 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Field of Application | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC49889 | 503O13 Featured |
503O13 is a next-generation, biodegradable lipid nanoparticle (LNP) engineered for highly efficient and targeted siRNA delivery. Designed through rational structure-activity criteria—including optimal tail length (O13), tertiary amines, and a surface pKa ≥5.5—this single-component LNP achieves unparalleled gene silencing with an ultra-low EC50 of 0.01 mg/kg in preclinical models.503O13 outperforms non-degradable counterparts (e.g., C12-200) with improved toxicity profiles—no hepatic necrosis or pancreatic inflammation—while maintaining rapid blood clearance (t1/2: 6 min) and organ-specific accumulation (liver/spleen).
More description
|

|
| DC65701 | L-369 Featured |
L-369 (Lipid 369,L369) is novel class of ionizable lipid for siRNA delivery with improved in vivo elimination profile with excellent translation across species,including NHP, wide safety margin.
More description
|

|
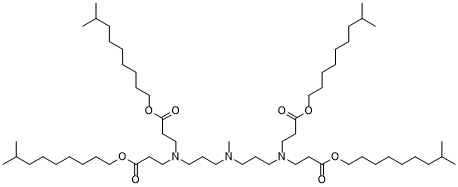
| DC80066 | 306Oi10 Featured |
306Oi10 is a branched-chain ionizable lipidoid that has shown significant promise in the generation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for mRNA delivery. Its unique structural and functional properties make it a highly efficient delivery vehicle for mRNA-based therapeutics.
More description
|
|
| DC49952 | 246C10 Featured |
246C10 is a synthesized ionizable lipid. 246C10 can be formulated into lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) with dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine (DOPE), cholesterol, and C16-PEG2000 ceramide (PEG-lipid) as well as mRNA. The lipid nanoparticle formulations can be used for mRNA delivery. To obtain iLNPs that could specifically target liver sinusoidal
endothelial cells (LSECs), six different ionizable lipids (241C10
to 246C10) were synthesized by an epoxide ring-opening
reaction with piperazine- or piperidine-containing amines.
Biodistribution and gene regulation of various iLNPs were
assessed in vivo, and the results showed that the 246C10
iLNPs (containing piperazine amine) had the highest luciferase
expression in the liver. When further analyzing the
246C10 iLNPs transfection efficiency in different types of liver
cells, it was found that tdTomato fluorescence was mainly concentrated
in hepatocytes, not in LSECs. Figure 6f shows that 80%
of hepatocytes are fluorescent, 40% of LSECs are fluorescent, and
20% of Kupffer cells are fluorescent. Due to the mannose receptor
on LSECs, mannose-PEG lipid was introduced into 246C10
iLNPs to alter the distribution of iLNPs in different liver cells. As
shown in Figure 6g, tdTomato fluorescence distribution was 15%
of hepatocytes, 70% of LSECs, and 15% of Kupffer cells, significantly
improved the ability of iLNPs to actively target LSECs.
In contrast, this work indirectly shows that the iLNPs with piperazine
head lipid are more able to deliver mRNA to the liver and
translate the target protein than the iLNPs with piperidine
head lipid. It is worth mentioning that the preparation buffer of 246C10
iLNPs could influence the encapsulation efficiency of mRNA.
With the addition of sodium chloride in the citrate buffer, the
encapsulation efficiency of CRISPR-Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA
was increased. These iLNPs were able to treat hemophilia safely,
without causing hepatotoxicity, the immune response induced by
Cas9 and off-target editing.
More description
|

|
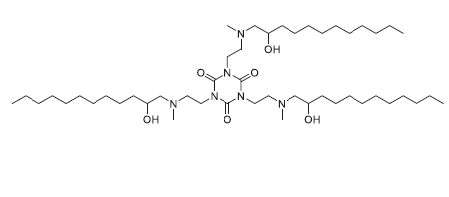
| DC83230 | TNT-b10 Featured |
TNT-b10 is a novel Lipid-like compound suitable for delivery of siRNA and mRNA both in vitro and in vivo TNT-b10 LLNs was more than 10-fold more potent than TNT-a10 LLNs formulated under the same condition.
