 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Field of Application | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
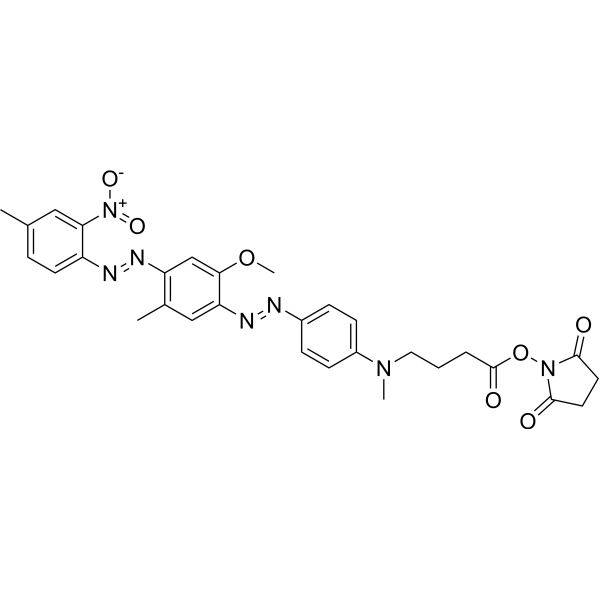
| DC67952 | HCQ-1 NHS Featured |
HCQ-1 NHS directly labeled by fluorescently labeled nucleotide.
More description
|
|
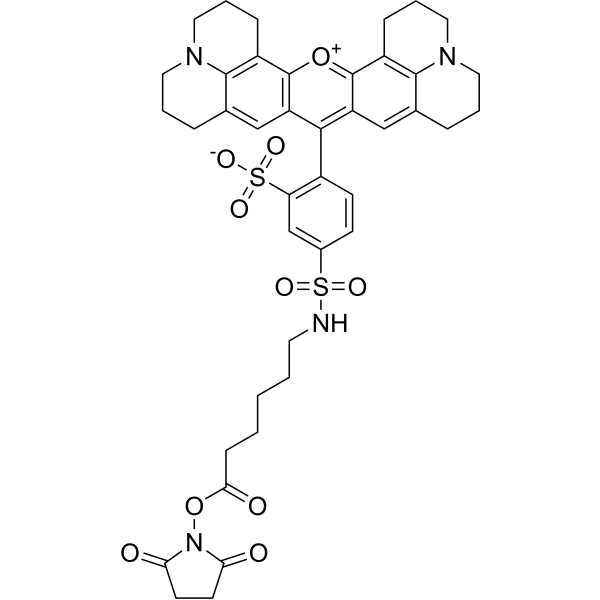
| DC67951 | Tex Red-X NHS Featured |
Tex Red-X NHS is a derivative of Texas Red (HY-101878), an amphoteric rhodamine red fluorescent dye. Texas Red is widely used to study neuronal morphology and as a cell type-selective fluorescent marker for astrocytes, both in vivo and in slice preparations.
More description
|
|
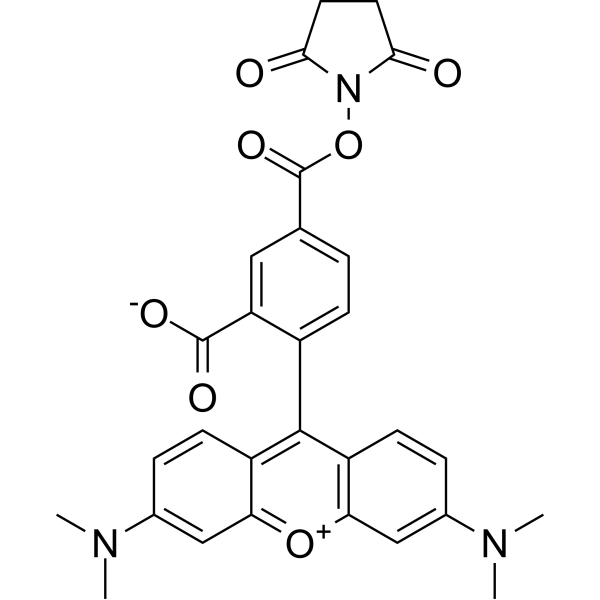
| DC67950 | 5-TAMRA NHS Featured |
5-TAMRA NHS is an amine-reactive fluorescent agent, and its conjugate produces bright, pH-insensitive orange-red fluorescence with good photostability (Ex/Em = 565/580 nm).
