 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Field of Application | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC67989 | Cl-4A3-LNSC8 Featured |
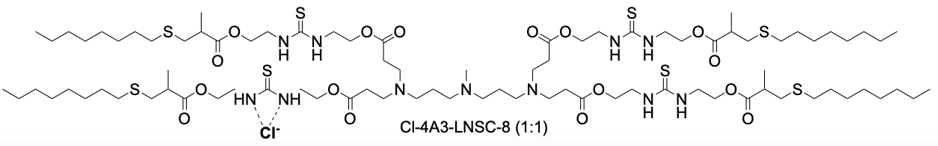
Cl-4A3-LNSC8 represents a novel class of thiourea-functionalized ionizable lipids engineered for selective organ-targeted mRNA delivery. Its core innovation lies in an anion-coordination strategy, where the parent lipid, 4A3-LNSC8, binds chloride ions (Cl⁻) via hydrogen-bonding interactions with its thiourea groups. This binding event is not merely structural but functionally critical, as it induces a significant shift in the surface pKa of the resulting lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) from approximately 5.54 to 8.79. This pKa modulation is the key mechanism that redirects the organotropism of the LNPs upon systemic administration. While the unmodified 4A3-LNSC8 LNPs preferentially deliver mRNA to the liver, Cl-4A3-LNSC8 LNPs effectivelyreprogram this tropism, enabling highly efficient mRNA delivery to secondary lymphoid organs (SLOs), particularly the spleen and lymph nodes. This platform demonstrates remarkable efficacy, achieving up to 65.7% gene editing efficiency in splenic macrophages in vivo, significantly outperforming benchmark delivery systems. Furthermore, by leveraging the coordination with different halides, such as iodine for computed tomography (CT) contrast, the system can be adapted for dual-modal theranostic applications, enabling simultaneous lymphatic metastasis imaging and therapeutic mRNA delivery.
More description
|
|
| DC67990 | 4A3-LNSC8 Featured |
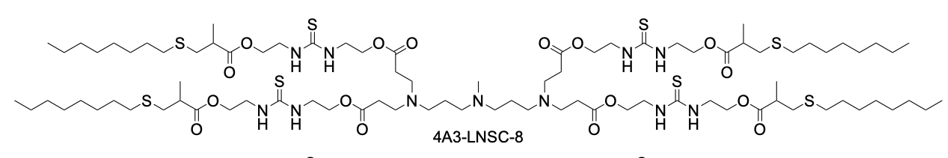
4A3-LNSC8 is a strategically designed thiourea-functionalized ionizable lipid that serves as the foundational core for a novel anion-coordination delivery platform. Its structure features a central 4A3 amine headgroup symmetrically extended with four hydrophobic tails, each incorporating a biodegradable ester linkage and a key thiourea-bridged linker. The inclusion of the thiourea group is the pivotal innovation, as it provides specific hydrogen-bonding sites capable of interacting with various halide anions (F⁻, Cl⁻, I⁻). When formulated into lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) without anion coordination, 4A3-LNSC8 itself exhibits a characteristic liver tropism, efficiently delivering mRNA to hepatocytes following systemic administration, with a measured surface pKa of approximately 5.54. However, its primary significance lies in its role as a versatile precursor. The strong anion-binding capability of its thiourea linkers allows for predictable modulation of the LNP's properties. Upon binding with anions like Cl⁻, the resulting complex (e.g., Cl-4A3-LNSC8) undergoes a significant pKa shift, which reprograms the LNP's in vivo fate, redirecting mRNA delivery from the liver to secondary lymphoid organs such as the spleen and lymph nodes. Thus, 4A3-LNSC8 is not merely an efficient ionizable lipid but a programmable scaffold that enables precise control over organ-targeting specificity through simple anion coordination, offering a powerful rational design strategy for advanced mRNA therapeutics.
