 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Field of Application | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
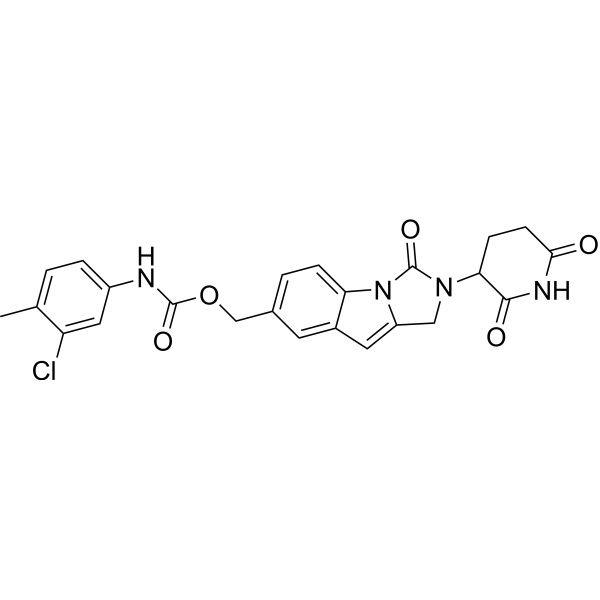
| DC67360 | GSPT1 degrader-4 Featured |
GSPT1 degrader-4 (compound 3) functions as a potent molecular glue targeting GSPT1, demonstrating a degradation concentration (DC50) of 25.4 nM. The compound exhibits strong anti-proliferative activity in CAL51 cells with an IC50 value of 39 nM.
More description
|
|
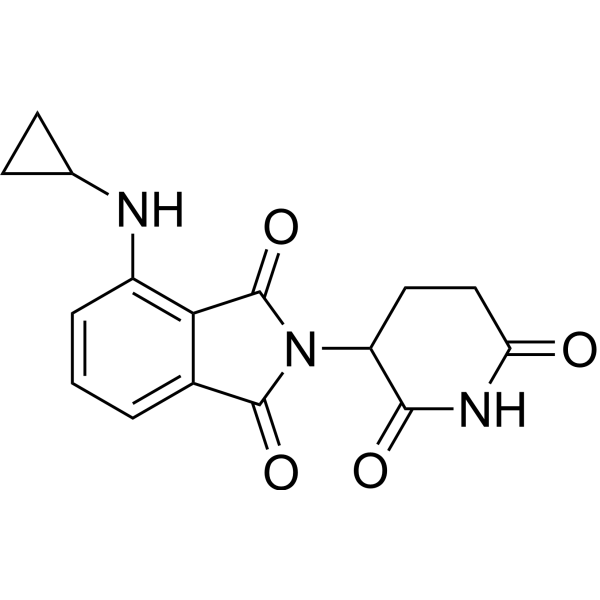
| DC67359 | FIZ1 degrader 1 Featured |
FIZ1 degrader 1 (compound 1) represents a novel IMiD-derived molecular glue compound engineered for targeted FIZ1 protein degradation.
More description
|
|
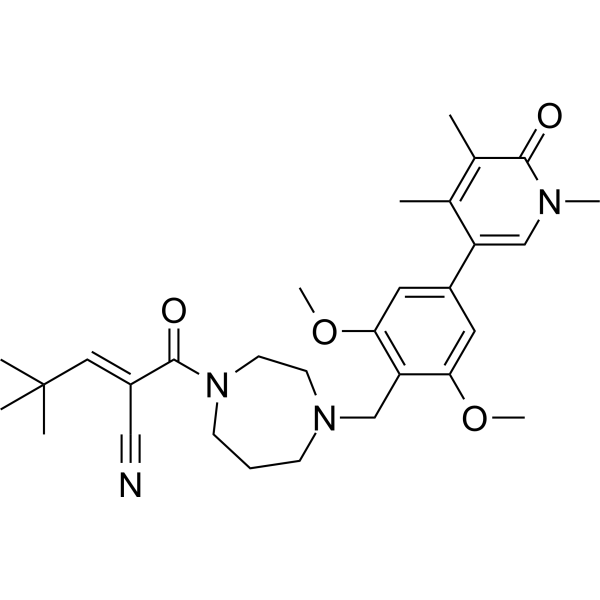
| DC67358 | BRD9 Degrader-4 Featured |
BRD9 Degrader-4 (BRD9c) is a highly potent bifunctional molecular glue compound that induces targeted degradation of BRD9, demonstrating exceptional activity with a DC50 value of 25 nM or lower. This degradative capability translates to significant anti-tumor efficacy, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent.