More description
|
|
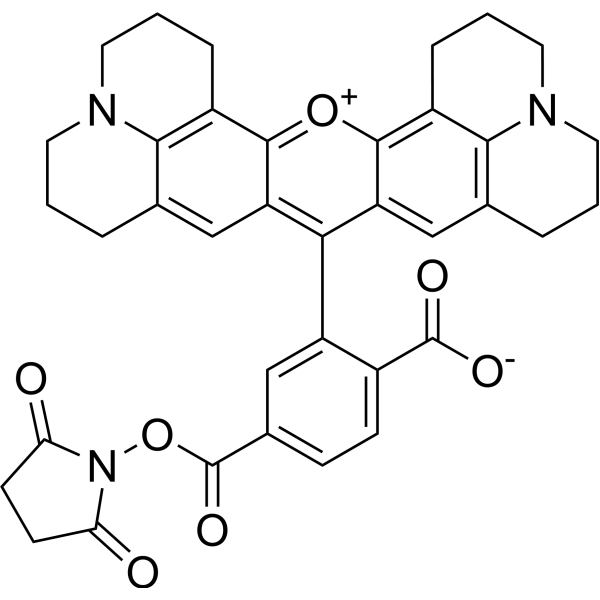
| DC67949 | 6-ROX NHS Featured |
6-Carboxy-X-rhodamine, succinimidyl ester (6-ROX, SE) is a fluorescent dye for oligonucleotide labeling and automated DNA sequencing.
More description
|
|
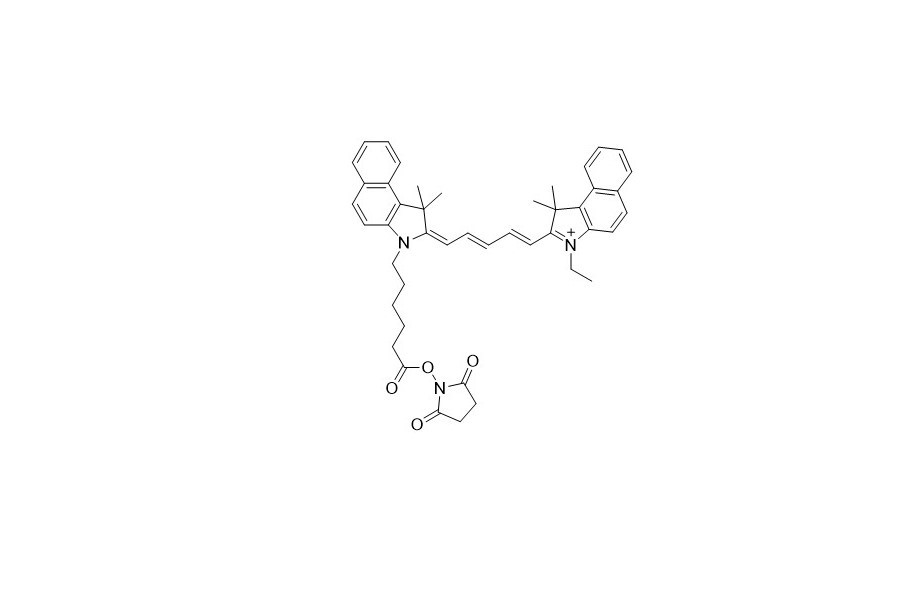
| DC67948 | Quassar 705 NHS Featured |
Quasar 705 fluorophore is an indocarbocyanine dye. It emits fluorescence in the deep - red region of the visible spectrum. This fluorescence can be effectively quenched by BHQ - 2 or BHQ - 3 dyes. The excitation wavelength of Quasar 705 is 690 nm, and its emission wavelength is 705 nm.
