 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Field of Application | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC67920 | (E)-10-Hexadecenal Featured |
(E)-10-Hexadecenal is a pheromone that can be isolated from the fruit-feeding type of yellow peach moth, Dichocrocis punctiferalis.
More description
|
-10-Hexadecenal.gif)
|
| DC67919 | (9Z)-Dodecen-1-ol Acetate Featured |
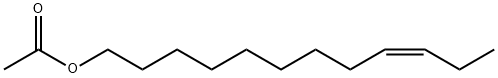
|
|
| DC67918 | 10-Hexadecen-1-ol, acetate, (Z)- Featured |
-.gif)
|
|
| DC67917 | (Z)-10-Hexadecen-1-ol Featured |
(Z)-10-Hexadecen-1-ol is a insect sex pheromones, which can be secreted by some female nocturnal moths, or by the heads of male bumblebees.
More description
|
-10-Hexadecen-1-ol.gif)
|
| DC67916 | 1,11-DODECADIENE Featured |
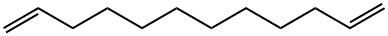
|
|
| DC67915 | (E)-oct-2-enyl acetate Featured |
-oct-2-enyl acetate.gif)
|
|
| DC67914 | 12-Amino-1-dodecanol Featured |
12-Amino-1-dodecanol is a PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
More description
|
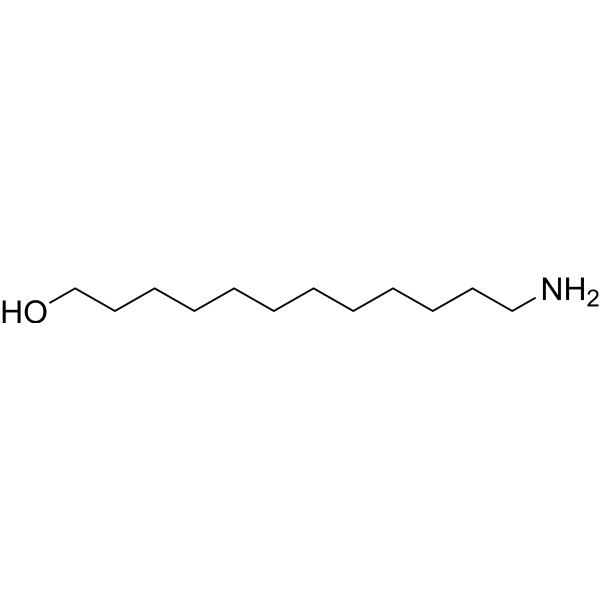
|
| DC67913 | 14-Bromotetradecan-1-ol Featured |
14-Bromotetradecan-1-ol is a PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
More description
|
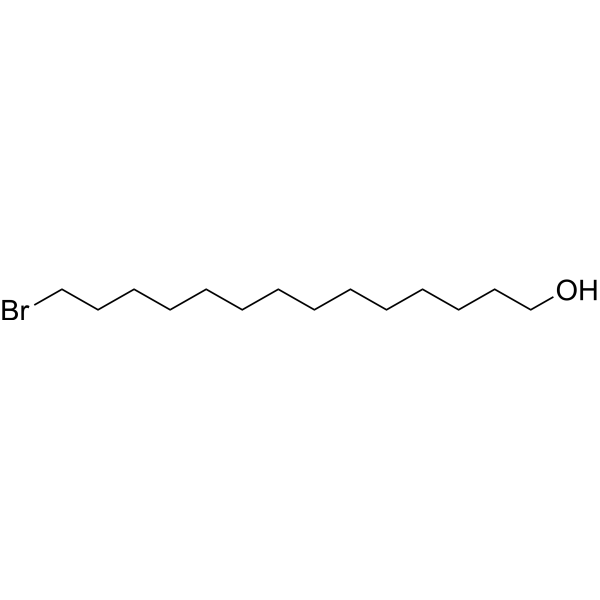
|
| DC67912 | Methyl 4-(bromomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylate Featured |
cyclohexanecarboxylate.gif)
|
|
| DC67911 | 7(Z)-Pentacosene Featured |
7(Z)-Pentacosene is an aggregation pheromone of the European earwig (Forficula auricularia). 7(Z)-Pentacosene can be used in the study of insect behavior and neurobiology.
More description
|
-Pentacosene.gif)
|
| DC67910 | 9-heptacosene Featured |