More description
|
|
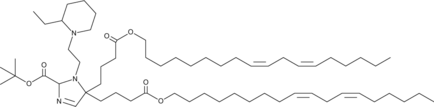
| DC60489 | LIPID 331 Featured |
Lipid 331 is a biodegradable cyclic ionizable lipid. LNPs containing Lipid 331 result in robust transfection in the nasal and lung tissues of mice and efficient transfection of lung epithelial cells and lung-resident APCs. Lipid 331 is a promising candidate for mRNA vaccine delivery, offering the potential for further enhancing the potency of mRNA vaccines.
More description
|
|
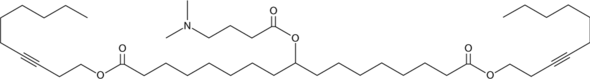
| DC80050 | LIPID A6 Featured |
Lipid A6 is an ionizable cationic and biodegradable alkyne lipid (pKa = 6.65).It has been used with other lipids in the formation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for the delivery of mRNA. LNPs containing lipid A6 and encapsulating mRNA encoding human erythropoietin (EPO) increase and then maintain homeostatic levels of hemoglobin in the blood in an adenine-induced mouse model of renal anemia.
More description
|
|
| DC57006 | L319 Featured |
L319 (LIPID 319) is a novel ionizable, biodegradable lipid for delivery of short interfering RNAs (siRNAs). L319-LPN displays rapid elimination with pKa of 6.38 and also shows well tolerated up to 10 mg/kg.
More description
|

|
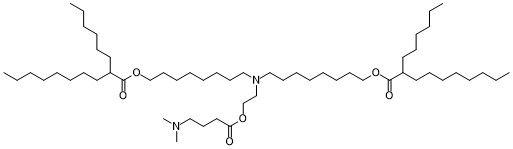
| DC82125 | lipid 14 Featured |
LIPID 14 is a novel ionizable lipid used for mRNA delivery.In 2021, Elia et al. used lipid 2 LNPs and lipid 14 LNPs to deliver mRNA encoding SARSCoV-2 human Fc-conjugated receptor binding domain (RBDhFc
mRNA). While both lipid 274 LNP RBD-hFc mRNA and
lipid 14 LNP RBD-hFc mRNA induced equal cellular and
humoral responses in mice at an mRNA dose of 5 μg, only lipid
14 LNP RBD-hFc mRNA exhibited strong immunogenicity
following intradermal administration. Both intradermal administration
and intramuscular administration of lipid 14 LNPs
could activate antigen presenting cells (APCs), thus inducing
cellular responses.
More description
|
|
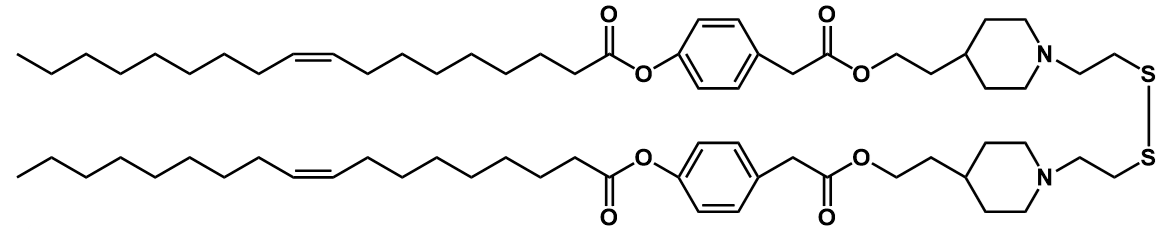
| DC59002 | ssPalmO-Phe Featured |
ssPalmO-Phe(SS-OP) is a self-degradable material for the delivery of oligonucleotides. ssPalmO-Phe is a self-degradable derivative of ssPalm that is self-degraded in the intraparticle space by a specific hydrolytic reaction. ssPalmO-Phe is beneficial for overcoming the plasma/endosomal membrane, LNP-ssPalmO-Phe can be used to deliver both nucleic acids.
More description
|
|
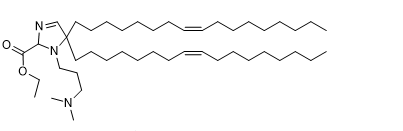
| DC82003 | A12-Iso5-2DC18 |
A12-Iso5-2DC18 is a novel amine containing lipid can be used for mRNA delivery, activate the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway, and exhibit anti-tumor immunity.