More description
|
|
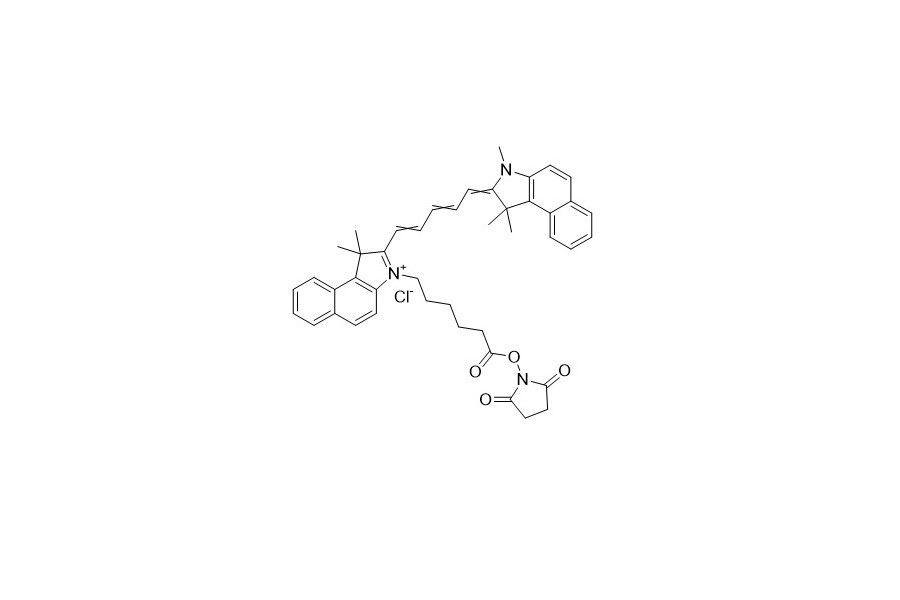
| DC67947 | Quasar 670 NHS Featured |
Quassar 670 NHS emits red fluorescence. It has an excitation wavelength of 670 nm and an emission wavelength of 644 nm.
More description
|
|
| DC67946 | Quasar 570 NHS Featured |
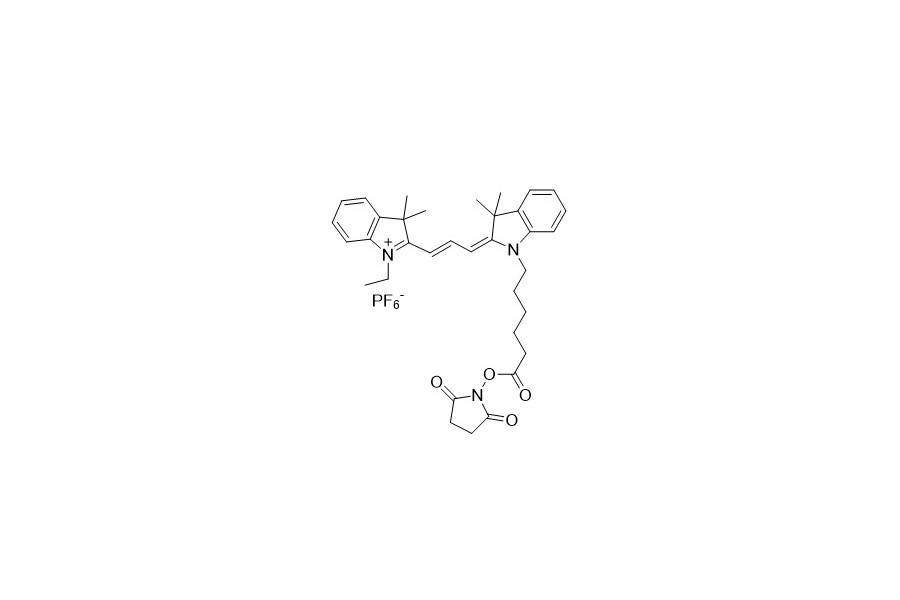
|
|
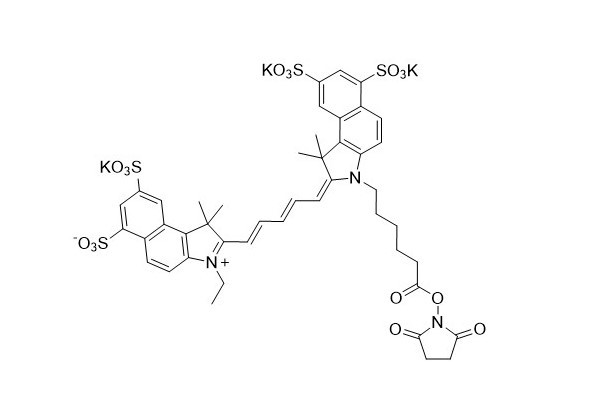
| DC67945 | Sulfo-Cy5.5 NHS Featured |
Sulfo-Cyanine5.5 NHS ester is an amine-reactive active ester of a sulfonated far-infrared Cyanine5.5 fluorophore (an analogue of Cy5.5). This reagent is the preferred choice for labeling antibodies, sensitive proteins, and other substances in reactions that require a pure water environment or minimal addition of organic co-solvents. The dye is highly suitable for non-invasive in vivo near-infrared imaging and applications that demand a low fluorescence background.