More description
|
|
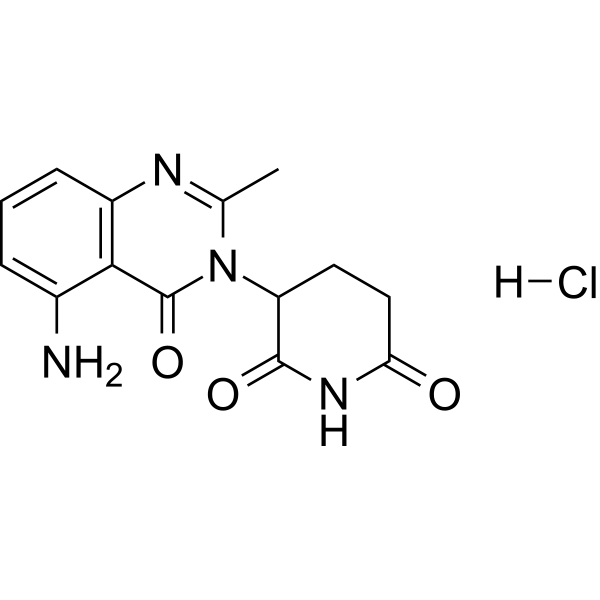
| DC31426 | Avadomide hydrochloride Featured |
Avadomide hydrochloride (CC-122 hydrochloride), the salt form of Avadomide (HY-100507), is an orally bioavailable cereblon-targeting agent that exerts potent antitumor and immunomodulatory effects. By modulating cereblon E3 ubiquitin ligase activity, this compound inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway and induces G1 phase cell cycle arrest, ultimately triggering apoptosis in PDAC cancer cells.
More description
|
|
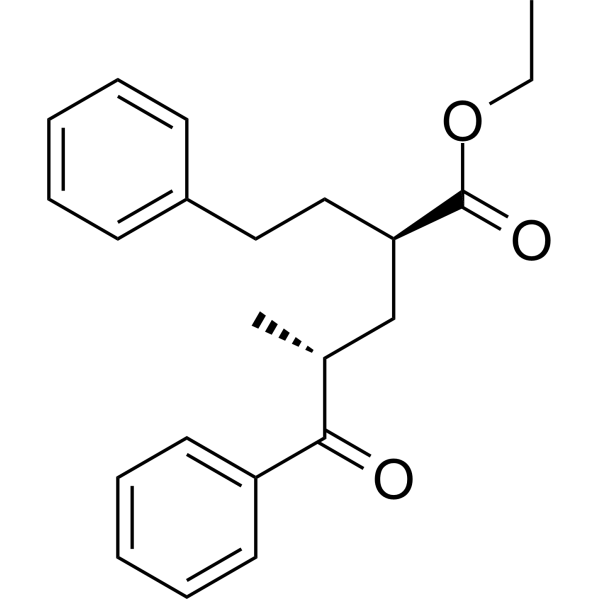
| DC67356 | IPS-06061 Featured |
IPS-06061 is an orally bioavailable molecular glue that mediates targeted degradation of KRAS G12D through formation of a CRBN-KRASG12D-IPS06061 ternary complex, demonstrating potent activity with a DC50 below 500 nM.
More description
|
|
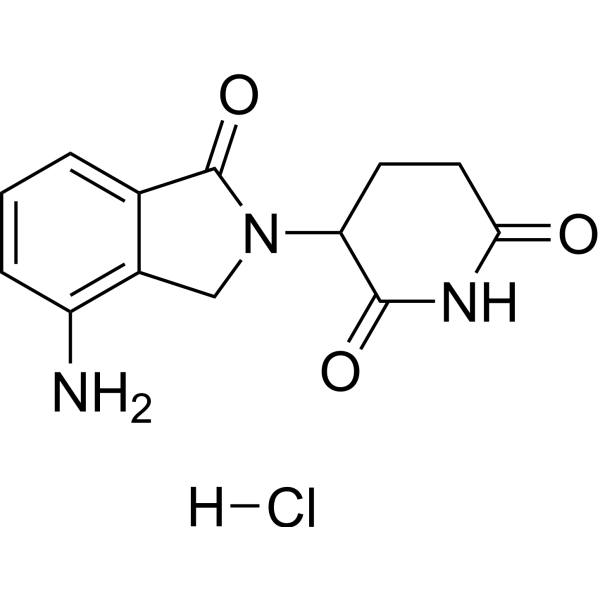
| DC67354 | Lenalidomide hydrochloride Featured |
Lenalidomide hydrochloride (CC-5013 hydrochloride), a thalidomide-derived molecular glue, functions as an orally bioavailable immunomodulatory agent. By binding to the ubiquitin E3 ligase cereblon (CRBN), it recruits the CRBN-CRL4 complex to induce selective ubiquitination and degradation of lymphoid transcription factors IKZF1 and IKZF3. This mechanism underlies its potent activity against mature B-cell malignancies, including multiple myeloma, while also stimulating IL-2 secretion from T cells.