More description
|
|
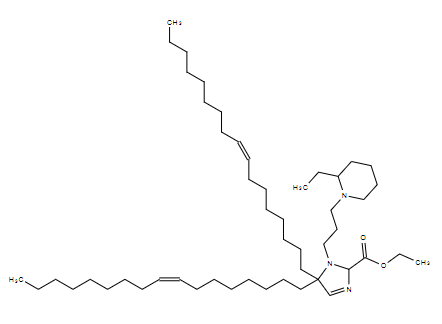
| DC80071 | A18-Iso5-2DC18 Featured |
A18-Iso5-2DC18 that could not only deliver mRNA vaccines robustly but also activate the stimulator
of interferon genes (STING) pathway. A18-Iso5-2DC18 strongly binds to the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) and induces potent cytolytic T lymphocyte responses, resulting in substantial antitumor immunity (Miao et al. 2019).
More description
|
|
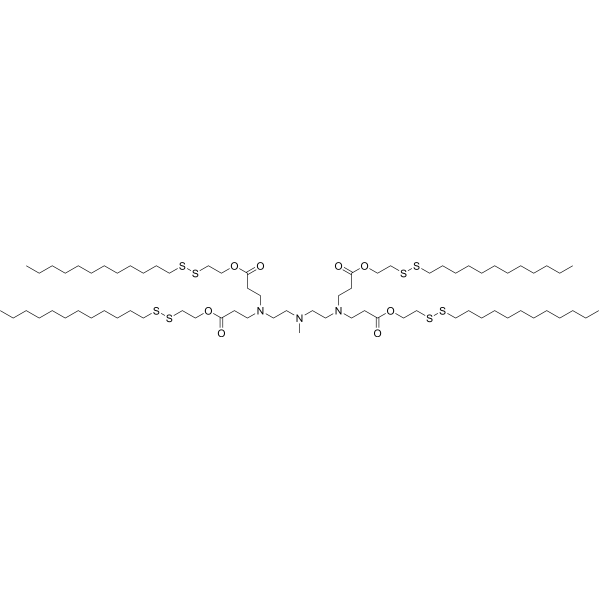
| DC82119 | 113-O16B Featured |
113-O16B is a disulfide bond-containing ionizable cationic lipidoid. It has been used in the generation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for the delivery of mRNA.
More description
|
|
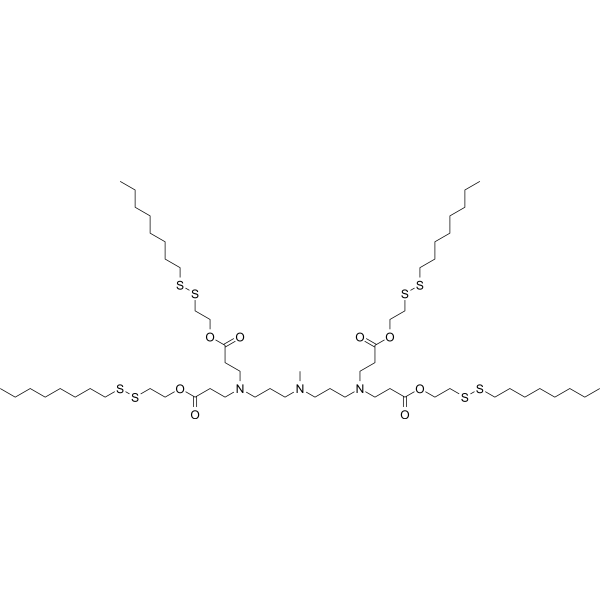
| DC80072 | 306-O12B (Triscormin) Featured |
306-O12B is a cationic lipidoid.306-O12B LNP is more efficient than MC-3 LNP in inducing loss-of-function mutations in Angptl3 through CRISPR-Cas9-based genome editing. It has been used in the generation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). Intravenous administration of LNPs containing 306-O12B and encapsulating an mRNA reporter accumulate specifically in the mouse liver. LNPs containing 306-O12B and encapsulating mRNA encoding the Cas9 nuclease (mCas9) and single-guide RNA targeting Angptl3 (sgAngptl3), the gene encoding angiopoietin-related protein 3, have been used to induce CRISPR-mediated gene knockdown in mice resulting in a reduction of serum Angptl3 protein, LDL, and triglyceride levels. A novel ionizable lipids library was constructed by a combinatory solvent-free Michael addition reaction between disulfide bondincorporated acrylate lipid tails and amine-containing heads. In this library, the tail-branched bioreducible ionizable lipid 306-O12B was screened out. Due to the presence of special ester bonds and branches in lipid tails, the accumulation of iLNPs in the liver was increased, and endosome escape was prompted. These iLNPs were used to deliver CRISPR-Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA targeting to angiopoietin-like 3 (Angptl3). Compared with FDA-approved MC3, 306-O12B induced more specific and efficient Angptl3 gene knockout in the liver, resulting in significant decrease in the levels of serum Angptl3 protein, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and triglyceride. According to the molecular shape hypothesis outlined several decades ago, the increase of branches can create ionizable lipids with more cone-shaped structure to enhance the destructiveness of the membrane structure of the endosome and increase mRNA release. However, it is unknown whether the structural stability of iLNPs will be sacrificed with the increase of branches. The optimal branches and chain length need to be further explored.
