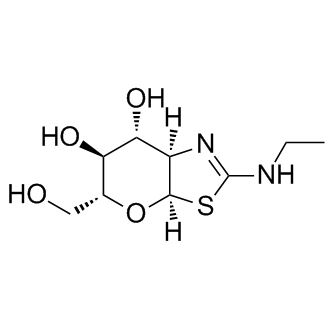
| Cas No.: | 1009816-48-1 |
| Chemical Name: | Thiamet-G |
| Synonyms: | Thiamet-G |
| SMILES: | CCN(C1=CC=C(C2=C(Cl)C(=O)C3=NC=CC=C3C2=O)C=C1)CC |
| Formula: | C9H16N2O4S |
| M.Wt: | 248.3 |
| Sotrage: | 2 years -20°C Powder, 2 weeks 4°C in DMSO, 6 months -80°C in DMSO |
| Description: | Thiamet-G is a potent and selective inhibitor of OGA, which acts to remove O-GlcNAc from modified proteins, with Ki of 20 nM for human OGA. |
| In Vivo: | Thiamet G (500 mg/kg/d) increases global and tau O-GlcNAc and reduces neurodegeneration. Thiamet G-treated group has 1.4-fold more motor neurons and hinders tau-driven neurodegeneration within this transgenic model. Thiamet G treatment therefore has no detectable effect on mice lacking the P301L transgene, indicating that prevention of neurodegeneration and weight loss is mediated by Thiamet G treatment only in the context of the P301L transgene. In Thiamet G-treated mice, the O-GlcNAc increases in the brain and spinal cord tissues[1]. Thiamet G (20 mg/kg, i.p.) increases O-GlcNAc levels in brain, liver, and knee of the C57BL/6 mice in a dose-dependent manner[2]. |
| In Vitro: | Thiamet G (1 μM) induces a clear increase in the accumulation of O-GlcNAcylated proteins of ATDC5 cells. O-GlcNAc accumulation induced by Thiamet G also evokes a clear increase in the activity of these MMPs. Thiamet G (1 μM) induces the phosphorylation of JNK, ERK, and p38 but not phosphorylation of Akt[2]. Thiamet G (0.1-10 μM) does not significantly affect the cell viability. Thiamet G decreases phosphorylation of tau and alters the microtubule dynamics[3]. |

 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.