More description
|
|
| DC60925 | Lipid H5T5 Featured |
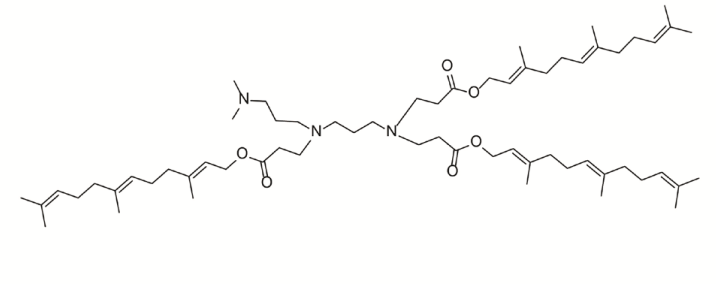
H5T5 is a leading ionizable lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulation optimized for in vivomRNA delivery, featuring a pKa of 6.51, a size of ~154 nm, and a narrow polydispersity index (PDI) of 0.05. It demonstrated superior in vitromRNA transfection efficiency in primary immune cells, such as bone marrow-derived macrophages. Following intravenous administration, H5T5 exhibits precise organotropism, predominantly targeting the spleen and bone marrow, where it effectively delivers mRNA to a broad spectrum of immune cells, including macrophages, dendritic cells, T cells, B cells, and NK cells. This capability enables its core application: the in vivogeneration of "pan-CAR" immune cells. When loaded with anti-HER2 CAR mRNA, the H5T5-based therapy achieved potent tumor regression and prolonged survival in multiple solid tumor models. Preliminary safety assessments indicated a manageable cytokine profile and no significant organ toxicity, positioning it as a promising platform for in vivocell engineering.
More description
|
|
| DC67450 | A28-C6B2 Featured |
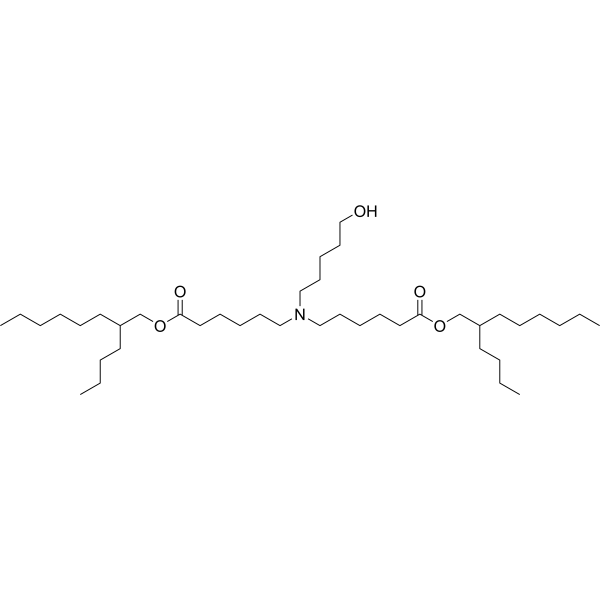
A28-C6B2 is an ionizable lipid (pKa 6.43) designed for mRNA encapsulation in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). Following intravenous injection in mice, these LNPs exhibit spleen-selective accumulation, particularly localizing in F4/80+ macrophages and CD11c+ dendritic cells, with moderate uptake by T lymphocytes.
More description
|
|
| DC49907 | 5A2-SC8 Featured |
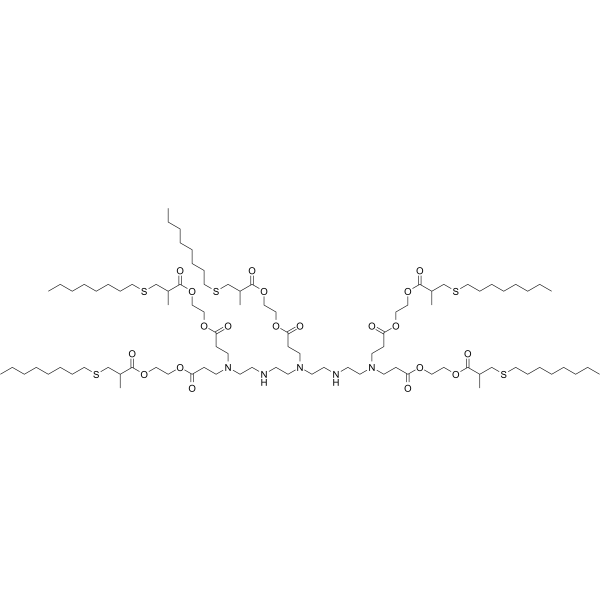
5A2-SC8 is a dendrimer for miRNA delivery to late-stage liver tumors with low hepatotoxicity. 5A2-SC8 shows potent EC50 < 0.02 mg/kg (siRNA against FVII (siFVII)) in dose-response experiments, and well tolerated in separate toxicity studies in chronically ill mice bearing MYC-driven tumors. 5A2-SC8 is a degradable lipid-like compound (ester-based dendrimer) for small RNAs delivery.5A2-SC8, was obtained by screening a large library of more than 1500 ester-based dendrimers
containing ionizable amino groups, which have three
tertiary amine heads and five lipid tails. Based on this library,
the in vitro transfection efficiency of different formulations of
5A2-SC8 iLNPs was evaluated, discovering the optimal formulation
(5A2-SC8, DOPE, cholesterol, PEG at a molar ratio of
15:15:30:3) of 5A2-SC8 iLNPs for delivering fumarylacetoacetate
hydrolase (FAH) mRNA to liver.After the intravenous injection
via tail, the model mice of hepatorenal tyrosinemia type I
had strong FAH protein expression, which prevented
body weight loss and increased the survival rate of hepatorenal
tyrosinemia mice . In addition to introducing utility of
5A2-SC8 iLNPs for the therapeutic intervention, the 5A2-SC8
iLNPs containing DOTAP have been used to establish complex
mouse models via intravenous injection, including in situ liverspecific
cancer model and in situ lung-specific cancer model.
