 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Field of Application | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
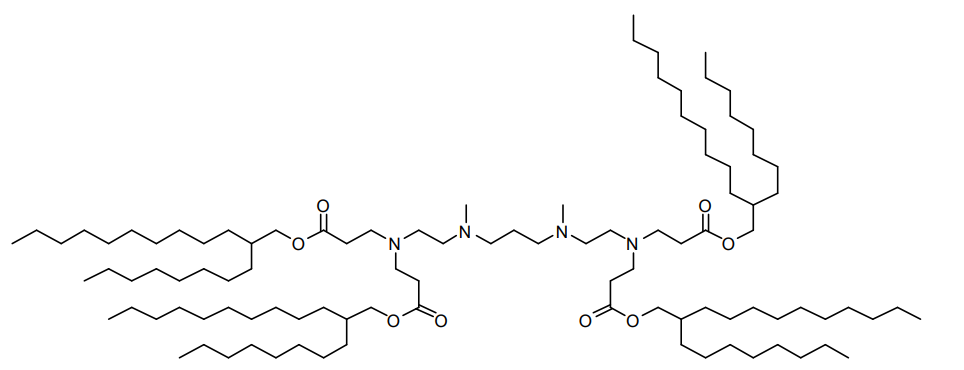
| DC60808 | 503O8,12 Featured |
503O8,12 is an ionizable lipidoid synthesized via Michael addition, combining a hydrophilic amine headgroup ("503" series) with two hydrophobic branched acrylate tails (C8 and C12 chains, likely with unsaturated bonds). Its design emphasizes organ-specific delivery, exhibiting spleen-tropic targeting in vivo.
More description
|
|
| DC67120 | YSK12-C4 (YSK12-MEND) Featured |
YSK 12C4 is an ionizable cationic lipid primarily used to enhance siRNA cellular delivery via multifunctional envelope-type nanodevices (MEND). YSK 12C4 promotes siRNA uptake and endosomal escape, effectively silencing genes in human immune cell lines.
More description
|

|
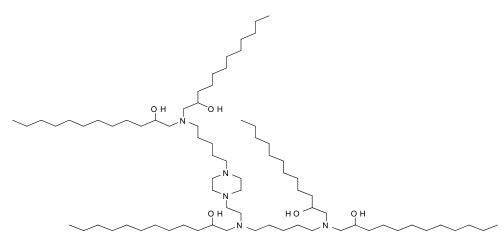
| DC60503 | C12-A1 Featured |
Lipid C12-A1 is an ionizable lipid. C12-A1-LPN is a potent and safe LNP platform to deliver Foxp3 mRNA to CD4+ T cells to engineer immunosuppressive FP3T cells. C12-A1 has a slightly lower average cell viability than C14-A1.
More description
|
|
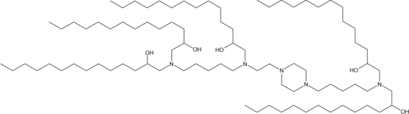
| DC60499 | C14-A1 Featured |
Lipid C14-A1 is an ionizable lipid. C14-A1-LPN is a potent and safe LNP platform to deliver Foxp3 mRNA to CD4+ T cells to engineer immunosuppressive FP3T cells.
More description
|
|
| DC67521 | Lipid TD5 Featured |
TD5 is a brain-targeting lipid nanoparticle (BLNP) engineered for efficient mRNA delivery to the central nervous system (CNS) via intrathecal injection. It incorporates a tryptamine-derived ionizable lipid headgroup, myristic acid hydrocarbon tails, and a biodegradable carbonate ester linker, enabling pH-dependent mRNA encapsulation (81.7% efficiency) and brain cell-specific targeting. With a hydrodynamic diameter of 107.5 nm, near-neutral pKa (7.30), and mild positive charge, TD 5 demonstrates superior CNS tropism through serotonin receptor (5-HT1A)-mediated endocytosis. In vitro, TD-5 achieved 80.8% GFP expression in SH-SY5Y neuronal cells, outperforming MC3 LNPs by 50-fold. Following intrathecal administration in mice, TD-5 mediated GFP expression in 29.6% of neurons and 38.1% of astrocytes brain-wide, with 10-fold higher CNS specificity than peripheral organs. Genome editing studies showed TD5-delivered Cas9/sgRNA induced tdTomato activation in ≈30% of neurons and 40% of astrocytes across key brain regions. Safety profiling revealed minimal systemic immune responses (lower IL-6, IL-12p40 vs MC3 LNPs), normal hepatic/renal biomarkers, and no histopathological toxicity. The optimized structure balances myristic chain hydrophobicity for membrane interaction, ionizable amines for mRNA complexation, and tryptamine-mediated targeting for enhanced CNS uptake, establishing TD5 as a promising platform for CNS gene therapies.