More description
|
|
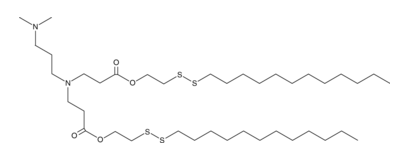
| DC82305 | 80-O16B Featured |
80-O16B is a disulfide bond-containing ionizable cationic lipidoid. It has been used in the generation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for the delivery of CRISPR complementary single-guide RNA (sgRNA) and Cas9 for genome editing in mice. LNPs containing 80-O16B conjugated to phenylboronic acid (PBA) and encapsulating an mRNA reporter increase luciferase reporter expression in HeLa cancer cells.2 LNPs containing 80-O16B conjugated to PBA and encapsulating p53 mRNA decrease the viability of DU145 prostate and SiHa and HeLa cervical cancer cells.
More description
|
|
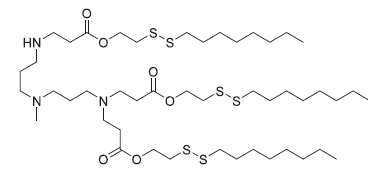
| DC82025 | 306-O12B-3 Featured |
306-O12B-3 is an ionizable lipidoid with cationic properties, commonly used in lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations for antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) delivery. When administered intravenously in mice, LNPs incorporating 306-O12B-3 exhibit liver-specific accumulation. Studies show that ASO-loaded LNPs containing 306-O12B-3 effectively silence hepatic PCSK9 expression by targeting the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 gene. Additionally, when combined with the cationic lipidoid NT1-O14B (Item No. 37095), these LNPs can deliver tau-targeting ASOs to the brain, reducing tau protein levels in mice.
More description
|
|
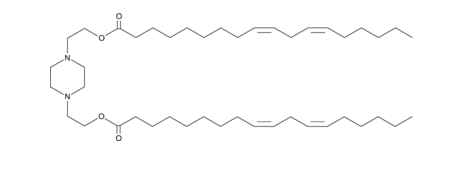
| DC82101 | AA3-DLin Featured |
AA3-DLin is an ionizable cationic amino lipid (pKa = 5.8) that has been used in combination with other lipids in the formation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for the delivery of mRNA.LNPs containing AA3-DLin and encapsulating mRNA for the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike glycoprotein induce immunogenicity in mice.
More description
|
|
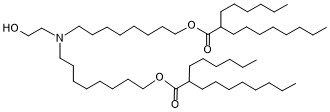
| DC83220 | ALC-0315 analogous-1 Featured |
ALC-0315 analogous-1 is a derivative of the ionizable cationic amino lipid ALC-0315. It has been used in the synthesis of ionizable cationic lipids used in the generation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs).