More description
|
|
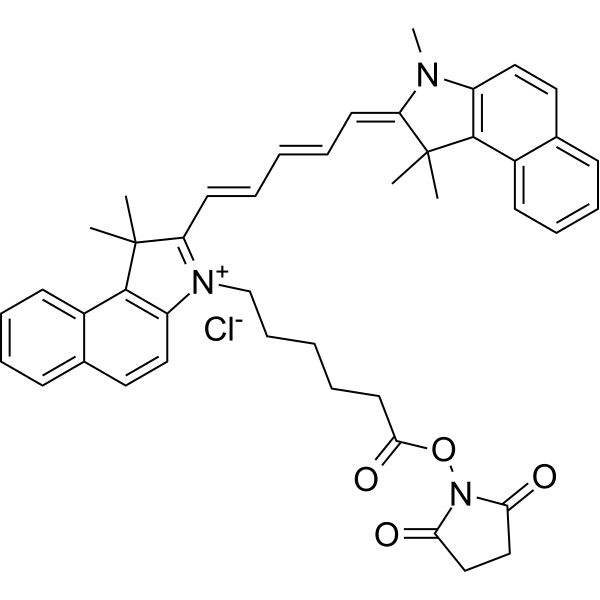
| DC67944 | Cyanine 5.5 NHS Featured |
Cyanine 5.5 NHS is a reactive dye for the labeling of proteins, and antibodies and small molecular compounds.
More description
|
|
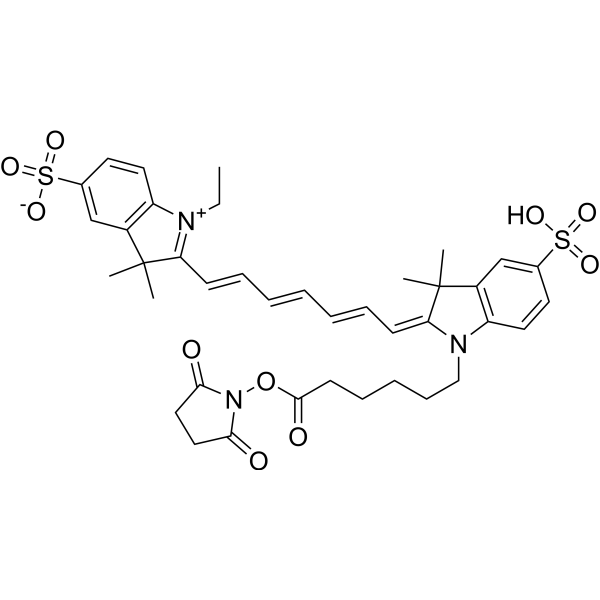
| DC67943 | Sulfo-Cyanine 7 NHS Featured |
Sulfo-Cyanine 7 NHS is a CY dye. CY, short for Cyanine, is a compound consisting of two nitrogen atoms connected by an odd number of methyl units. Cyanine compounds have the characteristics of long wavelength, adjustable absorption and emission, high extinction coefficient, good water solubility and relatively simple synthesis[1]. CY dyes are of en used for the labeling of proteins, antibodies and small molecular compounds. For the labeling of protein antibodies, the combination can be completed through a simple mixing reaction. Below, we introduce the labeling method of protein antibody labeling, which has certain reference significance.
More description
|
|
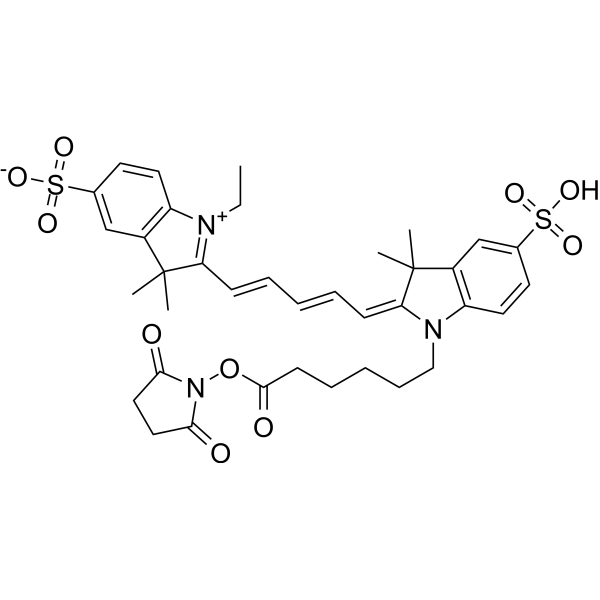
| DC67081 | CY5-SE Featured |
Cy5-SE (Cy5 NHS Ester) is a reactive dye for the labeling of amino-groups in peptides, proteins, and oligonucleotides. This dye requires small amount of organic co-solvent (such as DMF or DMSO) to be used in labeling reaction. This reagent is ideal for very cost-efficient labeling of soluble proteins, as well as all kinds of peptides and oligonucleotides. This reagent also works well in organic solvents for small molecule labeling. Excitation (nm):649, Emission (nm): 670.