Based on this iLNPs delivery system, 5A2-SC8 induced model
construction method overcomes the time-consuming and costly
disadvantages of traditional animal models establishing methods,
including transgenesis and gene engineering in embryonic
stem cells.
More description
|
|
| DC53130 | 93-O17S Featured |
93-O17S is an imidazole-based synthetic lipidoid for in vivo mRNA delivery. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) with 93-O17S promotes both the cross-presentation of tumor antigens and the intracellular delivery of cGAMP (STING agonist).
More description
|

|
| DC67281 | BNT-51 Featured |
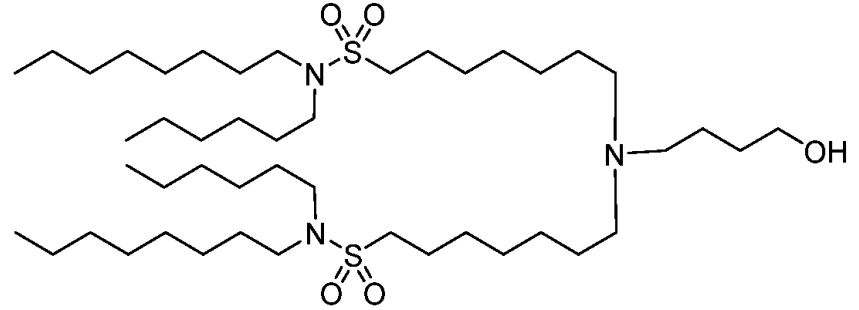
BNT-51 is an ionizable thiolipid developed by Biontech, characterized by its sulfur-containing moieties and a multiarm dendron-like architecture. Synthesized via reactions between amine-containing compounds and sulfur-based halides or sulfonates, it forms stable lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) optimized for mRNA delivery. The LNPs exhibit uniform particle size (80–100 nm, PDI <0.2), near-neutral zeta potential, and high mRNA encapsulation efficiency (>90%), while maintaining payload integrity through freeze-thaw cycles and extended storage. In vitro, BNT-51 demonstrates low cytotoxicity (>80% cell viability in C2C12, HepG2, and HEK293 cells) and superior transfection efficiency compared to conventional lipids, particularly in immune cells such as CD4+/CD8+ T cells within PBMCs. Its modular design allows integration of stealth lipids (e.g., PEG or vitamin E derivatives) to prolong circulation time and minimize immune activation, as evidenced by low hemolysis and complement activation risks. In vivo, BNT-51-based LNPs enable targeted mRNA delivery to splenic macrophages, achieving potent genome editing (e.g., Cre mRNA) and therapeutic protein expression (e.g., BACH1) in preclinical models. With its tunable structure, robust stability, and cell-specific tropism, BNT-51 holds promise for advancing mRNA therapeutics in gene editing, cancer immunotherapy, and regenerative medicine, offering a versatile platform for next-generation nanomedicine.