|
|
| DC67909 | 9Z-23 Featured |

|
|
| DC67908 | 5-Hexen-1-ol Featured |
5-Hexen-1-ol, is an aromatic substance with aromas similar to substances such as herbs, tea and citrus. Therefore, it is usually used in the food, fragrance and perfume industries, and is widely used in the preparation of various food flavors, fragrances, taste flavoring agents, essential oils and cosmetics and other products.
More description
|
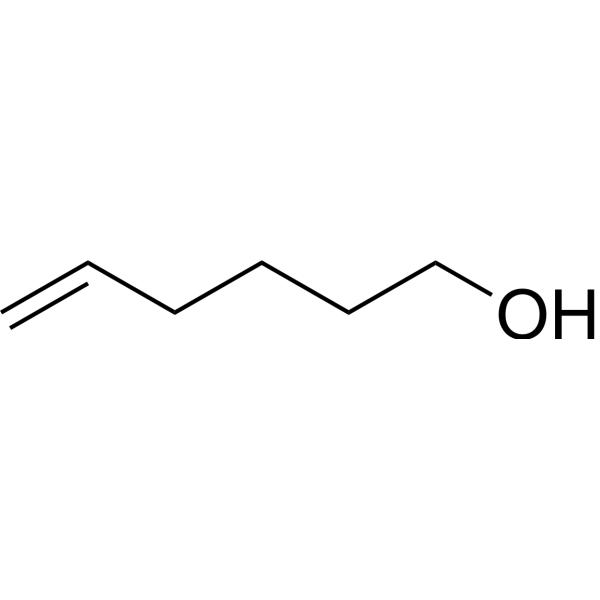
|
| DC67907 | Dodecanedioyl dichloride Featured |
Dodecanedioyl dichloride, Dodecanedioyl dichloride is commonly used in organic synthesis as a general building block for the preparation of various polymers and plastics, including nylon 12 and polyester resins, it can be used to introduce acid chloride groups into other organic molecules, which can then be further reaction to form more complex compounds, moreover, it has been used in medicinal chemistry as a starting material for the synthesis of various drugs and drug candidates.
More description
|
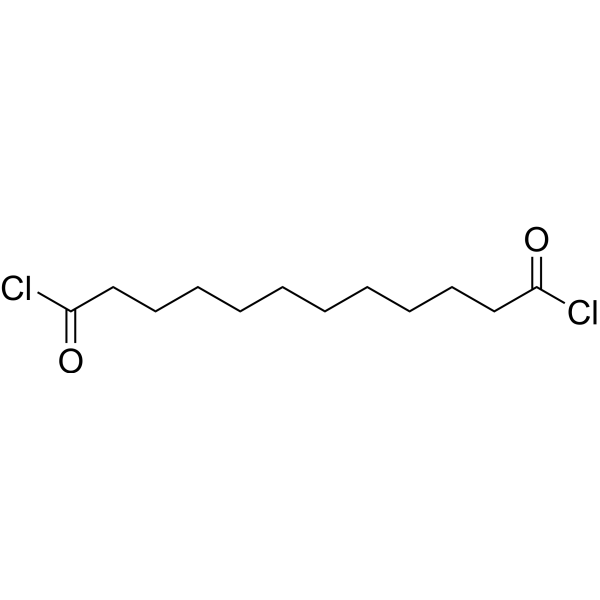
|
| DC67906 | Sebacoyl Chloride Featured |
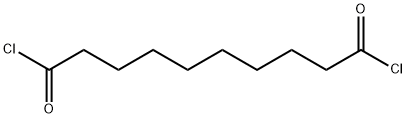
|
|
| DC67905 | 2-Hexene, 1-chloro-5,5-dimethyl- Featured |
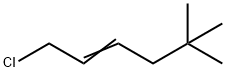
|
|
| DC67904 | 1-Dodecene, 12-bromo- Featured |

