 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Field of Application | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
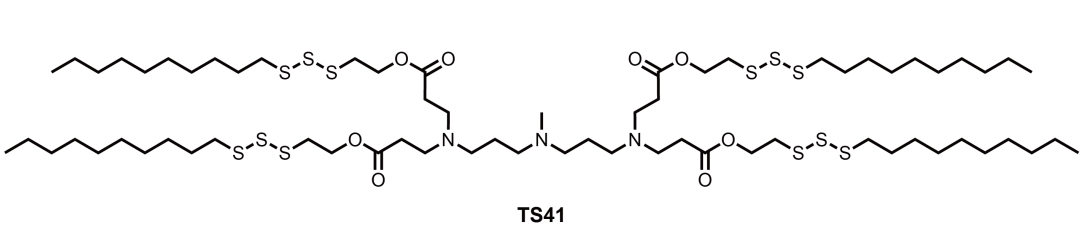
| DC67657 | Lipid TS41 Featured |
TS41 is a trisulfide-derived ionizable lipid engineered for lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to deliver mRNA therapeutics against multidrug-resistant bacterial pneumonia. Its optimized formulation, TS41S LNP, combines TS41 with helper lipids (e.g., DOPE, cholesterol) at a precise ratio, achieving a hydrodynamic diameter of ~105 nm, low polydispersity, and high mRNA encapsulation efficiency (~84%). This design enables efficient pulmonary delivery via intratracheal administration, with luminescence signals in lungs 4.8-fold higher than clinical benchmarks like SM-102 LNPs, ensuring targeted expression in epithelial cells, macrophages, and neutrophils. Crucially, TS41 LNPs exhibit potent anti-inflammatory properties by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS), reducing neutrophil infiltration and proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6, TNF-α) in infected lungs. In preclinical models, TS41S LNP encoding PB9 peptibody mRNA eradicated pathogens like Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, improved survival rates to 80%, and minimized tissue damage without systemic toxicity. Its ROS-scavenging capability synergizes with antibacterial effects, offering a promising, translatable platform for combating resistant infections while controlling inflammation. Future enhancements, such as codon optimization or inhalation delivery, could further broaden its therapeutic potential.
More description
|
|
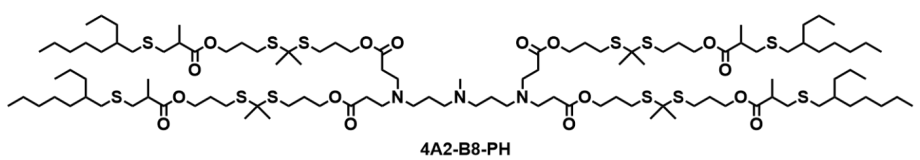
| DC67658 | Lipid 4A2-B8-PH Featured |
4A2-B8-PH is an optimally designed thioketal-incorporated biodegradable ionizable lipid (TBIL) for mRNA delivery to pancreatic ductal epithelial cells. It features a 4A2 headgroup with three tertiary amines, a biodegradable thioketal-based B8 linker, and a branched PH tail. The thioketal linker enables ROS-responsive degradation in the tumor microenvironment, enhancing endosomal escape and mRNA release. In vivo, 4A2-B8-PH LNPs achieve 98.3% pancreas-specific targeting after intraperitoneal administration, with a 218-fold improvement in delivery efficiency compared to previous benchmarks. It successfully transfects 30.5% of pancreatic ductal epithelial cells and induces complete tumor regression in orthotopic PDAC models via IL-12 mRNA therapy, demonstrating high efficacy and safety.
More description
|
|
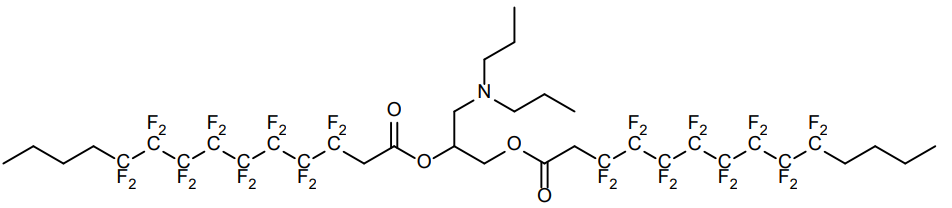
| DC67663 | Lipid 6F Featured |
6F Lipid is a Fluorinated Ionizable Lipid breakthrough in mitochondria-targeted gene delivery
More description
|
|
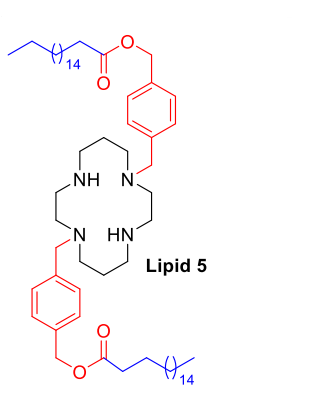
| DC67721 | Macrocyclic Lipid 5 Featured |
Lipid 5 is an ionizable lipid based on a macrocyclic cyclam headgroup. Its structure incorporates a benzylmethyl carbonate (BMC) linker, which contains an aromatic benzene ring, and a saturated C18 hydrophobic tail. Lipid 5 was mixed with helper lipids at a fixed molar ratio and formulated into mRNA-loaded lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) using microfluidic technology. Characterization data show that these LNPs have a hydrodynamic diameter of approximately 50-80 nanometers and a polydispersity index (PDI) below 0.2, indicating a small particle size with a uniform distribution. Their zeta potential at physiological pH is near neutral (ranging from -3 to +3 mV). The mRNA encapsulation efficiency, as determined by the Ribogreen assay, exceeds 95%. Cryo-transmission electron microscopy images reveal that the LNPs exhibit a typical spherical bilayer structure. In in vitro experiments, Lipid 5 LNPs mediated a higher level of luciferase protein expression in HEK293FT cells compared to the benchmark lipid DLin-MC3-DMA. In Balb/c mice, intravenous injection of LNPs encapsulating luciferase mRNA resulted in in vivo imaging signals predominantly concentrated in the lungs. Quantitative analysis indicated that the signal intensity in the lungs was over 100 times greater than that in the liver, with more than 95% of the total signal distributed in the lungs. In Ai9 reporter gene mice, two intravenous injections of Lipid 5 LNPs encapsulating Cre mRNA led to quantitative analysis of lung tissue sections showing that approximately 30% of lung cells were positive for tdTomato signal.