More description
|

|
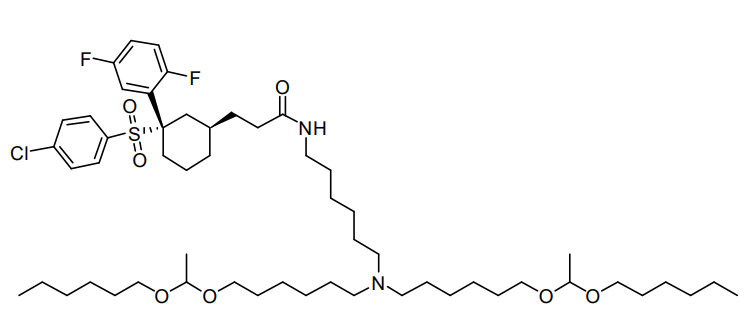
| DC67295 | Lipid MK16 Featured |
MK-16 is a specialized lipid designed to traverse the blood-brain barrier (BBB) for effective mRNA delivery. Its formulation, MK 16 BLNP, leverages dual mechanisms involving caveolae and γ-secretase to facilitate BBB penetration, ensuring the targeted and efficient transport of functional mRNA to diverse brain cell types. Demonstrating excellent tolerability across a range of dosing regimens, MK16 BLNP represents a promising platform for brain-targeted therapeutic applications.
More description
|
|
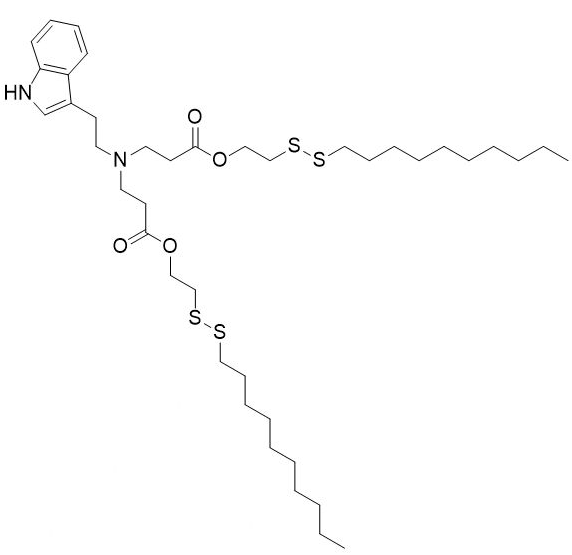
| DC60212 | NT1-O14B Featured |
NT1-O14B is a tryptamine-containing cationic lipidoid.1 It has been used in combination with other lipids in the formation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). Intravenous administration of LNPs containing NT1-O14B and encapsulating antisense nucleotides against tau decreases tau brain levels in mice.
More description
|
|
| DC41043 | NT1-O12B Featured |
NT1-O12B, an endogenous chemical and a neurotransmitter-derived lipidoid (NT-lipidoid), is an effective carrier for enhanced brain delivery of several blood-brain barrier (BBB)-impermeable cargos. Doping NT1-O12B into BBB-impermeable lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) gives the LNPs the ability to cross the BBB. NT-lipidoids formulation not only facilitate cargo crossing of the BBB, but also delivery of the cargo into neuronal cells for functional gene silencing or gene recombination.
More description
|

|
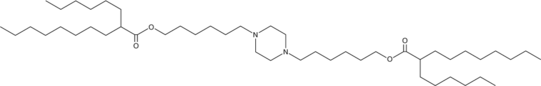
| DC67452 | Lipid PPz-2R1 |
PPz-2R1 is an ionizable cationic lipid engineered for mRNA delivery via lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). These LNPs demonstrate remarkable lung-selective accumulation in mice, showing significantly higher uptake compared to heart, liver, spleen, and kidney tissues. When loaded with PTEN mRNA, PPz-2R1 LNPs effectively restore tumor suppressor function in PTEN-deficient lung cancer cells and inhibit tumor progression in orthotopic models, with enhanced efficacy observed in combination with PD-1 blockade therapy.
More description
|
|
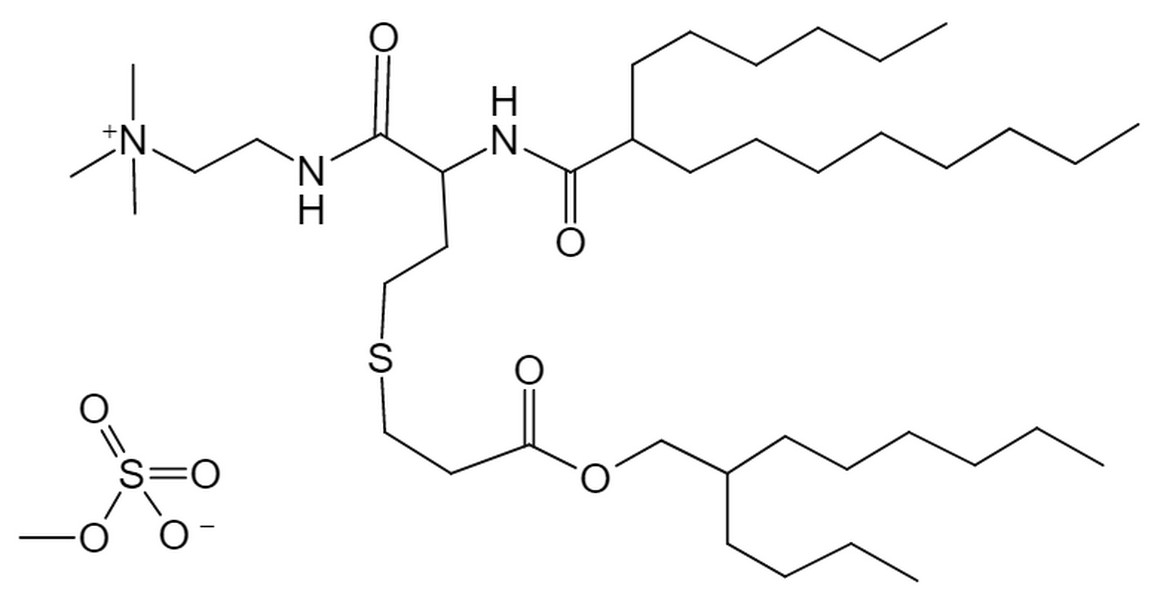
| DC60673 | (+)CP-LC-0729 |
(+)CP-LC-0729 is an cationic lipid derived from CP-LC-0729 and achieves significantly higher expression and selectivity highlights the advantages of this lipid system for lung-targeted delivery.