More description
|
|
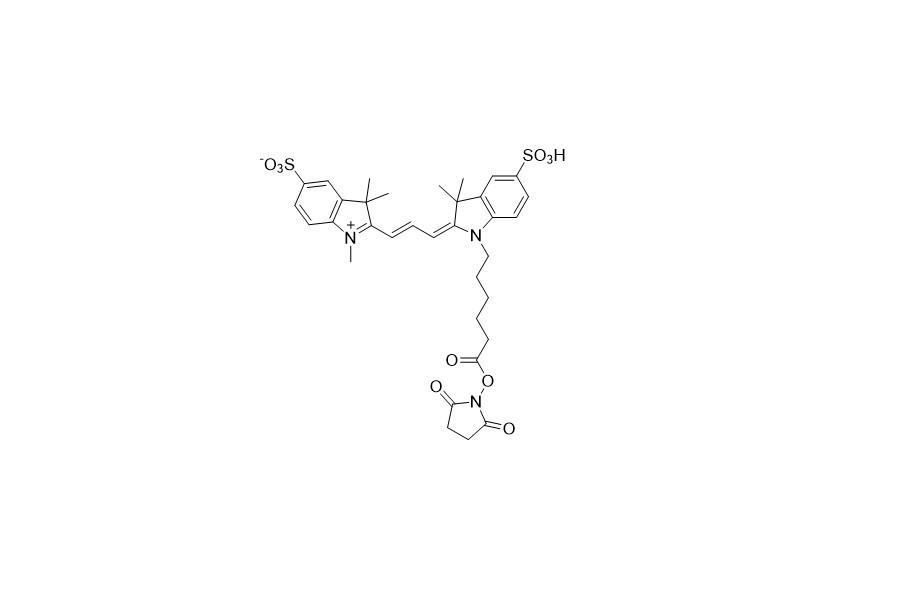
| DC67942 | Sulfo-Cyanine 3 NHS Featured |
Sulfo - Cyanine 3 NHS, a water - soluble and amine - reactive compound, can efficiently label proteins and polypeptides in pure aqueous solutions without the need for organic co - solvents. This makes it an ideal option for proteins with low solubility and those prone to denaturation.
Moreover, the Sulfo - Cyanine 3 NHS ester can serve as a substitute for Cy3, Alexa Fluor 546, and DyLight 549, offering a practical alternative in various experimental and research settings.