More description
|
|
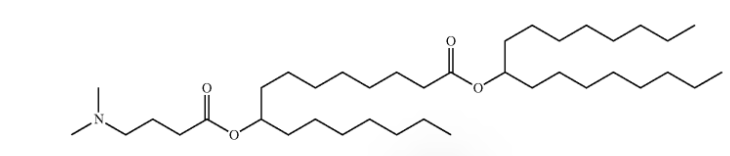
| DC67570 | Generation Lipid 87 Featured |
Lipid-87 is an ionizable lipid developed by Generation Bio, characterized by its tertiary amine group for pH-dependent protonation and dual C16/C17 aliphatic chains that enhance hydrophobic stability.As the core component (47.5–57.5 mol%) of stealth lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), Lipid87 enables extended blood circulation (>24-hour half-life vs. 30 min for conventional LNPs) by synergizing with steric-stabilizing polymers (e.g., DSG-PEG₂₀₀₀-OMe), achieves >95% encapsulation efficiency for mRNA/ceDNA with low cytotoxicity (IC₅₀ >100 μM), and drives liver-specific targeting (>80% hepatocyte transfection at 0.5 mpk), effectively restoring 40% FIX activity in hemophilia B models for over 7 days.
More description
|
|
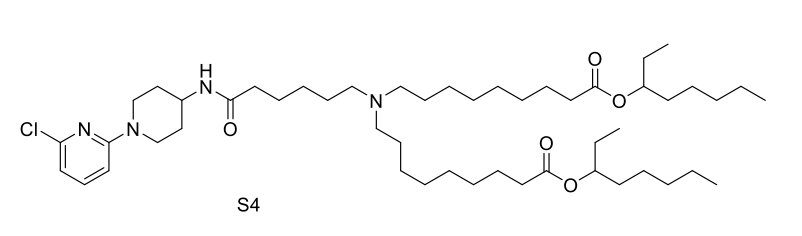
| DC67569 | Lipid S4 Featured |
Lipid S4 is an advanced ionizable lipid engineered for systemic mRNA delivery to the brain, leveraging SR-57227—a high-affinity 5-HT3 receptor ligand—as its core head group to enable targeted blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetration via receptor-mediated transcytosis, while incorporating amino linkers for pH-responsive ionization and biodegradable branched ester tails to facilitate efficient endosomal escape and intracellular mRNA release; optimized through orthogonal screening into OS4 LNP (formulated at S4/DOPE/Chol/DMG-PEG2k = 40:40:60:0.75 molar ratio), it demonstrated a 13.3-fold increase in brain mRNA expression compared to FDA-approved MC3 LNPs, and further conjugation with the Tat cell-penetrating peptide yielded OS4T LNP, boosting delivery efficiency by 12.7-fold over OS4 alone and enabling broad mRNA expression across neurons, astrocytes, microglia, and endothelial cells; validated in orthotopic glioblastoma models, OS4T delivered engineered IL-12 mRNA, suppressing tumor growth and extending median survival to 37 days (vs. 17 days for controls) with minimal systemic toxicity, positioning S4-based LNPs as a robust, translatable platform for CNS-targeted therapeutics.
More description
|
|
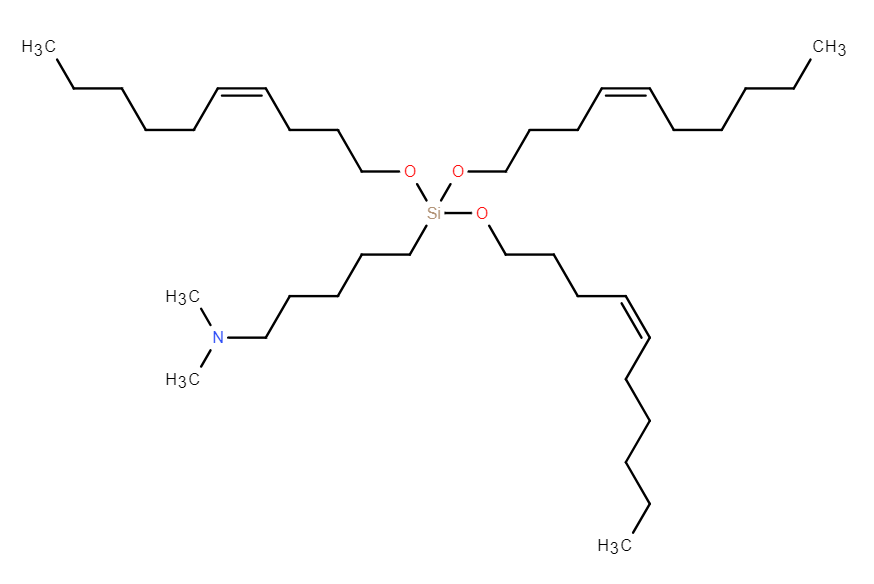
| DC67616 | GVS-18-B34 |
GVS-18-B34 is a highly potent, silicon ether-based ionizable lipid that enables efficient mRNA delivery via lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). Its key advantage lies in a biodegradable silyl ether linkage, which undergoes rapid, non-enzymatic hydrolysis, leading to near-complete clearance from the liver within 24 hours in both mice and non-human primates (NHPs). This degradation mechanism is species-agnostic, overcoming the variability associated with esterase-dependent lipids. In vivo, GVS-18-B34 LNPs demonstrated superior liver-specific protein expression and a high liver-to-spleen signal ratio, indicating minimal off-target accumulation and reduced immune stimulation compared to benchmarks like MC3 and SM-102. The LNPs exhibited excellent stability when stored frozen at -80°C, maintaining integrity over multiple freeze-thaw cycles. With its optimal pKa (~6.3) and efficient endosomal escape profile, GVS-18-B34 represents a promising candidate for therapeutic applications requiring frequent dosing, combining high potency with a favorable safety profile derived from its rapid clearance.