More description
|
|
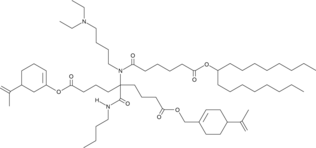
| DC60706 | FO-35 Featured |
FO35 is an artificial intelligence-guided designed ionizable lipid for RNA delivery to the muscle, lung and nose. FO-35 LNPs enable potent transfection throughout the whole ferret lung epithelium, from trachea to alveoli.
More description
|
|
| DC60705 | FO-32 Featured |
FO-32 is an artificial intelligence-guided designed ionizable lipid for RNA delivery to the muscle, lung and nose. FO-32 LNPs enable potent transfection throughout the whole ferret lung epithelium, from trachea to alveoli.
More description
|

|
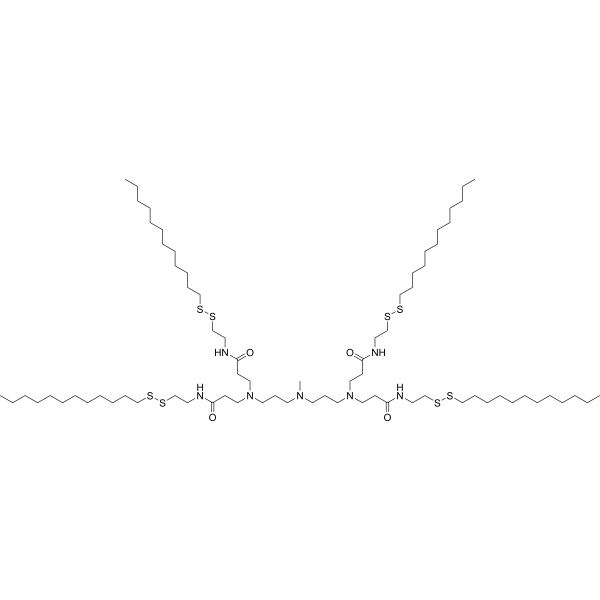
| DC65327 | 306-N16B Featured |
306-N16B is a lipidnanoparticle, and allows systemic codelivery of Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA. 306-N16B can transport mRNA to the pulmonaryendothelial cell. 306-N16B can be used for research of genome editing-based therapies. Based on the same lipid libraries with 306-O12B, the researchers also found that N-series ionizable lipids were able to selectively deliver mRNA to the lungs of mice. Compared with the liver-targeted O-series ionizable lipids which contained ester bond in lipid tail found in previous work, such as 306-O12B, the N-series ionizable lipids with
the lipid tail containing amide bond prefer to deliver mRNA to the lung. As a N-series ionizable lipid, the chemical structure of the 306-N16B is shown in Figure 4a,b. The difference of organ targeting may be due to their adsorption
of different protein coronas during blood circulation caused
by their different structures mentioned earlier.It has
shown that the second major protein of the protein
corona adsorbed by liver-targeting 306-O12B iLNPs was apolipoprotein
E (ApoE), while the three dominant proteins in the
protein corona adsorbed by lung-targeting 306-N16B iLNPs
were serum albumin, fibrinogen beta chain, and fibrinogen
gamma chain. However, the 306-N16B iLNPs showed less
organ selectivity when systematically codelivered Cas9
mRNA and sgRNA in vivo, which could simultaneously
activate tdTomato expression in the liver and lung of Ai14
mice, whereas single mRNA delivery could almost
exclusively deliver mRNA to the lungs. This surprising phenomenon
requires further investigation. Both the change of
iLNPs charge and the change of lipids functional group
can influence the distribution of iLNPs in vivo due to
the altering of protein corona composition. Therefore,
it is possible to control the organ targeting of iLNPs by
controlling the composition of the outer protein corona of
iLNPs.