More description
|
|
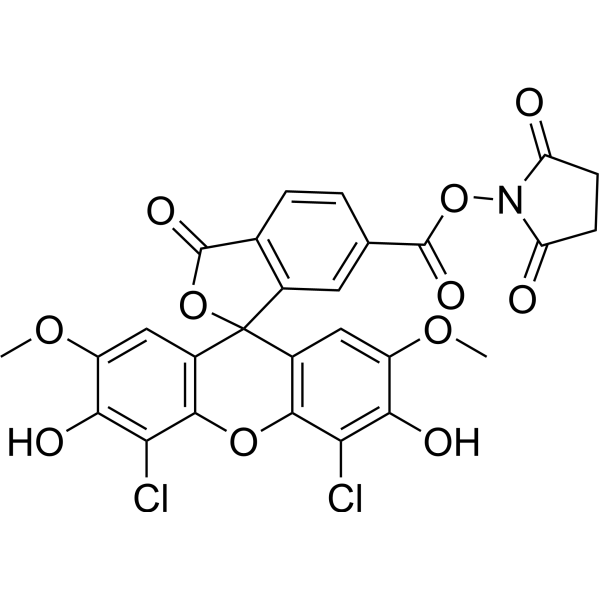
| DC67941 | 6-JOE NHS Featured |
6-JOE NHS is an amine-reactive fluorescent probe and is suitable for postsynthetic labeling of amino-modified oligonucleotides
More description
|
|
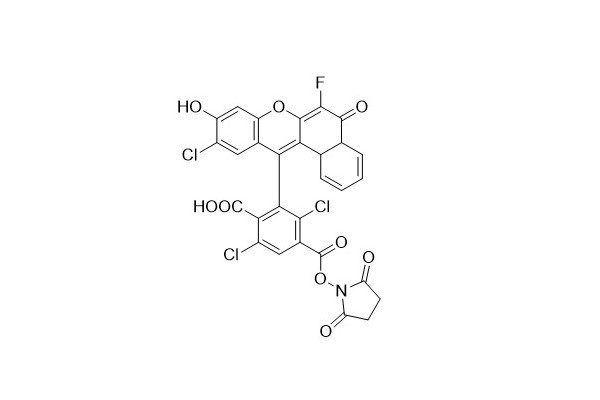
| DC67940 | 6-NED NHS Featured |
6 - NED can be employed in multiple applications, including fragment analysis, gene expression studies, genotyping, and PCR techniques.
6 - NED NHS is a highly stable fluorescent probe. It has seen widespread use in the field of labeling amino - modified oligonucleotides, contributing to more accurate and efficient research efforts in relevant biological and genetic studies.
More description
|
|
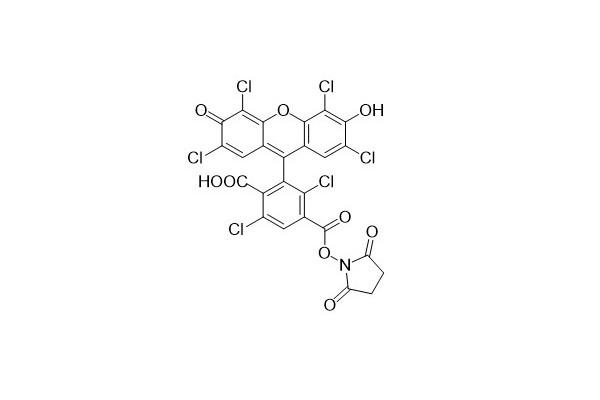
| DC67939 | 6-HEX NHS Featured |
6-HEX NHS is the amine-reactive succinimidyl ester of 6-HEX acid. It has found extensive applications in nucleic acid sequencing and related research fields. This NHS ester belongs to a class of amine-reactive dyes. It is utilized for labeling amine groups in various target molecules, such as proteins, peptides, and amino-modified oligomers.
More description
|
|
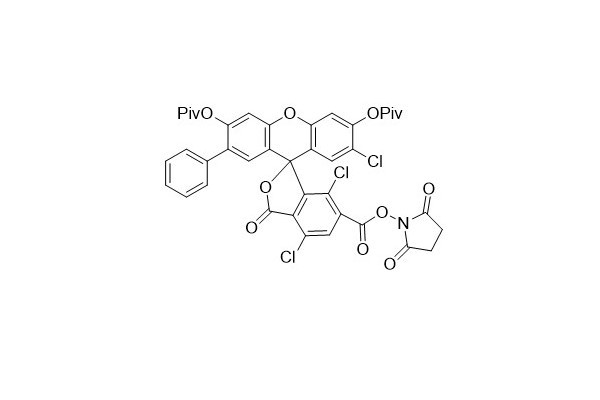
| DC67938 | 6-VIC NHS Featured |
|
|
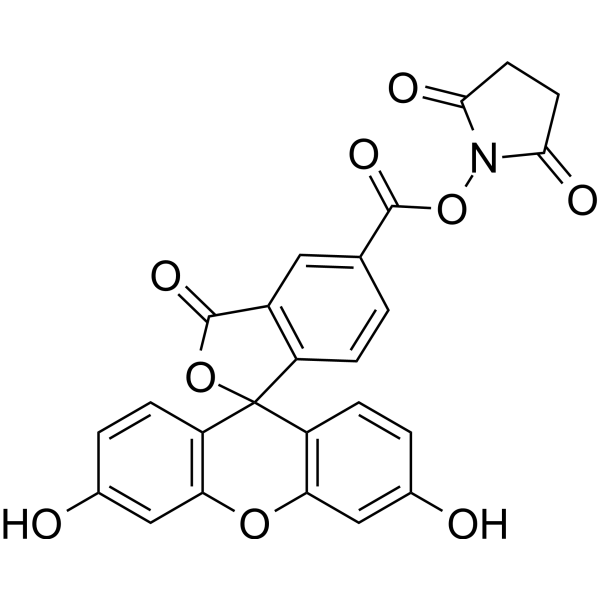
| DC9371 | 5-FAM SE Featured |
5-FAM SE is a single isomer, it is one of the most popular green fluorescent reagents used for labeling peptides, proteins and nucleotides.