More description
|
|
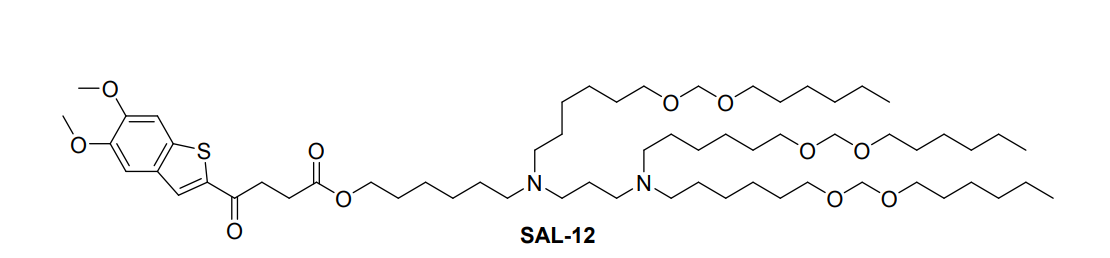
| DC67615 | STING Agonist Lipid SAL-12 |
SAL12 is a novel ionizable lipid derivative that integrates a non-nucleotide STING agonist (agonist 6) with an amino lipid tail through an ester bond, forming the core component of specialized lipid nanoparticles (SAL12-LNPs). These nanoparticles are designed for dual functionality: they efficiently encapsulate and deliver mRNA into dendritic cells while concurrently activating the STING pathway to stimulate innate immunity.
More description
|
|
| DC67618 | GVS-18-B35 |
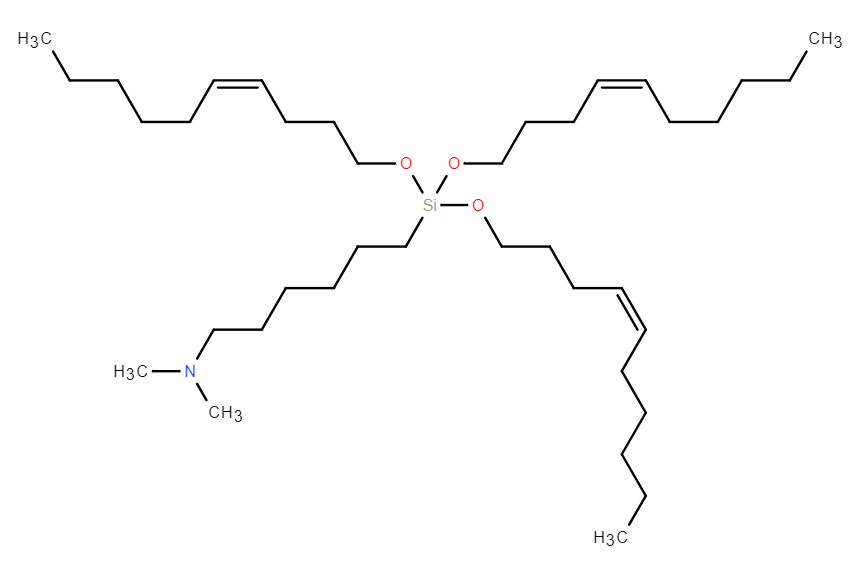
GVS-18-B35 is a leading silicon ether-based ionizable lipid that demonstrates exceptional performance in mRNA delivery. It features a biodegradable silyl ether linkage, which undergoes rapid, non-enzymatic hydrolysis, enabling near-complete clearance from the liver within 24 hours in both mice and non-human primates (NHPs). This degradation mechanism is independent of variable enzymatic activity, ensuring consistent pharmacokinetics across species. In vivo, GVS-18-B35 lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) achieve superior liver-specific protein expression with minimal off-target accumulation in the spleen, resulting in a high liver-to-spleen signal ratio and reduced immune stimulation. The LNPs exhibit excellent stability under frozen storage (-80°C) and maintain critical quality attributes, including particle size, polydispersity, and encapsulation efficiency, through multiple freeze-thaw cycles. With an optimal pKa (~6.3) and enhanced endosomal escape capability, GVS-18-B35 represents a robust and versatile platform for mRNA therapeutics, particularly suited for applications requiring frequent dosing due to its unique combination of high potency and rapid clearance profile.
More description
|
|
| DC67617 | iChol15-C4A2 |
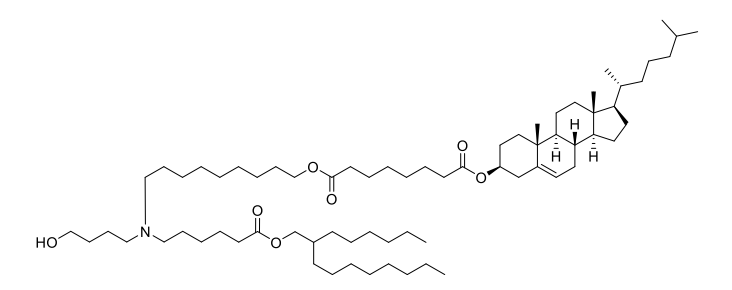
iChol15-C4A2 is a groundbreaking ionizable cholesteryl lipid, expertly designed to overcome the primary challenge of liver-centric accumulation in mRNA therapeutics. Its innovative "two-in-one" structure seamlessly integrates cholesterol with an ionizable headgroup, enabling the formation of stable, three-component Lipid Nanoparticles (Tc-LNPs).The key advantage of Tc-LNPs formulated with iChol15-CA2 is their significantly reduced adsorption of Apolipoprotein E (ApoE).This unique property directly attenuates ApoE/LDLR-mediated uptake by liver cells, dramatically shifting biodistribution toward extrahepatic tissues. Peer-validated research demonstrates a remarkable 20-50 fold increase in the spleen-to-liver mRNA expression ratio compared to standard LNPs like ALC-0315, unlocking unparalleled potential for targeting the immune system.