More description
|
|
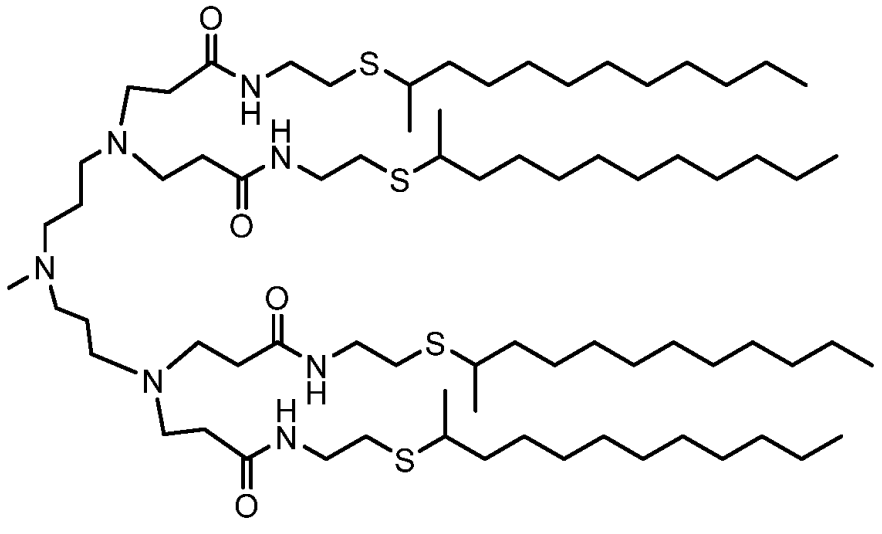
| DC67525 | Hopewell Lipid 649 Featured |
L649 is a next-generation, lung-targeting ionizable lipid specifically designed for systemic mRNA delivery developed by Hopewell. Belonging to the novel "N-series" lipid class, it features a unique structure with an amine-containing head group and hydrophobic tails incorporating amide bonds. This design enables L649 to form highly stable lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) that exhibit exceptional tropism for the lower respiratory tract (lungs, bronchi, trachea) following intravenous administration. It demonstrates superior efficiency in delivering therapeutic payloads (like mRNA) specifically to key lung cell types, including alveolar epithelial cells (AT1 and AT2) and bronchial cells, while minimizing off-target accumulation in organs like the liver. L649-based LNPs, particularly when formulated with helper lipids like POPE, combine high potency with significantly improved tolerability, allowing for effective dosing in vivo. This makes L649 a promising candidate for developing treatments for various lung diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis, COPD, lung cancer, and infectious diseases like COVID-19.
More description
|
|
| DC60506 | IR-117-17 |
IR-117-17 (A10-LIN) is an ionizable and biodegradable lipid specifically designed for nebulized mRNA delivery. When formulated into lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), IR-117-17 demonstrates remarkable efficacy, achieving a 300-fold enhancement in lung mRNA delivery compared to the best-performing LNP previously reported. Additionally, it shows a two-fold improvement over the leading PBAE-based delivery system, with up to a 45-fold increase in mRNA delivery efficiency to the large airways.
More description
|
.png)
|
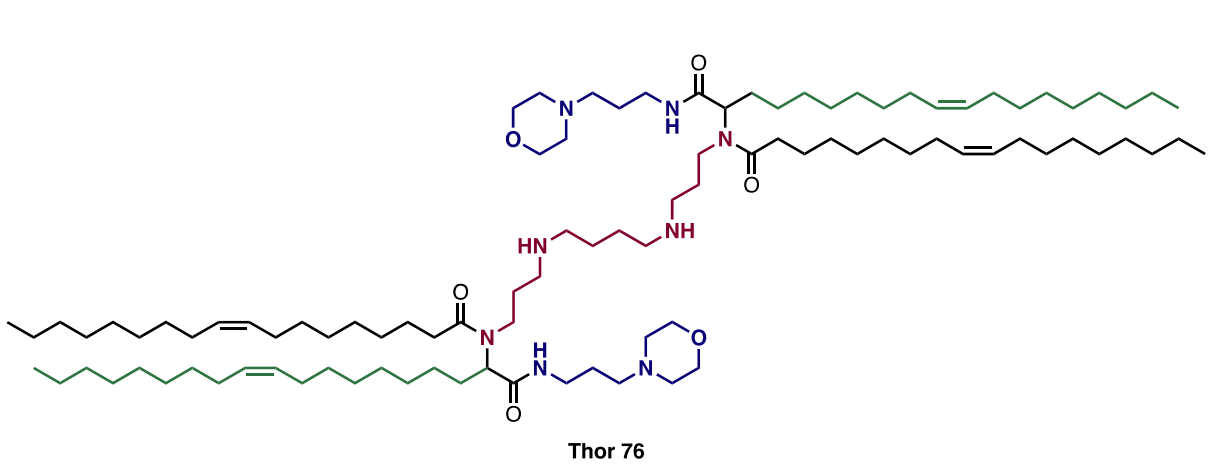
| DC60849 | THOR 76 Crude |
THOR 76 is an ionizable lipid developed for lung-targeted mRNA delivery, synthesized via a high-throughput Ugi four-component reaction (U4CR). It combines spermine (N3, amine core), oleyl aldehyde (A2), oleic acid (C2), and a morpholine-functionalized isonitrile (D3). Remarkably, its crude reaction mixture outperforms purified forms in efficacy, suggesting synergistic impurities or intermediates enhance function. Formulated into lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) with cholesterol, DOPE, and PEG-lipid, THOR 76 LNPs exhibit exceptional lung tropism with secondary spleen affinity after intravenous administration. They efficiently transfect pulmonary endothelial cells, enabling robust gene expression (e.g., Cre recombinase) and significant CRISPR-Cas9-mediated gene editing (1.22% at 0.1 mg/kg dose) in the lungs. With a particle size <150 nm, positive zeta potential, and >90% mRNA encapsulation, THOR 76 achieves targeted delivery while minimizing off-target effects in the liver. Its design overcomes limitations of cationic helper lipids, offering a potent, tolerable platform for treating pulmonary genetic disorders and cancers.