|
|
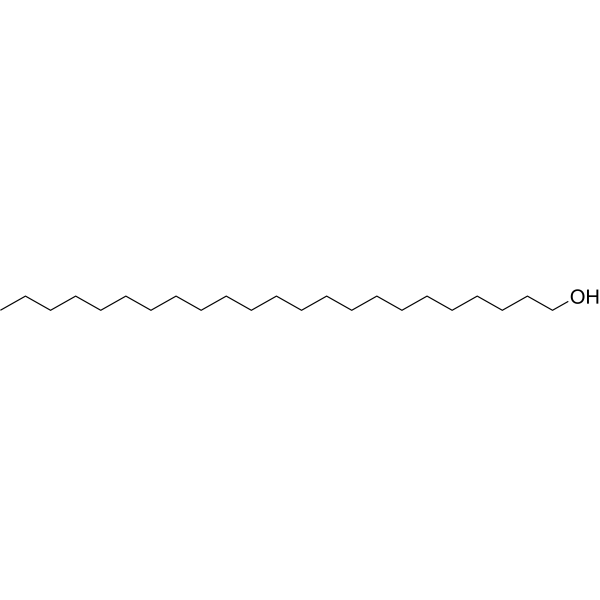
| DC67903 | 1-Tricosanol Featured |
1-Tricosanol is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
More description
|
|
| DC67902 | 15-Hydroxypentadecanoic acid Featured |
15-Hydroxypentadecanoic acid is a long-chain fatty acid found in various plant and animal sources and also produced by bacteria and fungi. It has potential health benefits and is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of other organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals and surfactants. Its unique chemical properties make it an essential ingredient in several industrial processes, especially in the fields of food science and nutrition.
More description
|

|
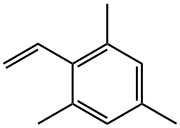
| DC67901 | 2,4,6-Trimethylstyrene Featured |
|
|
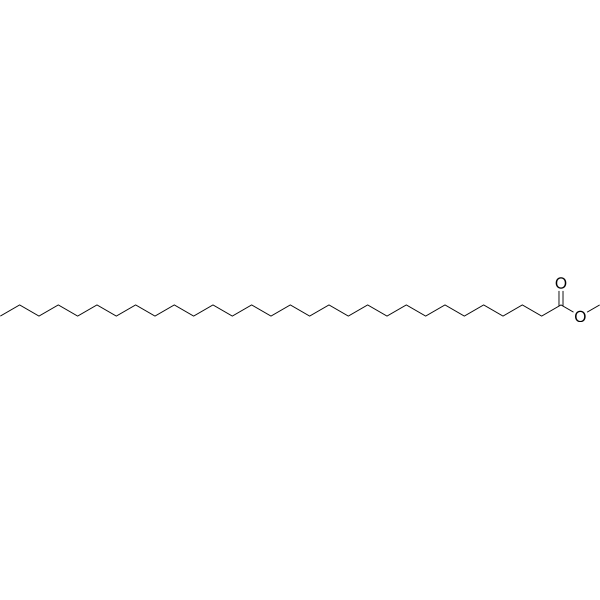
| DC67900 | Methyl triacontanoate Featured |
Methyl melissate is an organic compound commonly used as a flavoring and food additive. It can be used to prepare flavors and food seasonings with various flavors, and is widely used in food, flavors and cosmetics. In addition, this compound is also used as a substrate or intermediate in some biochemical reactions.
More description
|
|
| DC67899 | Tetratriacontane Featured |
Tetratriacontane is an ester product.
More description
|

|
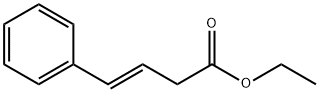
| DC67898 | Ethyl Trans-4-Phenyl-2-Butenoate Featured |
|
|
| DC67897 | Icosanal Featured |