Beyond its superior targeting capability, iChol15-C4A2 ensures high mRNA encapsulation efficiency, excellent colloidal stability, and proven biocompatibility. It offers a powerful, off-the-shelf solution to advance next-generation mRNA applications, from innovative vaccines and cancer immunotherapies to treatments for splenic disorders. Discover how iChol15-C4A2 can transform your delivery platform.
More description
|
|
| DC67567 | ARV-T1 Featured |
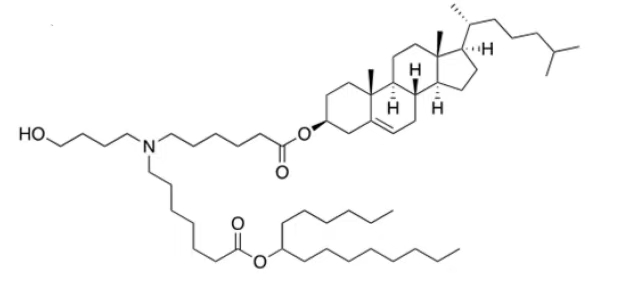
ARV-T1 is a novel ionizable lipid featuring a cholesterol moiety incorporated in its tail, designed to enhance mRNA delivery efficiency. With a pKa of 6.73, it exhibits optimal pH-dependent ionization for endosomal escape and mRNA release. Structurally, ARV-T1 contains a tertiary amine head group and ester-linked lipid tails, enabling rapid in vivo metabolism and improved biocompatibility.Compared to SM-102 (used in Moderna's vaccine), LNPs formulated with ARV-T1 demonstrate superior physicochemical properties: smaller particle size (~80 nm vs. 90 nm), lower polydispersity index (0.09 vs. 0.10), and higher absolute zeta potential (-10 mV vs. -5 mV). These characteristics correlate with >90% mRNA encapsulation efficiency and enhanced stability, maintaining performance for 12 weeks at -20°C.In vitro, ARV-T1 LNPs showed 7-fold higher protein expression than SM-102 LNPs. In vivo, they prolonged luciferase expression (>72 hours vs. <48 hours for SM-102) and induced 10-fold higher neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein at low doses. The cholesterol tail promotes endosomal membrane fusion, while ester linkages facilitate metabolic clearance, yielding an excellent safety profile in toxicity studies. This combination of efficacy and safety positions ARV-T1 as a promising platform for mRNA vaccines and therapeutics.
More description
|
|
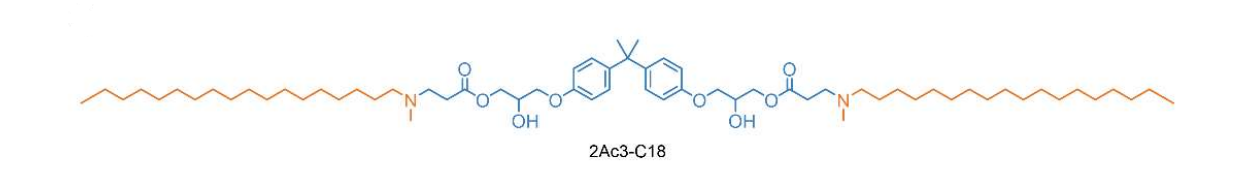
| DC60880 | 2Ac3-C18 Featured |
2Ac3-C18 is a unique ionizable lipid with a distinct degradable core structure:featuring 2 acrylate units and 3 amine groups—linked to a C18 alkyl chain. Its LNPs (formulated with DOPE/cholesterol/DMG-PEG2000) exhibit spleen-specific mRNA delivery in vivo.
More description
|
|
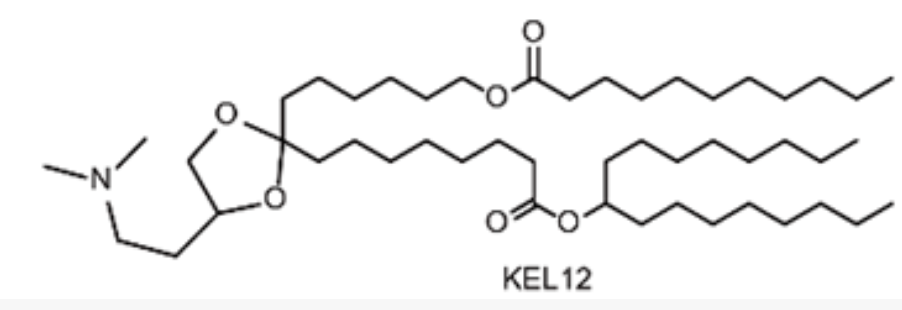
| DC67633 | Lipid KEL12 |
(4S)-KEL12 is a novel, biodegradable ionizable lipid developed for advanced mRNA vaccine delivery. It was rationally designed by incorporating both a ketal group in the linker and ester segments in the hydrophobic tails, a dual-degradable strategy aimed at enhancing its safety profile. Through iterative optimization, (4S)-KEL12 was identified as a lead candidate with an optimal pKa value of approximately 6.78, which is crucial for efficient mRNA encapsulation and endosomal release.
More description
|
|
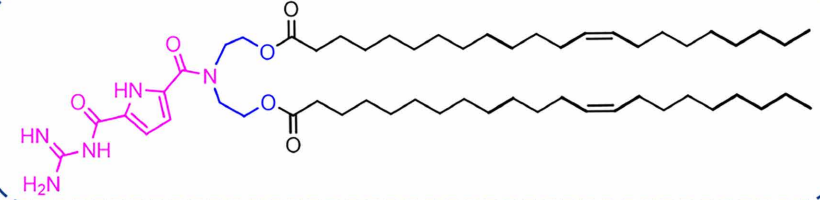
| DC67632 | Lipid GL5 |
GL5 is an ionizable guanidine-based lipid nanoparticle (G-LNP) designed for superior mRNA delivery. Its guanidinocarbonyl-pyrrole (GCP) headgroup enables pH-responsive behavior and strong mRNA binding via bidentate hydrogen bonds. The cholesterol-free GL5-3 formulation forms compact, stable nanoparticles (~90-120 nm) that exhibit excellent spleen-targeting capability after intravenous injection.GL5-LNPs efficiently deliver mRNA to antigen-presenting cells (APCs), enhancing antigen presentation and T cell activation. In cancer immunotherapy models, GL5-based mRNA vaccines provided complete tumor protection and induced durable immune memory. The platform also enables mRNA delivery to other organs like the pancreas via different administration routes, demonstrating remarkable versatility and therapeutic potential.