More description
|
|
| DC28973 | (R)-Thalidomide Featured |
The R-enantiomer of thalidomide, (R)-(+)-thalidomide, exhibits sedative effects distinct from its racemic counterpart.
More description
|

|
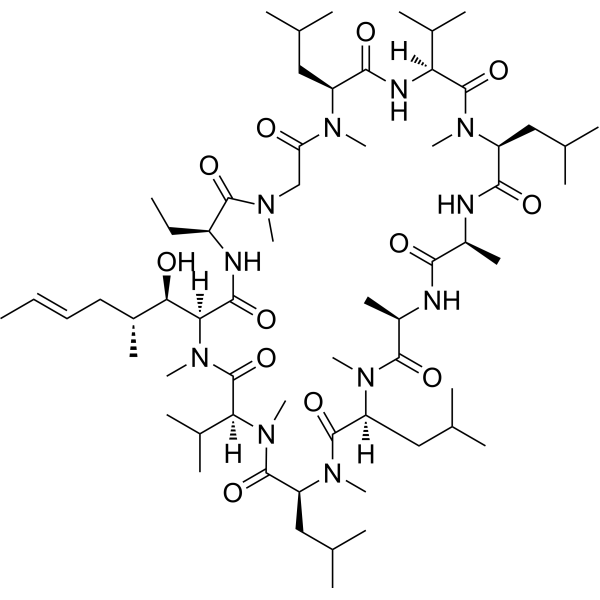
| DC4115 | Cyclosporin A Featured |
Cyclosporin A (Cyclosporine A) is a potent immunosuppressive agent commonly administered after allogeneic organ transplants to suppress immune system activity and prevent rejection.
More description
|
|
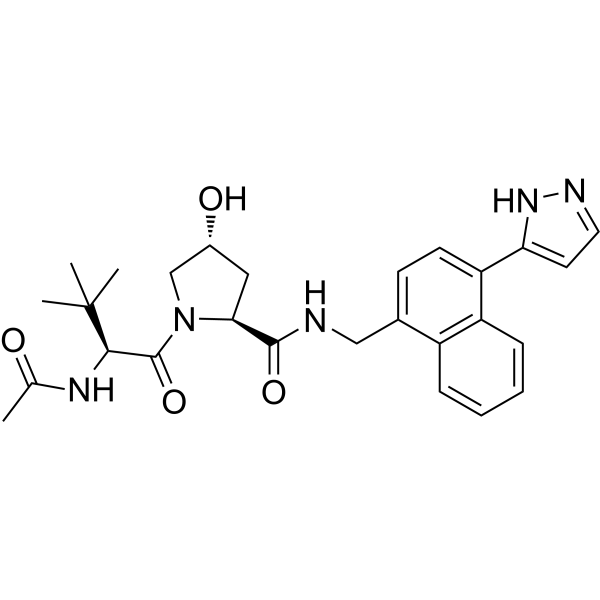
| DC60654 | CDO1 degrader-1 Featured |
CDO1 Degrader-1 (Compound 8) is a molecular glue that targets cysteine dioxygenase (CDO1) for degradation.
More description
|
|
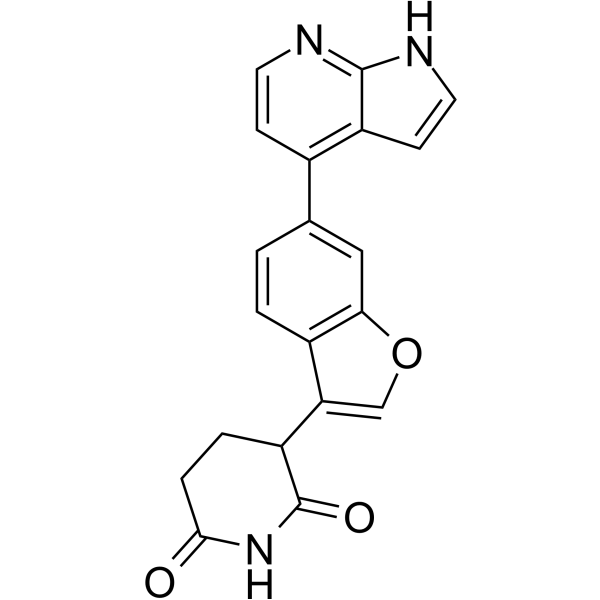
| DC67353 | HuR degrader 2 Featured |
HuR Degrader 2 (Compound 3) is a molecular glue that targets the RNA-binding protein HuR, degrading ~30% of HuR at 0.1 μM. It inhibits the proliferation of Colo-205 cancer cells with an IC50 ≤ 200 nM and exhibits high cereblon binding affinity, as evidenced by an HTRF ratio < 0.02.