More description
|
|
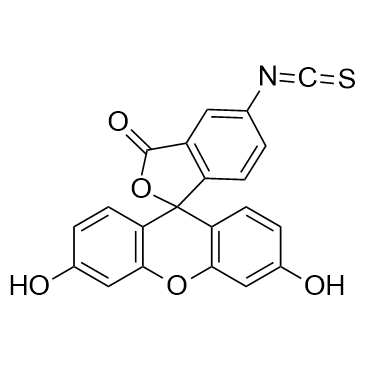
| DC22475 | FITC Featured |
Fluorescein isothiocyanate(FITC) is a derivative of fluorescein used in wide-ranging applications including flow cytometry.
More description
|
|
| DC67937 | N-[4-[[(2-Hydroxy-1-naphthalenyl)methylene]amino]phenyl]-α-methylbenzeneacetamide Featured |
methylene]amino]phenyl]-α-methylbenzeneacetamide.gif)
|
|
| DC67936 | 1-(6-(aminooxy)hexyl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione hydrochloride Featured |
hexyl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione hydrochloride.gif)
|
|
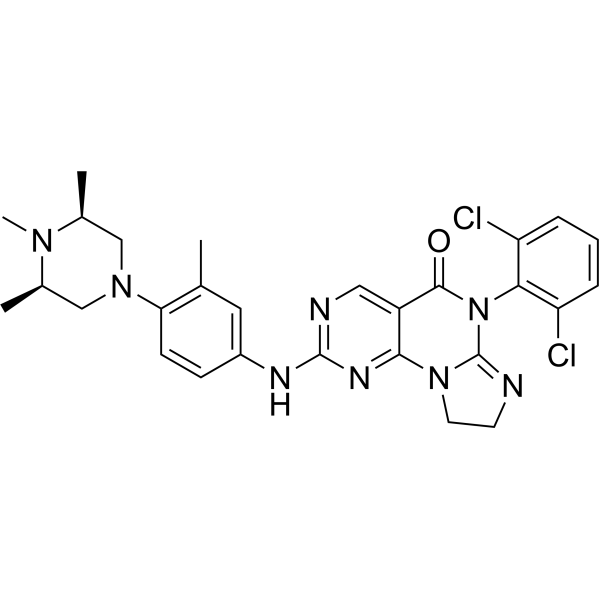
| DC67935 | WEE1-IN-10 Featured |
WEE1-IN-10 (compound 77) is a Wee1 kinase inhibitor. WEE1-IN-10 shows inhibitory activity on LOVO cell growth, with an IC50 of 0.524 μM. WEE1-IN-10 can be used for the research of diseases caused by abnormal activity of Wee1.
More description
|
|
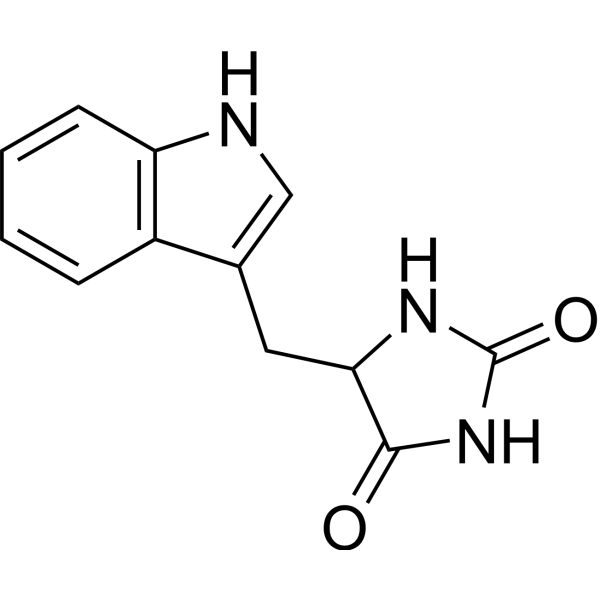
| DC67934 | DL-5-Indolylmethylhydantoin Featured |
DL-5-Indolylmethylhydantoin can be used as a substrate for the enzymatic production of L-tryptophan in some specific bacteria.