More description
|
|
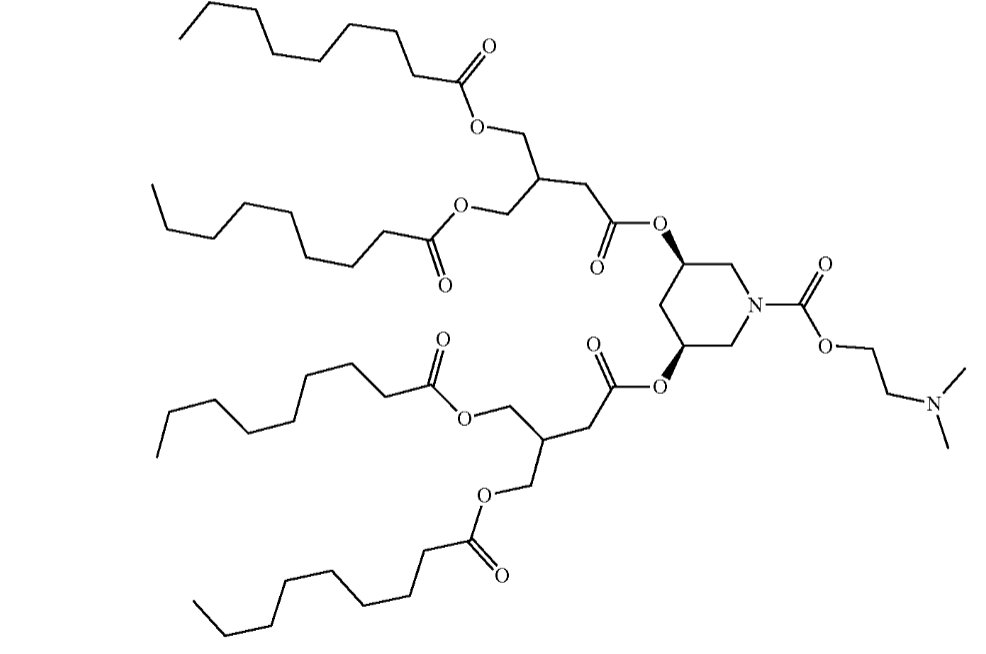
| DC67651 | CICL-238 |
Based on the data from patent US 20250127728A1, CICL-238 emerges as a highly promising ionizable lipid candidate, demonstrating notable advantages for targeted delivery applications. It achieves exceptional transfection efficiency—reaching approximately 90% of CICL-207's performance in splenic T-cells even at a reduced lipid ratio of 50% in LNP formulations. Additionally, CICL-238 exhibits minimal off-target expression in hepatocytes (<8%, comparable to CICL-207), underscoring its enhanced specificity for immune cells over liver tissues. Its optimized structure likely contributes to efficient endosomal escape and reduced Kupffer cell uptake, making it ideal for liver-related therapies (e.g., siRNA silencing for metabolic diseases) and potentially broadening applications to genetic medicine where precision and safety are paramount. Further validation in disease models could solidify its role as a versatile, low-toxicity alternative to benchmark lipids.
More description
|
|
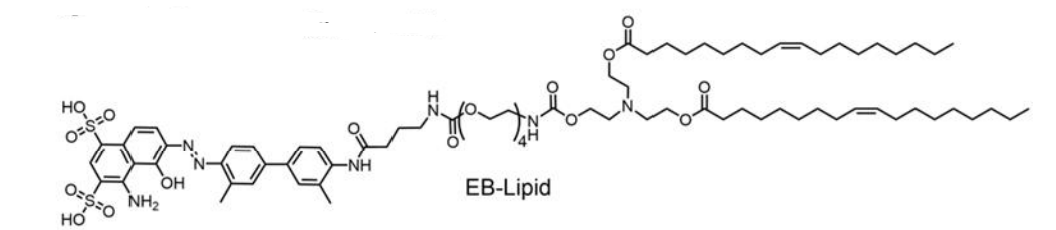
| DC67650 | EB-Lipid |
EB-Lipid is an innovatively engineered ionizable lipid designed to replace conventional PEG-lipid in mRNA vaccine formulations. Its structure comprises three key components: an Evans Blue-derived headgroup with high affinity for albumin, a tetraethylene glycol linker that enhances colloidal stability, and dual oleate tails for anchoring into lipid bilayers. This molecular design enables EB-Lipid to actively recruit endogenous albumin, forming an albumin-rich protein corona on the surface of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). Following intramuscular administration, these albumin-bound EB-LNPs are preferentially transported through lymphatic vessels rather than entering the bloodstream, thereby avoiding hepatic accumulation and associated hepatotoxicity risks.Experimental data demonstrate that EB-LNPs achieve significantly higher accumulation in lymph nodes, where they are efficiently internalized by dendritic cells via albumin receptor-mediated endocytosis (e.g., gp60). This process enhances antigen presentation and activates robust cellular and humoral immune responses. In both tumor models (B16-OVA and HPV-associated) and infectious disease models (H1N1 and SARS-CoV-2 Omicron), EB-LNP-based mRNA vaccines elicited potent cytotoxic T-cell activation and durable neutralizing antibody production at low doses. Unlike traditional PEG-LNPs, EB-LNPs show minimal liver distribution, reduced immunogenicity, and improved safety profiles after repeated administrations.By leveraging albumin’s natural trafficking pathway, EB-Lipid represents a transformative delivery platform that combines targeted lymph node delivery with enhanced biosafety, positioning it as a promising candidate for next-generation mRNA vaccines and therapeutics.