More description
|
|
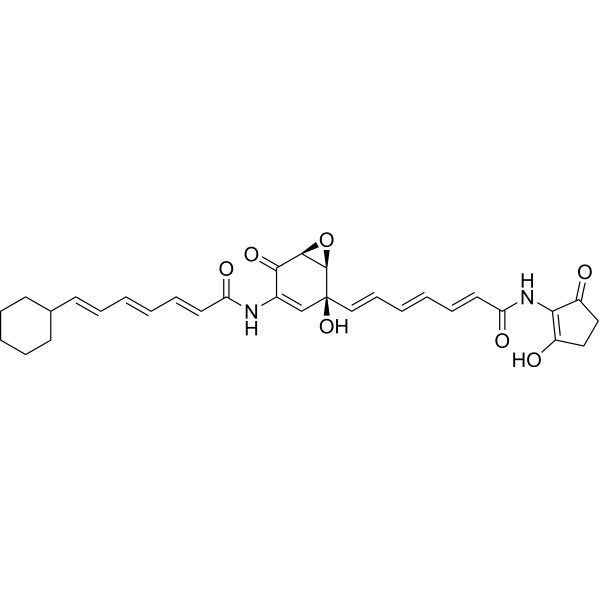
| DC36190 | Asukamycin Featured |
Asukamycin, a macrolide polyketide derived from Streptomyces nodosus subsp. asukaensis, exhibits dual antimicrobial and antitumor activities. This natural product demonstrates broad-spectrum antibiotic properties while selectively inhibiting tumor cell proliferation through caspase-8/3-mediated apoptosis induction.
More description
|
|
| DC10832 | (E/Z)-4-hydroxy Tamoxifen Featured |
(E/Z)-4-hydroxy Tamoxifen is an active metabolite of tamoxifen that is formed by the action of cytochrome P450 2D6 in human liver.
More description
|

|
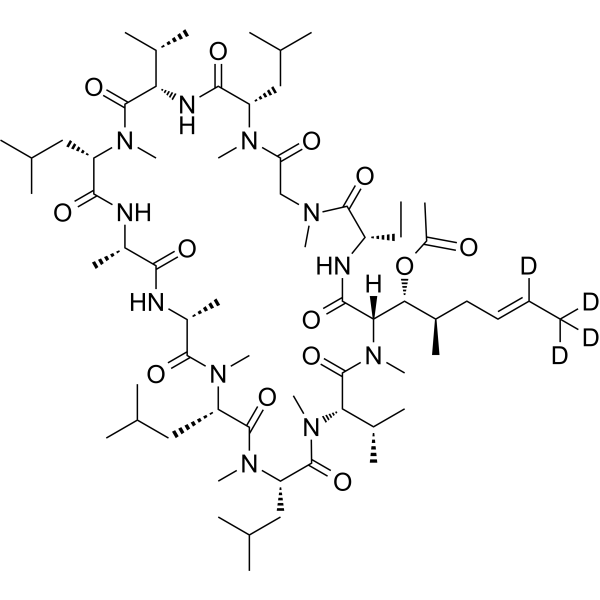
| DC67350 | Cyclosporin A acetate-d4 Featured |
Cyclosporin A acetate-d4 is a deuterium-enriched analog of the cyclic undecapeptide immunosuppressant, featuring four strategic deuterium substitutions that improve metabolic stability while preserving its dual mechanism of action.
More description
|
|
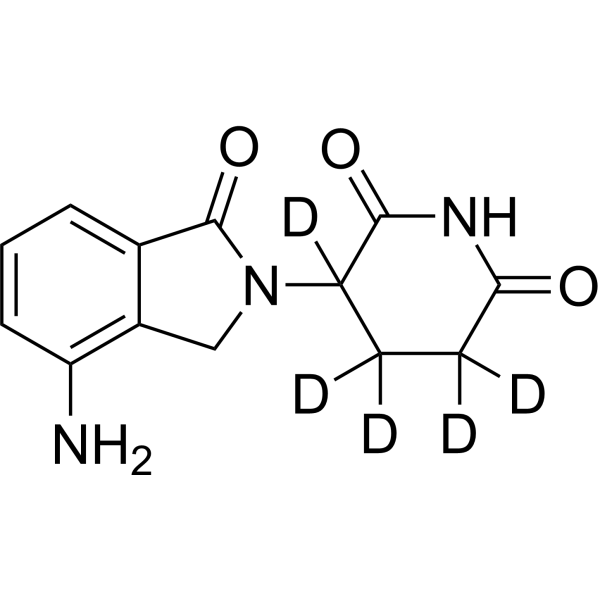
| DC67349 | Lenalidomide-d5 Featured |
Lenalidomide-d5 is a deuterium-enriched analog of the clinically validated immunomodulator lenalidomide (CC-5013), featuring five strategic deuterium substitutions that improve metabolic stability while preserving its molecular glue mechanism.
