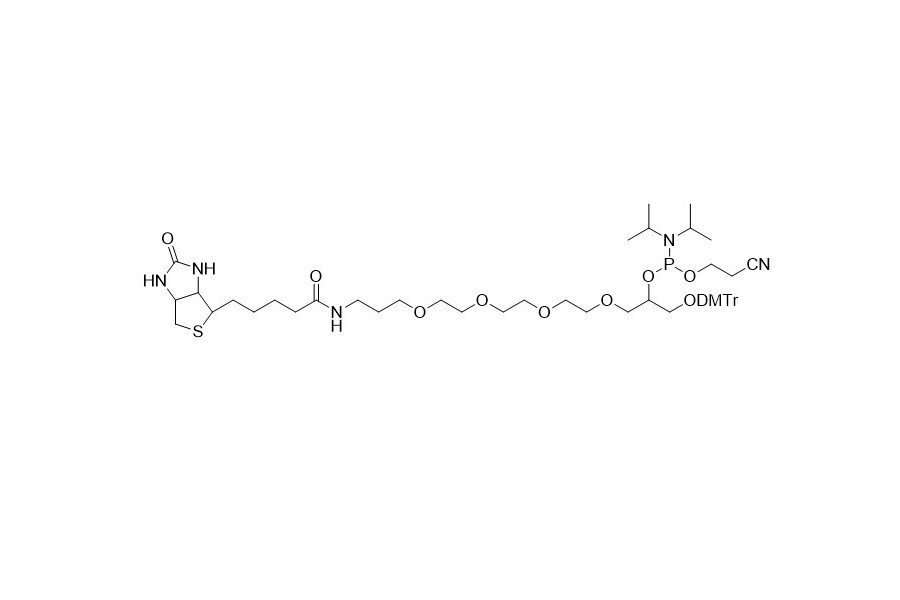
| DC67970 | Biotin-dT Featured |
Biotin - dT phosphoramidite contains a DMT (dimethoxytrityl) group, which enables quantitative coupling. It can be inserted into the target sequence as a substitute for the dT residue. This makes it an essential tool for adding biotin to the desired positions within an oligonucleotide sequence.
It complements the commonly used biotin phosphoramidite. The latter lacks the DMT group and can only be added to the 5' end of the oligonucleotide, thus bringing the synthesis process to an end.
More description
|
|
| DC67969 | Biotin TEG CE Phosphoramidite Featured |
Biotin TEG CE Phosphoramidite is a valuable reagent for attaching biotin to both the 3' - end and 5' - end of oligonucleotides. This phosphoramidite is equipped with a 15 - atom mixed - polarity extended spacer arm based on a triethylene glycol linker.
The extended spacer arm functions to physically separate the biotin moiety from the rest of the oligomer. This separation brings about several advantages that are particularly evident in practical applications. The distinct design of the spacer arm helps to optimize the performance of the biotin - labeled oligonucleotides, ensuring that the biotin's functionality is not compromised by the proximity of the oligomer structure.
More description
|
|