|
|
| DC67896 | nonyl nonan-1-oate Featured |
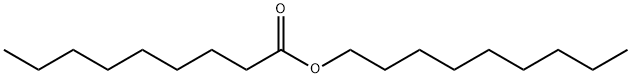
|
|
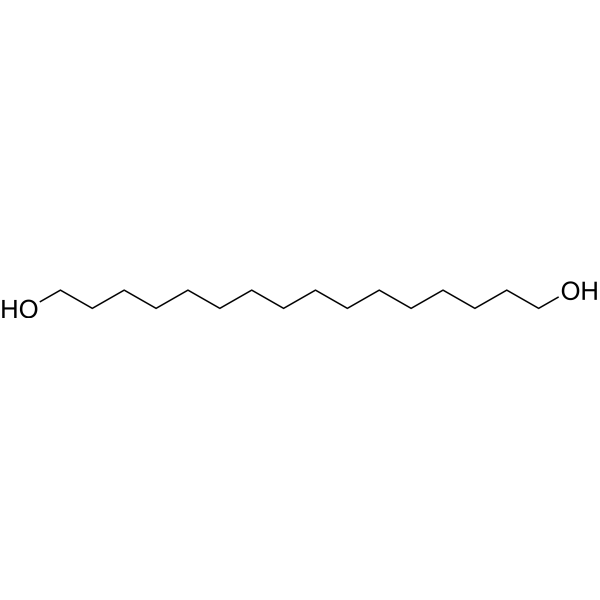
| DC67895 | 1,16-Hexadecanediol Featured |
1,16-Hexadecanediol (Hexadecamethylene glycol) is an ester product.
More description
|
|
| DC44845 | 4-Methoxyphenethyl alcohol Featured |
4-Methoxyphenethyl alcohol, an aromatic alcohol, is the major component in the anise-like odour produced by A. albispathus Hett. 4-Methoxyphenethyl alcohol can inhibits the protein, RNA and DNA synthesis in Escherichia coli.
More description
|

|
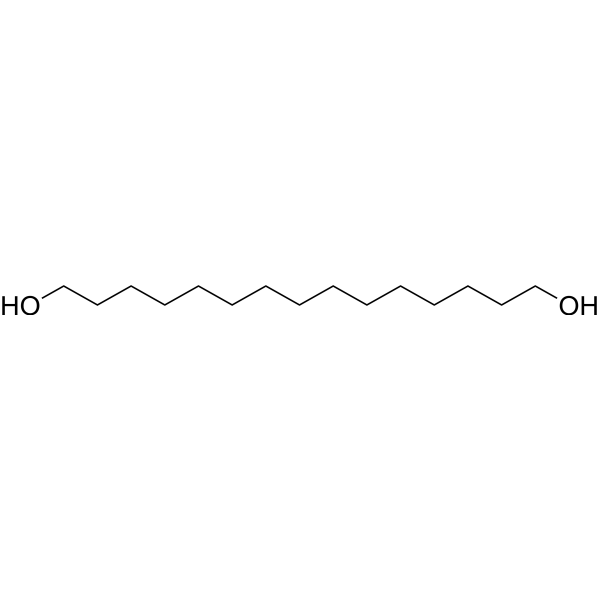
| DC67894 | 1,15-Pentadecanediol Featured |
1,15-Pentadecanediol is a PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
More description
|
|
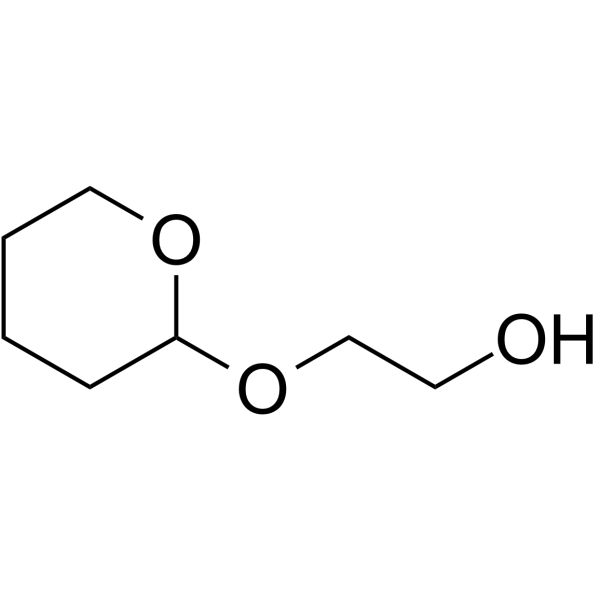
| DC44664 | THP-PEG1-alcohol Featured |
THP-PEG1-alcohol is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
More description
|
|
| DC67893 | 16-Hexadecanolide Featured |
16-Hexadecanolide is a lactone that is commonly used in ring-opening polymerization reactions and can be catalyzed by enzymes to form polymers at a relatively high polymerization rate.
More description
|
|