More description
|
|
| DC67348 | Thalidomide-d4 Featured |
Thalidomide-d4 is a deuterium-enriched analog of the prototypic immunomodulatory drug thalidomide, featuring four strategically positioned deuterium substitutions. This isotopically labeled compound retains the parent molecule's ability to bind cereblon (CRBN) with high affinity (Kd ≈ 250 nM), thereby modulating the activity of the CUL4-RBX1-DDB1-CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase complex.
More description
|
.gif)
|
| DC65182 | DSG-PEG2000 Featured |
DSG-PEG2000 is used for liposome preparation. DSG-PEG, MW 2,000 has become known for lipid nanoparticle (LNP) preparation for siRNA (small interfering RNA) delivery research. .
More description
|

|
| DC67347 | DMG-PEG 1000 (14:1) Featured |
A methoxy-terminated PEG1000 functionalized with 1,2-dimyristoleoyl-sn-glycerol via an ether linkage. This compound may be used in the formulation of lipid nanoparticles (LNP's) for delivery applications. Reagent grade, for research purpose. Please contact us for GMP-grade inquiries.
More description
|

|
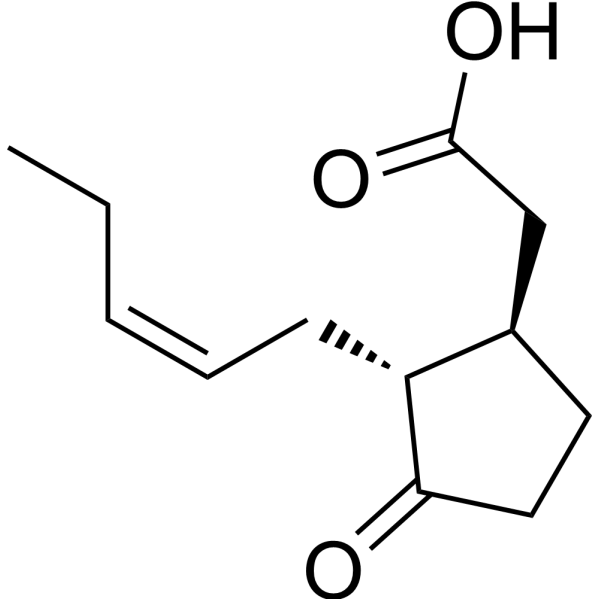
| DC67346 | Jasmonic acid Featured |
Jasmonic acid ((-)-Jasmonic acid) is a plant growth regulator and a derivative of α-Linolenic acid (HY-N0728). Jasmonic acid signaling can also induce the MAP kinase cascade pathway, calcium channel, and many processes that interact with signaling molecules.
More description
|
|
| DC47108 | Thalidomide-NH-CBP/p300 ligand 2 Featured |
Thalidomide-NH-CBP/p300 ligand 2 (P-007) represents a novel PROTAC architecture that simultaneously targets CBP and p300 for proteasomal degradation.
More description
|
|
| DCS-103 | Lycorine Featured |
Lycorine is a natural alkaloid extracted from the Amaryllidaceae plant. Lycorine is a potent and orally active SCAP inhibitor with a Kd value 15.24 nM. Lycorine downregulates the SCAP protein level without changing its transcription. Lycorine is also a melanoma vasculogenic inhibitor. Lycorine can be used for the study of prostate cancer and metabolic diseases.
More description
|

|
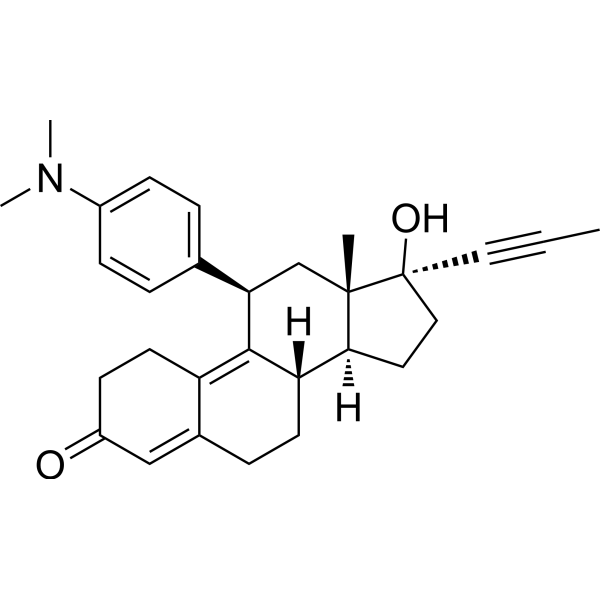
| DC31256 | Mifepristone (RU486) Featured |
Mifepristone (RU-486) is a potent steroidal antagonist exhibiting subnanomolar affinity for progesterone receptors (PR IC₅₀ = 0.2 nM) and nanomolar activity against glucocorticoid receptors (GR IC₅₀ = 2.6 nM). This dual-receptor modulator competitively blocks endogenous hormone binding while inducing distinct conformational changes that prevent coactivator recruitment, demonstrating differential antagonism between PR and GR signaling pathways.