More description
|
|
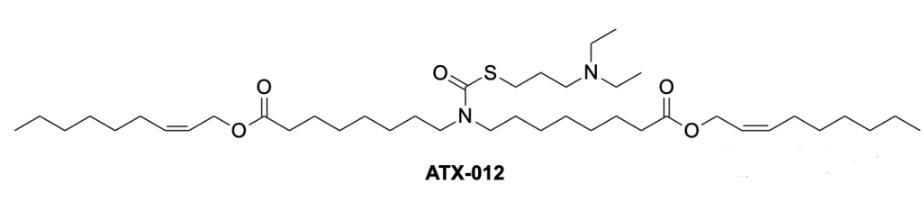
| DC67654 | ATX-012 |
ATX-012 is an ionizable cationic lipid specifically designed for mRNA delivery systems. Its unique chemical structure enables key functions in lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations, such as facilitating mRNA encapsulation and enhancing endosomal escape for efficient intracellular delivery.
More description
|
|
| DC67605 | PyCB lipid Featured |
PyCB lipid (MeDZ) is a rationally designed zwitterionic ionizable lipid that serves as a core functional component in the novel three-component (ThrCo) lipid nanoparticle (LNP) platform. It is synthesized by covalently attaching a zwitterionic PyCB structure to the hydroxyl group of the clinically available ionizable lipid ALC-0315.Its key feature is its pH-responsive behavior. At physiological pH (~7.4), the PyCB headgroup exhibits zwitterionic properties, forming charge-assisted hydrogen bonds with water molecules (PyCB-H₂O complexes). This confers high hydrophilicity to the LNP surface, enhancing stability in aqueous environments and reducing nonspecific protein adsorption in the bloodstream. This zwitterionic surface effectively mimics and replaces PEGylated lipids, thereby avoiding PEG immunogenicity and the associated Accelerated Blood Clearance (ABC) effect upon repeated administrations.Crucially, in the acidic environment of endosomes (pH ~6.5), the PyCB group undergoes strong protonation, rapidly transforming into a cationic state (PyCB-H₃O⁺ complexes). This promotes efficient fusion with and disruption of the endosomal membrane, facilitating the escape and cytoplasmic release of encapsulated mRNA.By replacing both cholesterol and PEGylated lipids in traditional LNPs, PyCB lipid enables the redirection of LNP biodistribution from the liver to the spleen, achieving superior spleen-specific mRNA translation and enhancing antigen presentation for potent immune activation.
More description
|
|
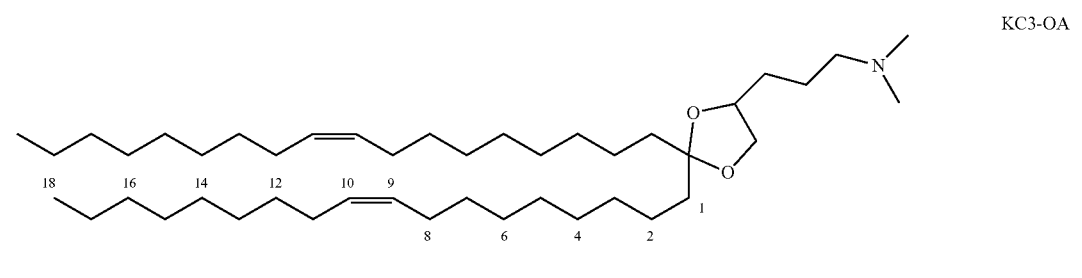
| DC67785 | KC3-OA Featured |
KC3-OA, chemically known as 3-((S)-2,2-di((Z)-octadec-9-en-1-yl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine, is an ionizable cationic lipid (ICL) optimized for lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations in nucleic acid delivery, particularly for mRNA vaccines. It features a unique structure with mono-unsaturated alkyl chains (C18:1), which enhances oxidative stability compared to polyunsaturated analogs like KC3, while maintaining efficient membrane fusion and endosomal escape capabilities. In LNP compositions, KC3-OA is typically incorporated at 46–54 mol% of total lipids, with an N/P ratio of 4–6 relative to mRNA, ensuring high encapsulation efficiency and transfection potency.
Experimental data demonstrate that KC3-OA-based LNPs achieve superior mRNA expression in human dendritic cells, outperforming alternatives like KC3-PA or KC3-01 in both in vitro and in vivo models. For instance, in FIG. 2, KC3-OA LNPs showed ~2-fold higher mCherry expression at low mRNA doses (0.1 μg/mL) due to improved cellular uptake and reduced degradation. Its synergy with anionic phospholipids like DPPS (5 mol%) further enhances dendritic cell targeting via receptor-mediated internalization, leading to robust CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses against Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens. This balance of stability, efficiency, and immunogenicity makes KC3-OA a leading candidate for next-generation vaccines.
More description
|
|
| DC67812 | CL15F 6-4 Featured |
CL15F 6-4 is a short-tail ionizable lipid from the piperidine-based CL15F series, characterized by its symmetric branched structure with a 6-carbon main chain and 4-carbon side chain. This specific tail length critically determines the lipid nanoparticle's (LNP) properties, resulting in larger particles with a high surface density of the phospholipid DSPC. This elevated DSPC density reduces interactions with serum proteins like ApoE, minimizing rapid liver clearance and shifting mRNA delivery preference towards the spleen. Consequently, CL15F 6-4 LNPs achieve efficient, endogenous spleen-targeted delivery, making them a highly promising candidate for enhancing vaccine efficacy by preferentially transfecting antigen-presenting cells without complex functionalization.
More description
|
|
| DC67984 | L31(Lipid 31) Featured |
L31 is identified as a novel, proprietary ionizable cationic lipid that serves as the critical functional component within lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) engineered for CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). It was selected from a screened library of lipids for its superior performance. LNPs formulated with L31 exhibited excellent physicochemical properties, including a uniform size of 80-100 nm, low polydispersity, and high encapsulation efficiency (>85%) for both Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA. In vitro, L31-based LNPs demonstrated outstanding therapeutic efficacy, achieving approximately 68% gene editing of the oncogene SOX2 and an 88% reduction in cancer cell viability.For in vivo applications, L31-LNPs were further functionalized with anti-EGFR antibodies using the ASSET linker strategy to create targeted nanoparticles (tLNPs). This modification enhanced specific uptake by tumor cells. In a xenograft mouse model, intratumoral injection of these targeted L31-cLNPs co-encapsulating Cas9 mRNA and sgSOX2 led to potent tumor growth inhibition (90%) and a significant increase in survival, with tumor disappearance observed in half of the treated mice. In conclusion, L31 is a highly efficient ionizable lipid that forms the foundation of a potent targeted LNP platform for precise CRISPR-based cancer therapy against solid tumors.