More description
|
|
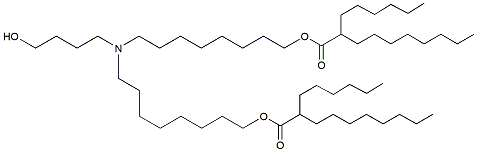
| DC65349 | ALC-0315 analgous-3 Featured |
ALC-0315 analgous-3 is an butanolamine ionizable lipid with both ester bonds located adjacent to C8 relative to the amine head. The introduction of ester linkages can improve the clearance of the lipid in the liver. This compound is analgous to ALC-0315.
More description
|
|
| DC65334 | Lipid 15 Featured |
Lipid 15 is an ionizable amino lipid used for the generation of Lipid nanoparticles .
More description
|

|
| DC65434 | SM102 Analog 1 Featured |
An analog of SM-102. The ethanolamine amino lipid head enhances encapsulation of mRNA. The lipid has primary esters at C7 position relative to the amine nitrogen. The primary lipid tail has 8 carbon tail. The lipid can be used for mRNA-based therapies which depends on the availability of a safe and efficient delivery vehicle.
More description
|

|
| DC65329 | ALC-0315 analogue-2 Featured |
ALC-0315 analogue-2 is an analogue of ALC-0315. ALC-0315 is an ionisable aminolipid that is responsible for mRNA compaction and aids mRNA cellular delivery and its cytoplasmic release through suspected endosomal destabilization. ALC-0315 can be used to form lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery vehicles. Lipid-Nanoparticles have been used in the research of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.
More description
|

|
| DC65180 | DLin-MC2-DMA Featured |
D-Lin-MC2-DMA(MC2) is a cationic lipid that has been synthesized for Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to deliver the siRNA.
More description
|

|
| DC65179 | Dlin-MC4-DMA Featured |
D-Lin-MC4-DMA(MC4) is a cationic lipid that has been synthesized for Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to deliver the siRNA.
More description
|

|
| DC65682 | RCB-4-8 Featured |
RCB-4-8 is a biodegradable ionizable lipid nanoparticle (LNP) engineered for efficient pulmonary mRNA delivery and in vivo genome editing, as detailed in the primary research article "Combinatorial design of nanoparticles for pulmonary mRNA delivery and genome editing" (Li et al., Nature Biotechnology 2023). Synthesized from a combinatorial library of 720 biodegradable lipids via a three-component reaction system, RCB-4-8 features an alkyne-containing lipid tail and tertiary amine headgroup, optimized through high-throughput screening for superior lung-targeting capabilities. Its unique molecular design incorporates hydrolyzable ester and carbonate groups, enabling rapid biodegradation (<30% lung retention at 48 h vs. >90% for conventional lipids) while maintaining high transfection efficiency. When formulated with DOTAP instead of DOPE, RCB-4-8 LNPs achieved 100-fold higher luciferase mRNA expression in murine lungs compared to FDA-approved MC3 LNPs and mediated 95% GFP knockout in vitro. In Ai9 reporter mice, intratracheal delivery of RCB-4-8 loaded with Cre mRNA edited 53% of total lung cells after three doses, while codelivery with Cas9 mRNA/sgRNA yielded 7.2% tdTomato+ cells, rising to 17% when combined with AAV-sgRNAs. With an optimal particle size of 85.7 nm (PDI 0.11) and >87% mRNA encapsulation, RCB-4-8 supports repeat dosing and represents a transformative platform for inhalable gene therapies targeting congenital lung diseases like cystic fibrosis.
More description
|

|
| DC60855 | 4A3-SC7 Featured |
4A3-SC7 is a proprietary, ionizable lipid component central to the SORT LNP platform developed for targeted organ delivery. It features a unique branched-tail structure designed to enhance mRNA encapsulation and endosomal escape. In the study, it served as the primary ionizable lipid in both Liver SORT LNPs and updated Lung SORT LNPs. For liver targeting, it was formulated at 15.04 mol% alongside helper lipids (DOPE: 23.04%, Cholesterol: 38.72%), PEG-lipid (DMG-PEG2000: 3.2%), and the liver-targeting lipid 4A3-Cit (20 mol%). This specific composition (Total lipid:RNA = 20:1 wt/wt) yielded LNPs with ~74 nm size, low PDI (0.17), and high encapsulation efficiency (87%) for large mRNAs like ABE editors (~5000 nt). Its branched-tail architecture was critical for stabilizing nanoparticles encapsulating large RNAs, overcoming a key limitation of previous formulations. 4A3-SC7-based Liver SORT LNPs enabled >40% base editing in hepatocytes in vivo, achieving durable correction of the disease-causing SERPINA1 mutation in PiZ mice and significantly reducing pathological protein aggregates. In the updated DualSORT system, 4A3-SC7 was also paired with DORI (instead of DOTAP) for improved lung targeting, demonstrating its versatility as a foundational ionizable lipid for multi-organ gene editing therapeutics.