More description
|
|
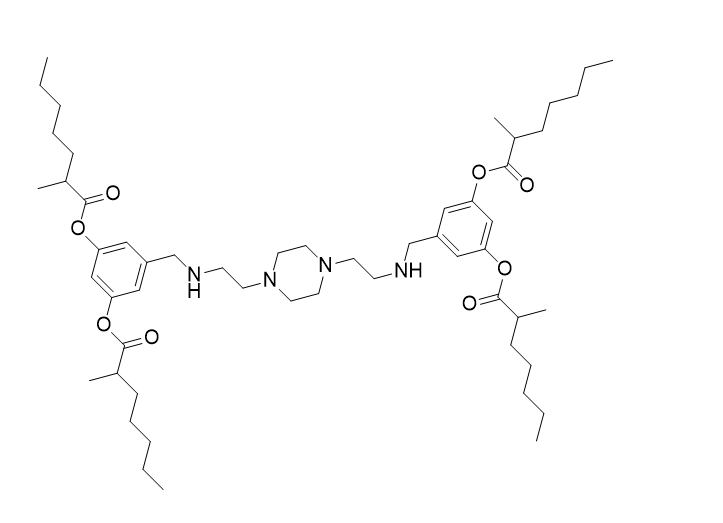
| DC60566 | Lipid CAD9 (3-A2-7b) |
Lipid CAD9 (3-A2-7b is a cationic degradable (CAD) lipid. 3-A2-7b formulated LNP, LNP-CAD9, can deliver FLuc mRNA to the lungs in vivo. LNP-CAD9 co-delivering Cas9 mRNA/VEGFR2 single guide RNA (sgRNA) effectively induces VEGFR2 knock out in lung endothelial cells of female mice.
More description
|
|
| DC60838 | A3T2C7 (CP-LC-1495) |
A3T2C7 (CP-LC-1495) is a biodegradable ionizable lipid featuring three β-propionate linkers and an azetidine polar head, formulated in four-component LNPs. It demonstrates exceptional lung-targeted mRNA delivery with 97.1% selectivity and high protein expression (1.21×10⁸ p/s) in mice. Its slightly positive zeta potential (~3.5 mV) correlates with lung tropism, likely mediated by protein corona enrichment of vitronectin and prothrombin. The β-propionate structure enables pH-sensitive biodegradability for enhanced endosomal escape while maintaining low cytotoxicity (>90% cell viability). This lipid enables organ-specific mRNA delivery without permanently charged additives, outperforming conventional SORT strategies in selectivity and expression efficiency.
More description
|
.png)
|
| DC67565 | IAJD249 |
IAJD 294 is a single-component ionizable amphiphilic Janus dendrimer that autonomously coassembles with mRNA via simple injection into uniform monodisperse dendrimersome nanoparticles (DNPs, 85 nm diameter, PDI<0.2), eliminating complex multi-component formulations. Its optimized 3,5-benzoyl ester linkage and symmetric hydrophobic tails enable dual-organ targeting:
Spleen: 2.97 × 10⁷ RLU (50% of total activity)
Lymph nodes: 10⁶ RLU (10× higher than IAJD 87)
through partial hydrophobic interdigitation (stabilizing DNPs for enhanced lymphatic uptake) and pKa ~6.5 (facilitating endosomal escape), validating constitutional isomerism for precision delivery.
More description
|
|
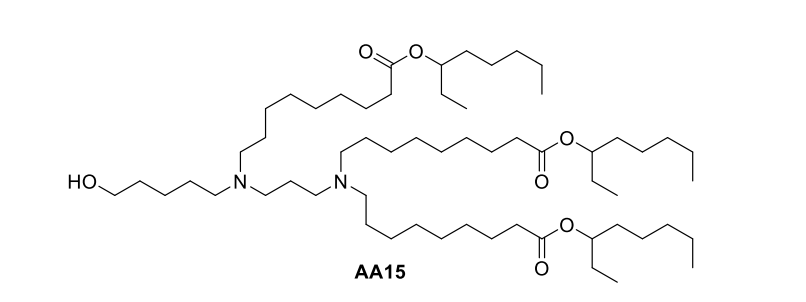
| DC67315 | Lipid AA15 |
The AA15 lipid, an amino acid-derived ionizable lipid, integrates a carboxylic acid-containing headgroup and biodegradable branched ester tails (R2) to enhance mRNA delivery. Optimized as AA15V LNP, it exhibits a hydrodynamic diameter of 102.3 ± 4.1 nm, low polydispersity (PDI <0.15), and slightly positive zeta potential (+4–6 mV), enabling efficient tumor-targeted delivery. With a pKa ~6.1–6.4, AA15V ensures protonation in acidic endosomes, promoting mRNA release. It achieves >85% mRNA encapsulation efficiency, critical for stable saRNA delivery. In vitro, AA15V LNP-sSE-SCTs induced sustained SE-SCT expression (69% H-2Kb+β2m+ B16F10 cells at 72 h), outperforming mRNA formulations. In vivo, a single intratumoral dose of AA15V LNP-sSE-SCTs suppressed tumor growth by 22-fold in vaccinated mice, synergizing with checkpoint inhibitors (anti-PD-1/CTLA-4) for complete regression in 28.6% of lymphoma models. Ex vivo, AA15V enabled SE-SCT expression in human glioblastoma (7.1% CD45− cells) and lung cancer samples (5.8–8.7%), underscoring clinical potential. Key data: pKa ~6.3; encapsulation: 85–89%; zeta: +4–6 mV; size: 102.3 ± 4.1 nm.