More description
|
|
| DC67933 | (2-Chloro-9H-carbazol-9-yl)(4-methoxyphenyl)methanone Featured |
(4-methoxyphenyl)methanone.gif)
|
|
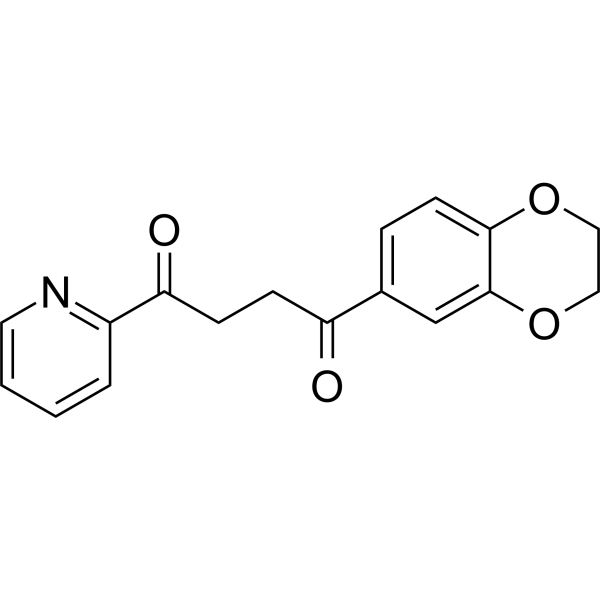
| DC67932 | Wnt pathway activator 2 Featured |
Wnt pathway activator 2 (compound 2) is a potent Wnt activator with an EC50 of 13 nM.
More description
|
|
| DC67931 | 8-bromo-7-(4-chlorobenzyl)-3-methyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione Featured |
-3-methyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione.gif)
|
|
| DC67930 | 2-AMino-3-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-4,5-diMethylthiophene Featured |
-4,5-diMethylthiophene.gif)
|
|
| DC5143 | JZL184 Featured |
JZL184 is a strong and selective inhibitor of Monoglyceride Lipase
More description
|
|
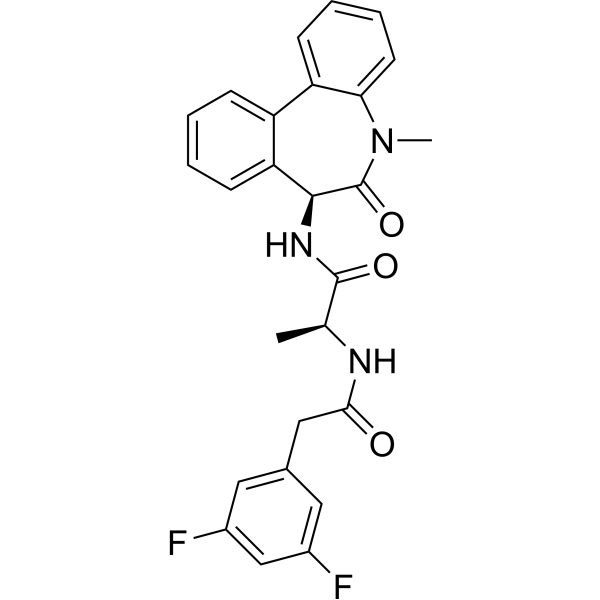
| DC8217 | YO-01027(Dibenzazepine) Featured |
YO-01027 (Dibenzazepine, DBZ) is a dipeptidic g-secretase inhibitor with IC50 of 2.6 and 2.9 nM for APPL and Notch, respectively.
More description
|
|
| DC41085 | 8-Hydroxy-DPAT hydrobromide Featured |
8-Hydroxy-DPAT hydrobromide (8-OH-DPAT hydrobromide) is a potent and selective 5-HT1A agonist with a pIC50 of 8.19. 8-Hydroxy-DPAT hydrobromide has selectivity of almost 1000 fold for a subtype of the 5-HT1 binding site.
More description
|

|
| DCC1335 | CeMMEC13 Featured |
CeMMEC13 is a potent inhibitor of TAF1 (2) bromodomain, with an IC50 of 2.1 μM.
More description
|
|