More description
|
|
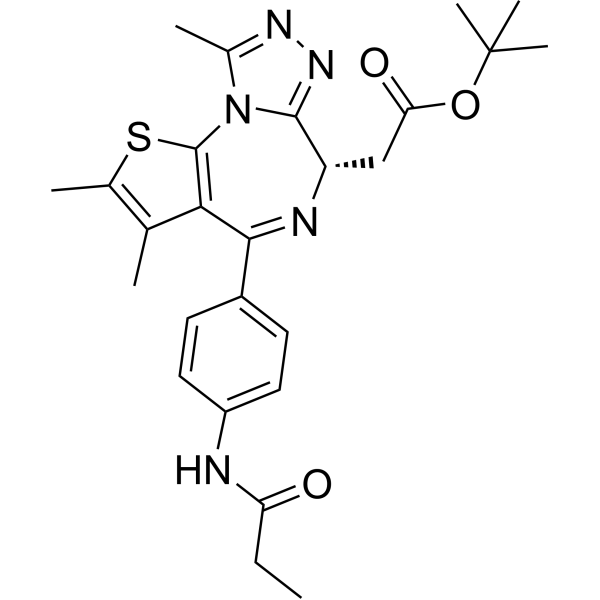
| DC67345 | MMH1-NR Featured |
MMH1-NR is a purpose-designed negative control compound for the DCAF16-based BRD4 degrader MMH1, featuring a strategically incorporated non-reactive ethyl group that abolishes degradation activity while maintaining structural similarity.
More description
|
|
| DC67344 | Pomalidomide-d3 Featured |
Pomalidomide-d3 is a stable isotope-labeled analog of the clinically important immunomodulatory drug Pomalidomide, where three hydrogen atoms are replaced with deuterium.
More description
|
.gif)
|
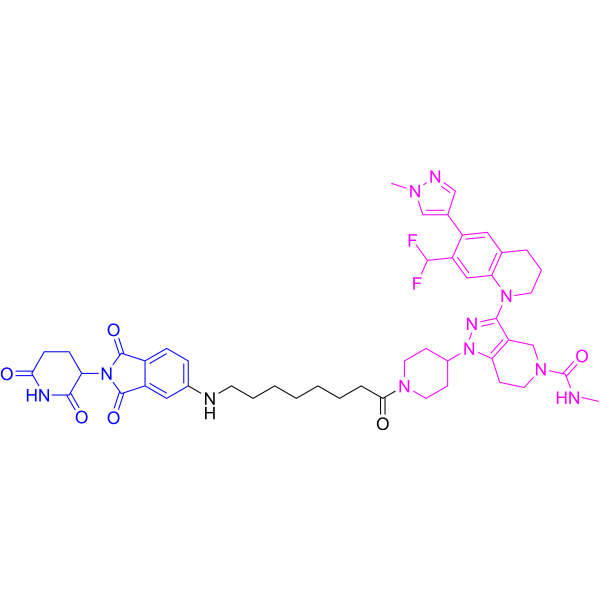
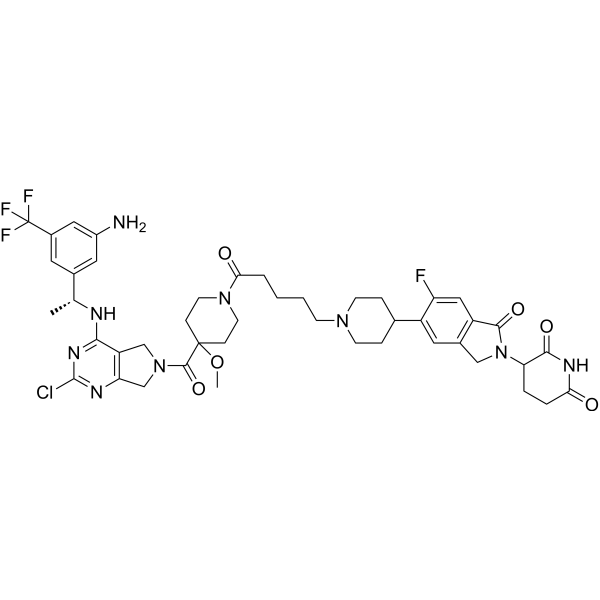
| PR0049567 | BTX-7312 Featured |
BTX-7312 is a cereblon-based SOS1 bifunctional degrader and a molecular glue. BTX-7312 reduces downstream signaling markers pERK and pS6 and shows antiproliferative activity in various KRAS-mutated cells.