More description
|
.png)
|
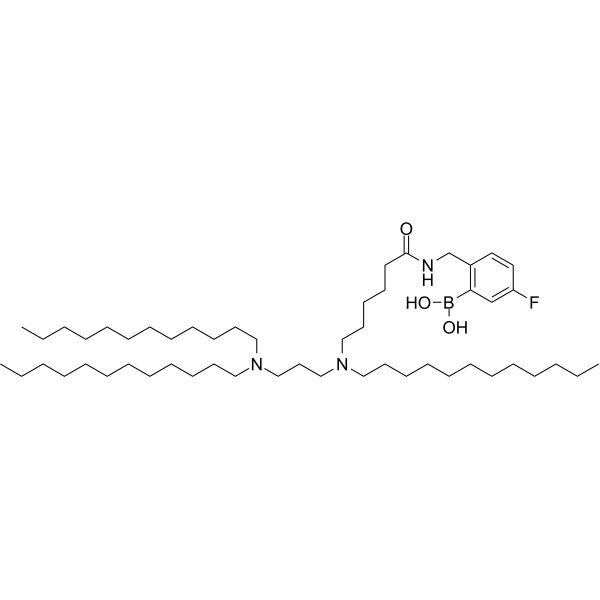
| DC67981 | Diamino lipid DAL4 Featured |
Diamino lipid DAL4 is diamino lipid for the preparation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) encapsulated with mRNAs encoding cytokines including IL-12, IL-27 and GM-CSF. Diamino lipid DAL4 delivers mRNA to tumor cells to exert anti-tumor activity.
More description
|
|
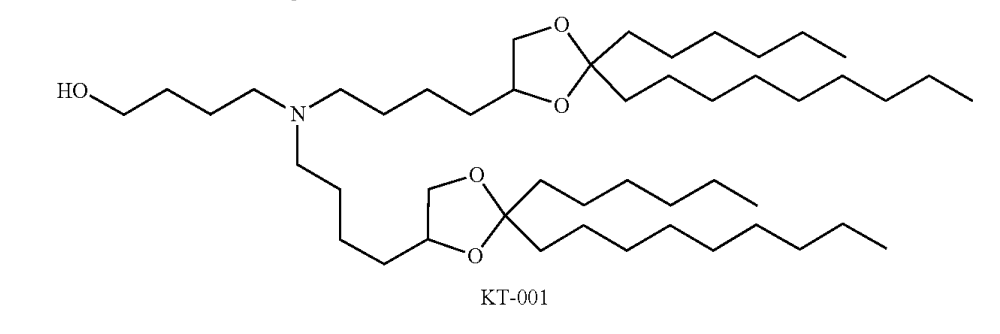
| DC67988 | KT-001 Featured |
KT-001 is a novel ionizable cationic lipid disclosed in patent US 2026/0007612 A1
More description
|
|
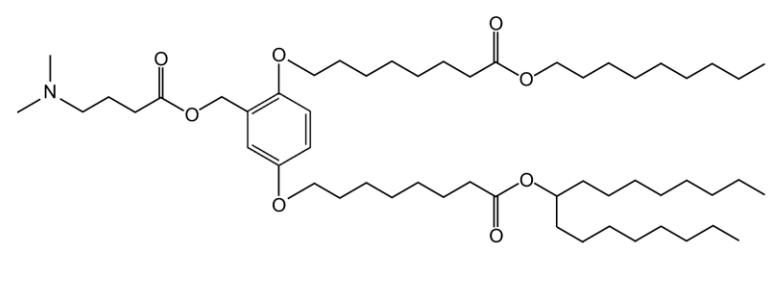
| DC67983 | XH-07 Featured |
XH-07 is an innovative ionizable cationic lipid that forms the backbone of the JCXH-211 lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery system. This complex is engineered to encapsulate and deliver self-replicating RNA (srRNA) encoding interleukin-12 (IL-12), a potent immunostimulatory cytokine. The LNP formulation featuring XH-07 exhibits optimal physicochemical properties, such as a mean particle size of approximately 82.12 nm with low polydispersity, and a near-neutral zeta potential around -3.181 mV, which facilitates stable circulation and efficient cellular uptake upon intravenous administration. Upon delivery, the srRNA leverages the host cell's machinery to produce sustained levels of IL-12p70, as demonstrated in B16F10 tumor-bearing mice, where a single dose led to peak cytokine production in sera and tumors. This induced IL-12 expression activates T cells and NK cells, generating a robust antitumor response. In murine models of melanoma and breast cancer, JCXH-211 monotherapy resulted in significant tumor regression and complete responses in some subjects, and it synergized with anti-PD-1 therapy to enhance efficacy. Importantly, the safety profile was acceptable, with transient liver enzyme elevations in mice that normalized quickly, and no significant adverse events in cynomolgus monkeys after repeated dosing, as evidenced by stable clinical observations and pathology tests. Thus, XH-07 is pivotal for enabling the safe and effective delivery of IL-12 encoding RNA, positioning JCXH-211 as a promising cancer immunotherapy.
More description
|
|
| DC67602 | ILB-3132(E12LA6B603) Featured |
E12LA6B603(ILB3132,ILB-3132) is a novel ionizable amino lipid disclosed in patent WO2024198497A1, developed by MagicRNA, representing a highly efficient component for lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery systems.When formulated into LNPs, E12LA6B603 LNP achieves a remarkable 98.26% encapsulation efficiency for mRNA. It mediates superior in vitro transfection in dendritic cells (1.8E+05 intensity) and demonstrates best-in-class in vivo protein expression after intramuscular injection (2.2E+09 intensity). Most notably, in a B16-OVA melanoma model, therapeutic OVA-mRNA vaccines delivered by E12LA6B603 LNPs induced 100% complete tumor regression, highlighting its superior efficacy over benchmarks like DLin-MC3 and SM-102. Its biodegradable ester linkages and balanced structure make it a promising, potent candidate for next-generation mRNA vaccines and therapeutics.