More description
|
|
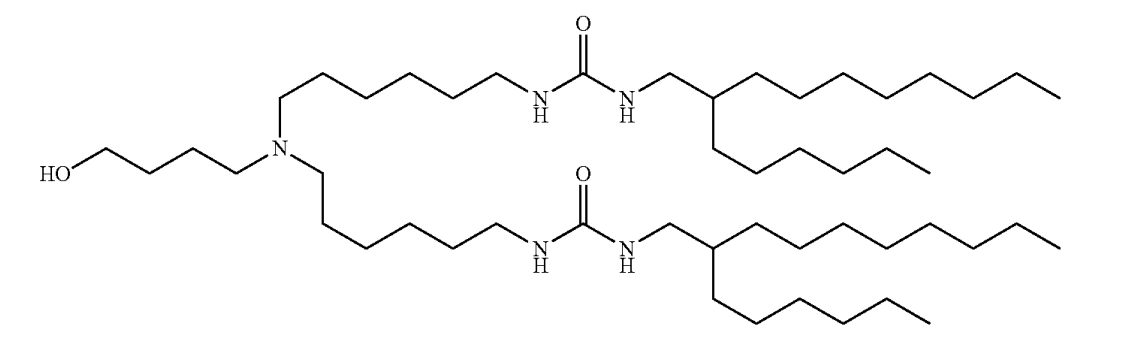
| DC67517 | Westgene lipid 8 |
Westgene lipid 8 is a cationic lipid featuring a tertiary amine core with three alkyl chains (C1-C15) and two unsaturated C18 linoleate-like tails. Its ionizable amine enables pH-dependent charge for mRNA encapsulation in LNPs. Key structural elements include branched alkyl groups (X1/X2: C4, X3: C2) and ester-linked unsaturated R1/R2 chains, enhancing membrane fusion and endosomal escape. N Used in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) with DOPE, cholesterol, and PEG-DMG, it demonstrates low cytotoxicity, high mRNA delivery efficiency, and spleen-targeted immune activation, making it suitable for vaccine/therapeutic delivery.
More description
|
|
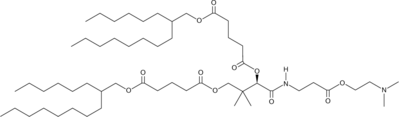
| DC60684 | Lipid I97 |
Lipid I97 is a vitamin B5-derived ionizable lipid for mRNA vaccine delivery. Lipid I97 LNP specifically delivers the mRNA to the spleen and lymph nodes in model mice, induces balanced Th1/Th2 immune responses, and elicits the production of high levels of neutralizing antibodies with low toxicity.
More description
|
|
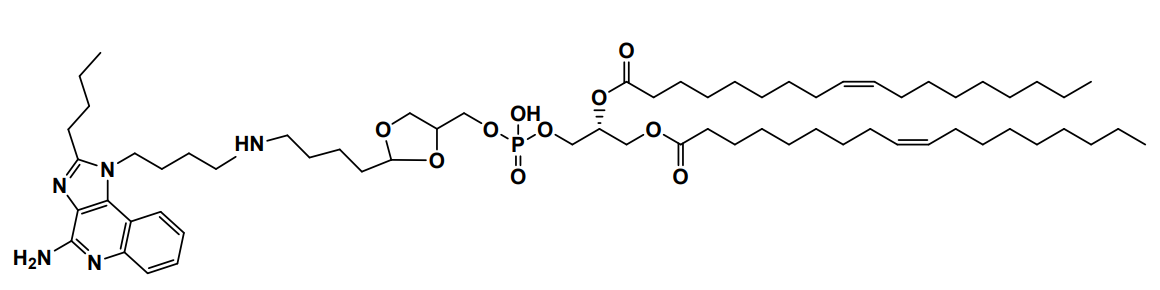
| DC60828 | YK-TLR-001 Featured |
YK-TLR-001 is a cyclic acetal-based ionizable lipid for mRNA delivery. YK-TLR-001 LNPs are demonstrated to enhance mRNA expression in the spleens and to induce exceptional maturation of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and to promote antigen presentation.