More description
|

|
| DC65412 | Acuitas Lipid III-2 Featured |
Acuitas Lipid III-2 is an ionizable amine lipid with two identical ester tails adjacent to C6 position relative to amine from patent:WO2017075531A1 with the similar activity as ALC-0315. The head of lipid is propanolamine which can effectively encapsulate mRNA used in gene therapies which depends on the availability of a safe and efficient delivery vehicle.
More description
|

|
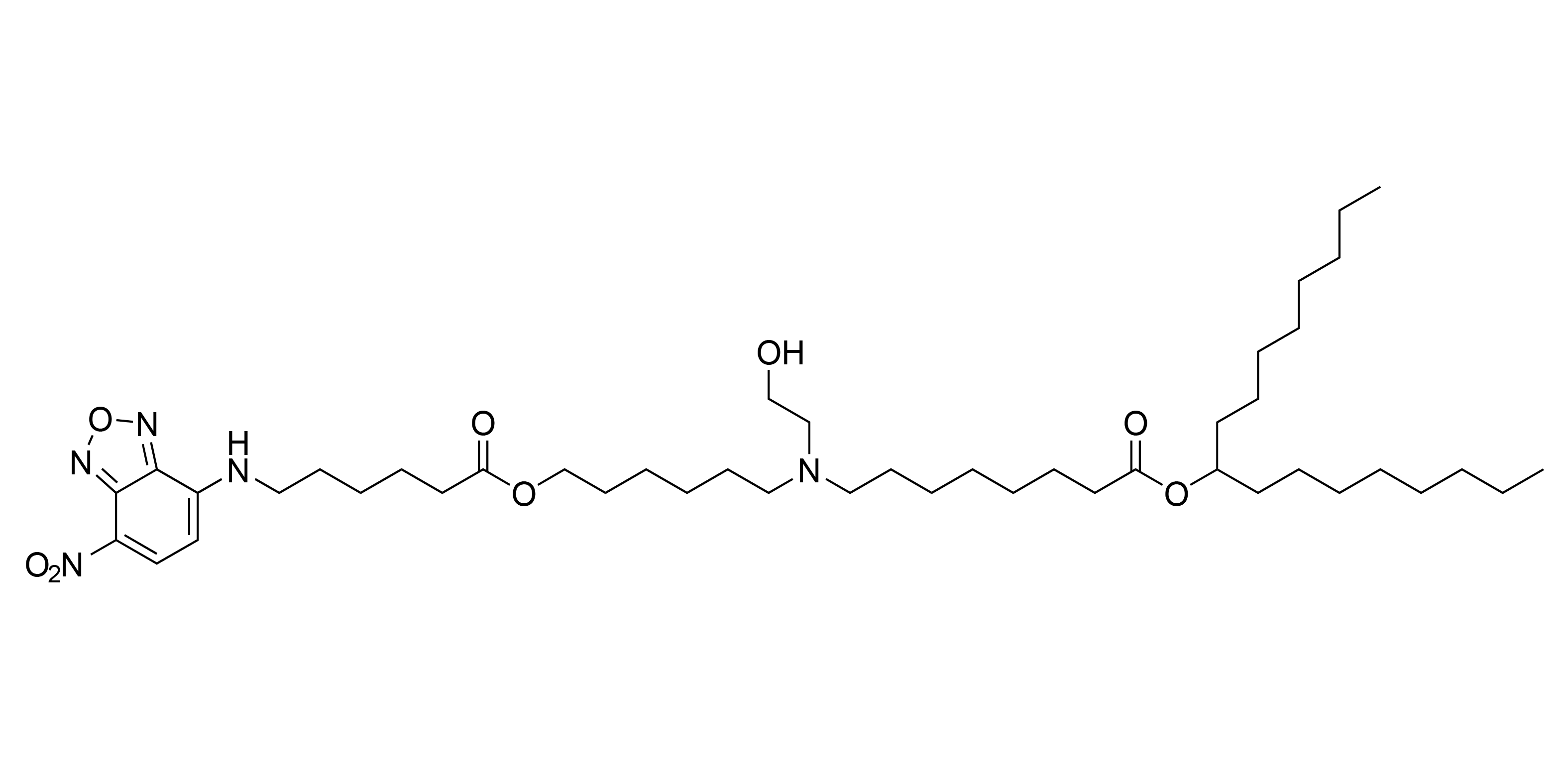
| DC67109 | Fluorescent-SM102 Featured |
A fluorescent molecule-conjugated SM-102 derivative for tracking and locating the position of SM-102.