More description
|

|
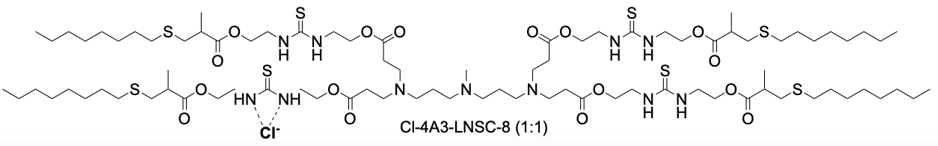
| DC67989 | Cl-4A3-LNSC8 Featured |
Cl-4A3-LNSC8 represents a novel class of thiourea-functionalized ionizable lipids engineered for selective organ-targeted mRNA delivery. Its core innovation lies in an anion-coordination strategy, where the parent lipid, 4A3-LNSC8, binds chloride ions (Cl⁻) via hydrogen-bonding interactions with its thiourea groups. This binding event is not merely structural but functionally critical, as it induces a significant shift in the surface pKa of the resulting lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) from approximately 5.54 to 8.79. This pKa modulation is the key mechanism that redirects the organotropism of the LNPs upon systemic administration. While the unmodified 4A3-LNSC8 LNPs preferentially deliver mRNA to the liver, Cl-4A3-LNSC8 LNPs effectivelyreprogram this tropism, enabling highly efficient mRNA delivery to secondary lymphoid organs (SLOs), particularly the spleen and lymph nodes. This platform demonstrates remarkable efficacy, achieving up to 65.7% gene editing efficiency in splenic macrophages in vivo, significantly outperforming benchmark delivery systems. Furthermore, by leveraging the coordination with different halides, such as iodine for computed tomography (CT) contrast, the system can be adapted for dual-modal theranostic applications, enabling simultaneous lymphatic metastasis imaging and therapeutic mRNA delivery.
More description
|
|
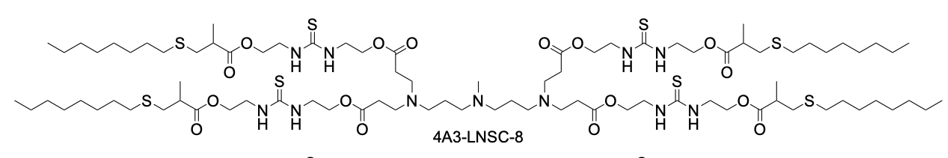
| DC67990 | 4A3-LNSC8 Featured |
4A3-LNSC8 is a strategically designed thiourea-functionalized ionizable lipid that serves as the foundational core for a novel anion-coordination delivery platform. Its structure features a central 4A3 amine headgroup symmetrically extended with four hydrophobic tails, each incorporating a biodegradable ester linkage and a key thiourea-bridged linker. The inclusion of the thiourea group is the pivotal innovation, as it provides specific hydrogen-bonding sites capable of interacting with various halide anions (F⁻, Cl⁻, I⁻). When formulated into lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) without anion coordination, 4A3-LNSC8 itself exhibits a characteristic liver tropism, efficiently delivering mRNA to hepatocytes following systemic administration, with a measured surface pKa of approximately 5.54. However, its primary significance lies in its role as a versatile precursor. The strong anion-binding capability of its thiourea linkers allows for predictable modulation of the LNP's properties. Upon binding with anions like Cl⁻, the resulting complex (e.g., Cl-4A3-LNSC8) undergoes a significant pKa shift, which reprograms the LNP's in vivo fate, redirecting mRNA delivery from the liver to secondary lymphoid organs such as the spleen and lymph nodes. Thus, 4A3-LNSC8 is not merely an efficient ionizable lipid but a programmable scaffold that enables precise control over organ-targeting specificity through simple anion coordination, offering a powerful rational design strategy for advanced mRNA therapeutics.
More description
|
|
| DC67662 | Lipid 48 Featured |
Lipid 48 is a leading ionizable lipid designed for therapeutic nucleic acid delivery. Its key function is to form the core of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) that efficiently encapsulate and deliver cargoes like mRNA and CRISPR guide RNAs into cells. Its optimized structure allows it to remain neutral in the bloodstream for low toxicity but become positively charged in acidic cellular compartments (endosomes), where it disrupts the membrane to release the therapeutic payload. Data from the patent demonstrates its superior profile: it achieves high gene editing efficiency (e.g., ~80% indel rates in vitro and 16.2% in vivo in mouse liver) while maintaining low cytotoxicity (cell viability >80% at effective doses), establishing it as an ideal candidate for gene therapy applications due to its exceptional balance of potency and safety.
More description
|
.png)
|
| DC60878 | Lipid A-12 Featured |
Lipid A-12 is an ionizable cationic lipid from Capstan Therapeutics and a close analog of CICL-1 (L829). The structure was modified by the extension of the headgroup linker from a two-carbon (C2) to a three-carbon (C3) spacer compared to CICL-1 (L829).
More description
|
|
| DC67994 | 244-9-cis Featured |
244-9-cis is a novel ionizable lipid disclosed in United States Patent US 2026/0014075 A1, specifically engineered for advanced lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery systems. Its distinctive molecular architecture features biodegradable ester bonds, which contribute to excellent physicochemical properties such as a near-neutral surface charge (approximately -3 mV) for improved biocompatibility, an optimal pKa of about 6.2 to facilitate endosomal escape, and consistently high nucleic acid encapsulation efficiency exceeding 90%. In vivo studies confirm significantly enhanced delivery to hepatocytes and markedly higher therapeutic protein expression compared to control formulations, positioning 244-9-cis as a promising candidate for next-generation genetic medicines.
More description
|
|