More description
|
|
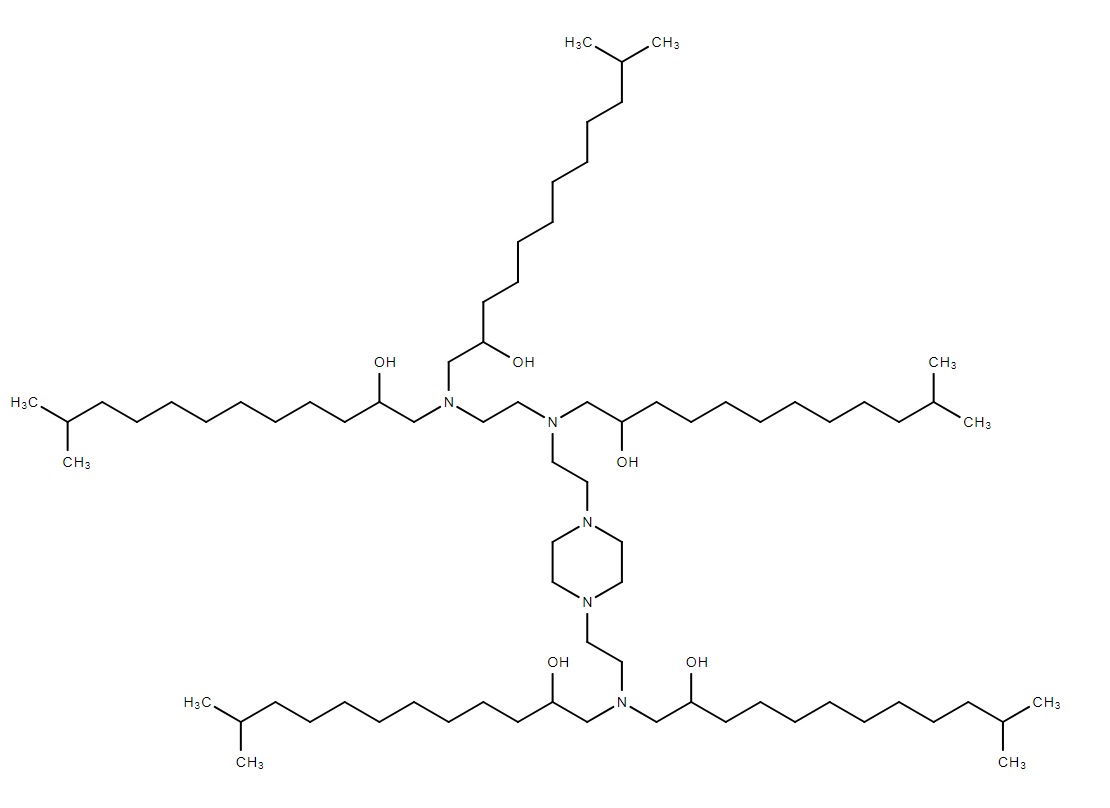
| DC13058 | E8i-200 |
E8i-200 is a novel Branched Endosomal Disruptor (BEND) ionizable lipid, designed to enhance the efficiency of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) in drug delivery, particularly for mRNA and protein delivery. Its unique structure, featuring terminal branching, improves endosomal escape, a critical step in the delivery of therapeutic cargo into cells.E8i-200 is designed to enhance endosomal escape, a key bottleneck in mRNA and protein delivery. Its terminal branching structure provides several advantages:Improved Endosomal Membrane Penetration: The branched structure allows E8i-200 to more effectively disrupt endosomal membranes, facilitating the release of mRNA and proteins into the cytoplasm.Enhanced Gene Editing Efficiency: E8i-200 has been shown to significantly improve the delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes, enabling efficient gene editing in vivo.E8i-200 significantly enhanced mRNA expression in the liver, outperforming traditional linear lipids like C12-200 in mouse models.E8i-200 effectively delivered CRISPR-Cas9 RNP complexes, achieving high editing efficiency in the liver, surpassing that of linear lipids.E8i-200 also showed high transfection efficiency and low cytotoxicity in T cells, making it a promising candidate for CAR-T cell engineering and other immunotherapies.
More description
|
|
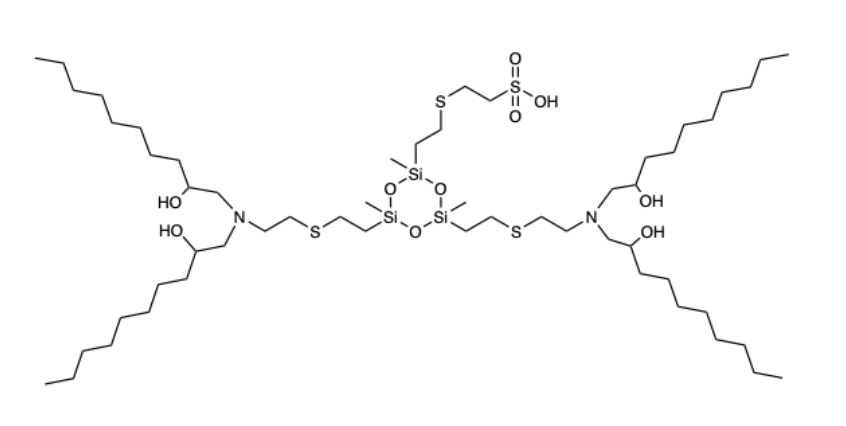
| DC60664 | Si12-C10 |
Si12-C10 is a siloxane-incorporated lipid for spleen-targeting mRNA delivery. The siloxane moieties enhance cellular internalization of mRNA-LNPs and improve their endosomal escape capacity, augmenting their mRNA delivery efficacy.