More description
|
|
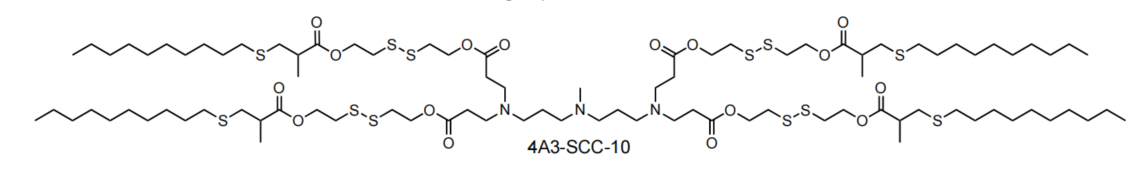
| DC60508 | 4A3-SCC-10 Featured |
4A3-SCC-10 is a disulfide bond-containing biodegradable ionizable cationic lipid (pKa = 6.22) that has been used in the generation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for the delivery of mRNA in vitro and in vivo. LNPs containing 4A3-SCC-10 and encapsulating a Cy5-RNA reporter have improved endosomal escape ability over Cy5-RNA-encapsulated LNPs containing 4A3-SC-10, which does not contain disulfide bonds, in HeLa cells. Intravenous administration of LNPs containing 4A3-SCC-10 and encapsulating an mRNA luciferase reporter selectively accumulate in mouse liver.
More description
|
|
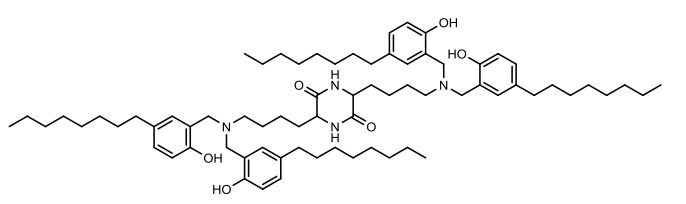
| DC67564 | C-a16 Featured |
C-a16 is an ionizable lipid engineered through Mannich reaction chemistry, designed to revolutionize mRNA delivery by synergizing high efficiency with minimized immune activation. Synthesized by reacting a phenolic tail derivative, formaldehyde, and a branched tertiary amine core under optimized ethanol conditions, this lipid integrates antioxidant phenol groups directly into its structure. These phenol moieties serve as intrinsic radical scavengers, effectively neutralizing intracellular reactive oxygen species that typically degrade mRNA and trigger inflammation.In lipid nanoparticle formulations, C-a16 constitutes the functional backbone, enabling superior mRNA encapsulation efficiency while maintaining a stable nanoparticle size of approximately 80–100 nm. Critically, it outperforms conventional lipids like DLin-MC3-DMA by achieving significantly higher target-protein expression in vivo alongside markedly reduced pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion. The antioxidant capability is not incidental but fundamental—quenching the phenol groups drastically diminishes both ROS suppression and delivery efficacy, confirming the design's mechanistic elegance.C-a16 represents a paradigm shift: its biomimetic antioxidant architecture addresses the chronic trade-off between delivery potency and immunogenicity, unlocking safer therapeutic applications for vaccines and gene therapies.
More description
|
|