More description
|
|
| DC67342 | BRD4 degrader-1 Featured |
BRD4 Degrader-1 (Compound ML 1-50) represents a novel class of monovalent, covalent molecular glues that selectively degrade bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) through an E3 ligase-dependent mechanism. Unlike traditional bivalent PROTACs, this compound utilizes a unique covalent binding strategy to recruit the DCAF16 E3 ubiquitin ligase, inducing potent degradation of both BRD4 long (BRD4-L) and short (BRD4-S) isoforms in cellular systems.
More description
|
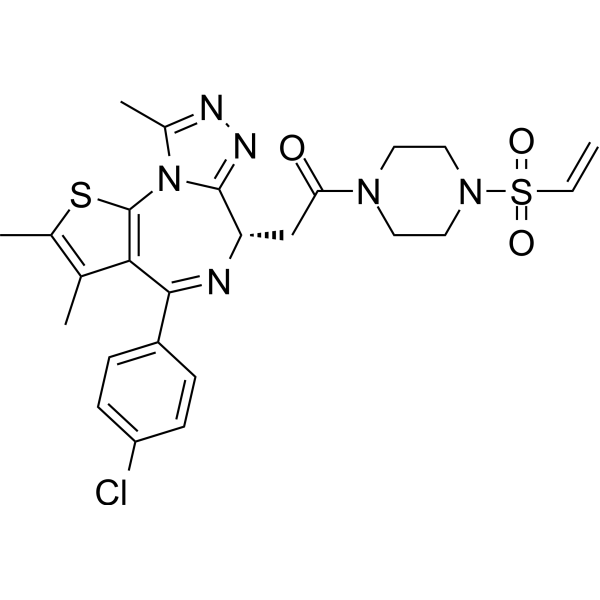
|
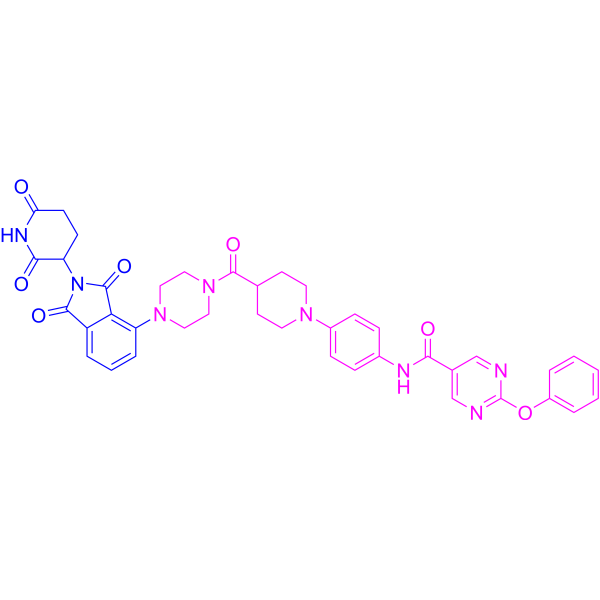
| DC49208 | PROTAC(H-PGDS)-7 Featured |
PROTAC(H-PGDS)-7 represents a breakthrough in targeted protein degradation, achieving unprecedented picomolar efficacy (DC50 = 17.3 pM) against hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase (H-PGDS).
More description
|
|
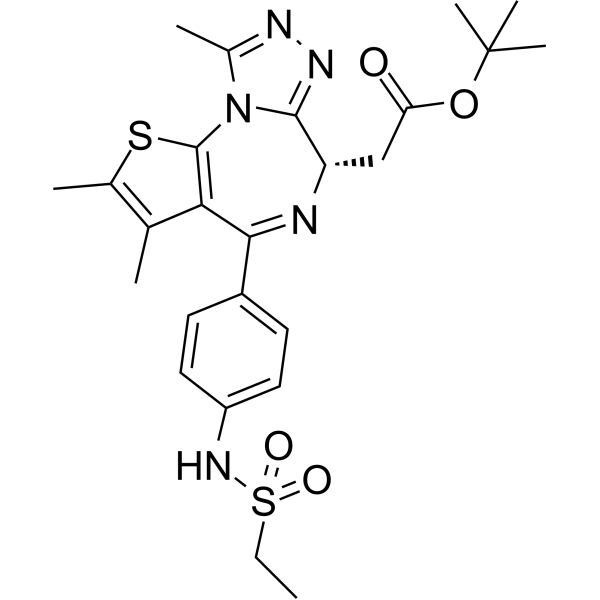
| DC67341 | MMH2-NR Featured |
MMH2-NR serves as an essential negative control compound for MMH2, a novel DCAF16-dependent BRD4 degrader. While MMH2 mediates targeted protein degradation by recruiting the CUL4-DCAF16 E3 ligase complex to bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4), MMH2-NR is structurally analogous but lacks degradation activity, making it critical for mechanistic validation.