More description
|
|
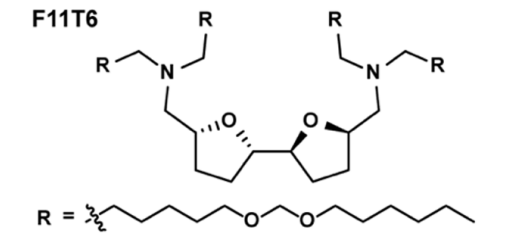
| DC60841 | Lipid F11T6 |
F11T6 is a next-generation lipid nanoparticle (LNP) optimized for ultra-efficient neuron-targeted mRNA delivery, featuring a dual-tetrahydrofuran (THF) core and four pH-responsive acetal tails. Its unique bis-THF architecture enhances lipid bilayer stability and promotes brain-specific biodistribution, achieving 16.4% GFP+ neurons in vivo—the highest reported among CNS-targeting LNPs. Cryo-EM reveals a compact spherical structure (Ø~150 nm) with 93.2% mRNA encapsulation efficiency, while THF-acetal synergy enables rapid endosomal escape (Pearson coefficient: 0.16 vs. 0.27 for F10T5). Preclinical studies show F11T6 leverages meningeal lymphatic transport for brain accumulation, yielding 13.0% neuron-specific tdTomato expression in Ai14 mice, surpassing F10T5 (8.93%) and SM102 (0.1%). Mechanistically, the dual-THF core strengthens interactions with lipoprotein receptors on brain endothelial cells, whereas acetal tails undergo acid-triggered hydrolysis in endosomes, releasing mRNA into the cytoplasm. Despite slightly higher liver/spleen accumulation than F10T5, toxicology assessments confirm no hepatorenal toxicity (BUN/ALT/AST within normal ranges) or histopathological changes. Co-localization analyses demonstrate superior penetration into deep brain regions like the hippocampus, critical for treating neurodegenerative disorders. With a LogD of 12.3, F11T6 balances lipid solubility and biodegradability, outperforming clinical benchmarks in both efficiency (40× SM102) and neuron specificity. This platform holds transformative potential for delivering CRISPR-Cas9, siRNA, or neurotrophic factors, particularly in diseases demanding high-dose CNS transfection with minimal off-target effects.
More description
|
|
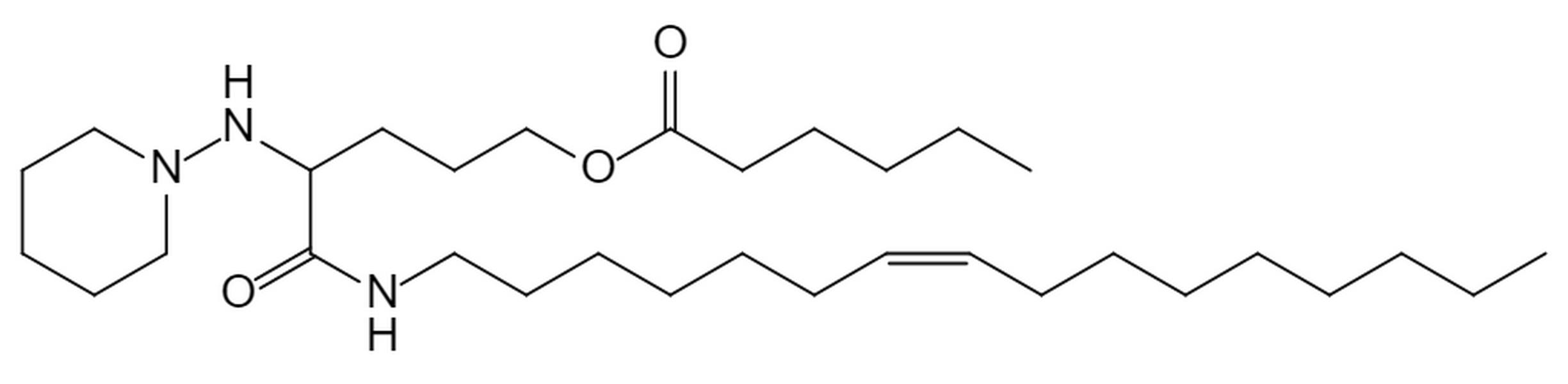
| DC60466 | Lipid H9 |
H9 is a new ionizable lipid driven from AI-Guided Ionizable Lipid Engineering (AGILE) platform for mRNA delivery. H9 LNPs shows superior mRNA transfection potency compared to LNPs containing (D-Lin-MC3-DMA).
More description
|
|
| DC82115 | BAMP-TK-12 |
BAMP-TK-12 is ROS‐degradable lipid used for gene/RNA delivery.
More description
|
|
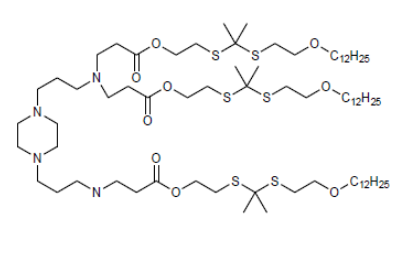
| DC60483 | LIS10W |
LIS10W is a sugar-alcohol-derived ionizable lipid with L-sorbitol as the precursor.
More description
|
|
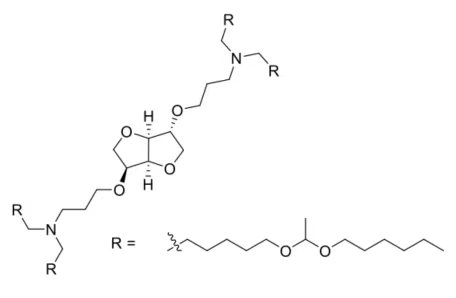
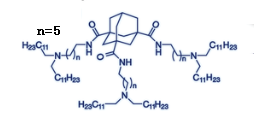
| DC88888 | Lipidoid XMaN6 |
Lipidoid XMaN6 is an ionizable lipid with universality was screened
out from the adamantyl-based ionizable lipid series, which could
functionally deliver highly diverse types of nucleic acids.
More description
|
|