More description
|
|
| DC60494 | 76-O17Se |
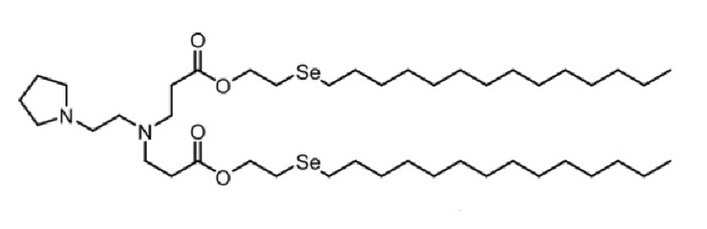
76-O17Se is a lipidoid for the efficient delivery of antiCD19 mRNA CAR to murine primary macrophages. 76-O17Se is more efficient than delivery with lipofectamine 2000 (LPF2K) or MC3
More description
|
|
| DC60578 | TE-EP8-S |
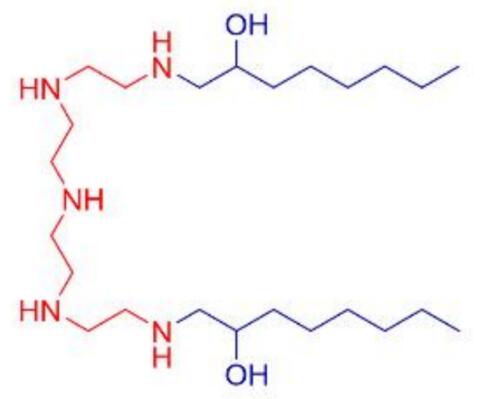
TE-EP8-S is a single-component, ionizable cationic lipid designed specifically for the targeted delivery of mRNA to T cells within the spleen. This innovative lipid formulation enhances the efficiency and precision of mRNA-based therapies by ensuring optimal cellular uptake and expression in immune cells. Its unique structure and properties make it a promising tool for advancing immunotherapeutic applications.
More description
|
|
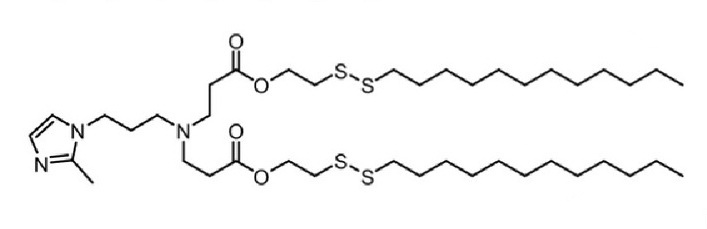
| DC60495 | 9322-O16B Featured |
9322-O16B is a lipidoid for the efficient delivery of antiCD19 mRNA CAR to murine primary macrophages. LNP 9322-O16B is more efficient than delivery with lipofectamine 2000 (LPF2K) or MC3.
More description
|
|
| DC67557 | Tidal Lipid 40 |
Tidal Lipid 40is an ionizable cationic lipid engineered to deliver RNA with high precision to immune cells like macrophages. Based on Tidal Therapeutics' patent US 20250205169A1, Its pH-responsive design shifts from a +8 mV charge at pH 5.5 (enabling endosomal escape) to near-neutral at pH 7.4 (reducing off -target binding), ensuring efficient intracellular release while maintaining blood stability. In lipid nanoparticles, Lipid 40 achieves 65% transfection efficiency in human macrophages—surpassing benchmarks like ALC-0315—and protects >95% of RNA payloads from degradation. Critically, it maintains particle integrity after freeze-thaw cycles with minimal size drift (<5 nm) and excels in in vivo targeting, driving potent gene expression in tumor-associated macrophages while avoiding liver/spleen accumulation. This combination of precision delivery, stability, and low toxicity makes it ideal for immunotherapies, such as reprogramming M2 macrophages to anti-tumor M1 states.
More description
|

|
| DC67544 | HCQ Lipid 4(HCQ-4) |
HCQ-4 is a rationally engineered ionizable lipid derived from hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), featuring a ditetradecylamine-derived twin-C14 saturated hydrocarbon tail linked to the HCQ headgroup via a succinic acid spacer. Synthesized through a three-step route involving HCQ deprotonation, ditetradecylamine carboxylation, and EDC/DMAP-mediated amidation, this lipid forms the core of optimized lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) at a molar ratio of 60:10:40:0.5 (HCQ-4:DOPE:cholesterol:DMG PEG2000). The structure enables dual functionality: (1) Spleen-selective mRNA delivery (2.3-fold higher splenic vs. hepatic transfection) via 80-100 nm particle size, near-neutral charge (-3 mV), and low PEG density, facilitating immune cell uptake; (2) Tumor microenvironment modulation through HCQ-mediated repolarization of M2 macrophages to antitumor M1 phenotype (iNOS+ cells ↑2.5-fold, CD206+ cells ↓60%). This bifunctional design synergistically enhances mRNA cancer vaccine efficacy, demonstrating superior prophylactic/therapeutic antitumor activity and antimetastatic effects compared to clinical benchmarks like MC-3 LNP.
More description
|

|
| DC80065 | 113-O12B Featured |
113-O12B is a disulfide bond-containing ionizable cationic lipidoid. 113-O12B LNP, an LN-targeting LNP delivery system, is developed for a mRNA cancer vaccine. The 113-O12B/mRNA shows enhanced expression in APCs compared with ALC-0315/mRNA, indicating the LN-specific targeting ability.
More description
|
.gif)
|