More description
|
|
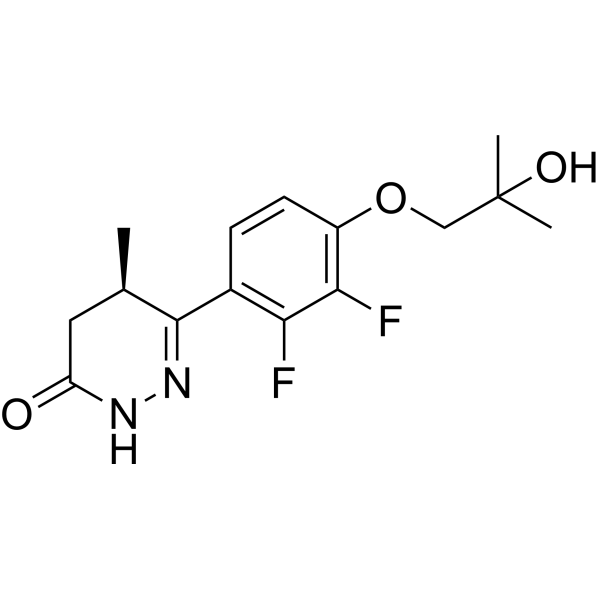
| DC60624 | OPB-171775 Featured |
OPB-171775 represents a breakthrough in GIST treatment as a first-in-class, non-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (non-TKI) compound that demonstrates potent antitumor activity independent of KIT mutation status. Unlike conventional TKIs that target oncogenic kinases, OPB-171775 operates through an innovative mechanism by orchestrating a protein-protein interaction between phosphodiesterase 3A (PDE3A) and Schlafen 12 (SLFN12).
More description
|
|
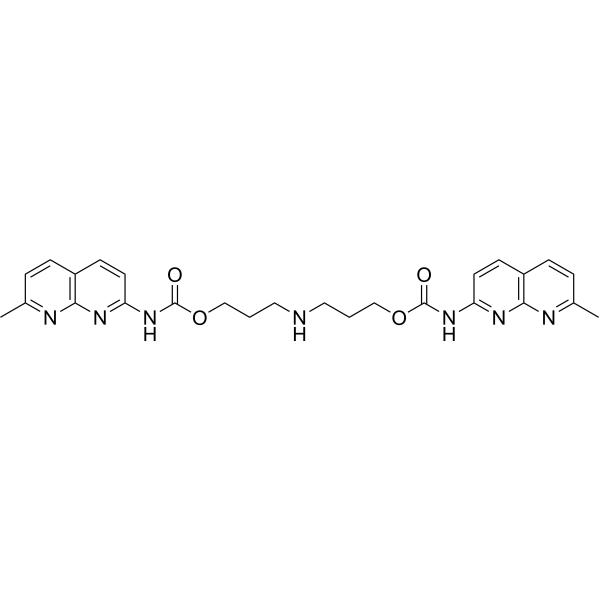
| DC67340 | Naphthyridine carbamate dimer Featured |
Naphthyridine Carbamate Dimer (NCD) is a synthetic DNA molecular glue engineered to induce programmable structural rearrangements in functional DNA. Unlike conventional small-molecule binders, NCD operates by non-covalently crosslinking specific DNA sequences, enforcing conformational changes that modulate DNA’s biological activity.
More description
|
|
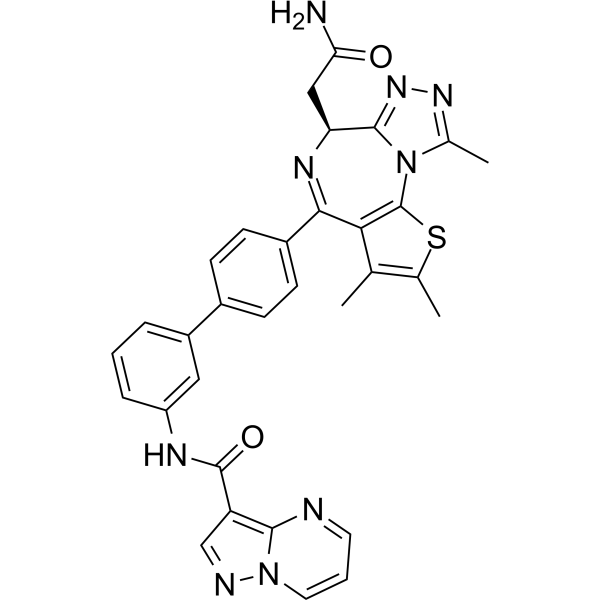
| DC67339 | PLX-3618 Featured |
PLX-3618 is a targeted molecular glue that induces the degradation of BRD4, a key epigenetic regulator implicated in cancer. It achieves potent BRD4 degradation (DC50 = 12.2 nM) by recruiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase adapter DCAF11, which tags BRD4 with polyubiquitin chains for proteasome-mediated destruction.
More description
|
|