 To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
To enhance service speed and avoid tariff delays, we've opened a US warehouse. All US orders ship directly from our US facility.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Field of Application | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
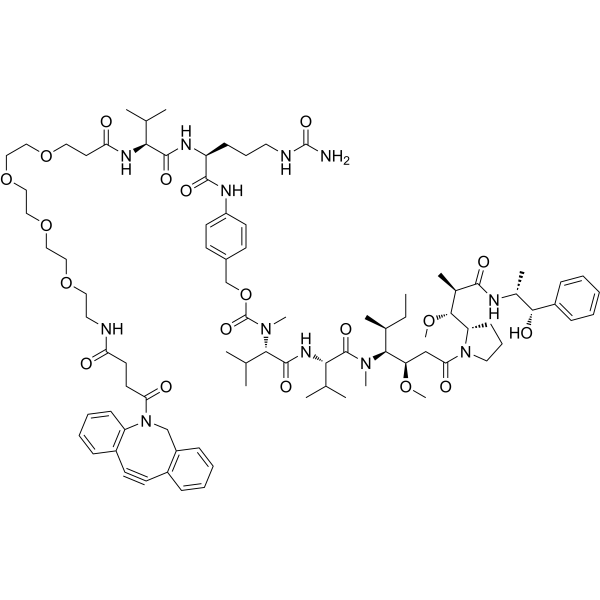
| DC67846 | DBCO-PEG4-VC-PAB-MMAE Featured |
DBCO-PEG4-VC-PAB-MMAE consists a ADC linker (DBCO-PEG4-VC-PAB) and a tubulin polymerization inhibitor MMAE (HY-15162). DBCO-PEG4-VC-PAB-MMAE can be used in the synthesis of antibody-agent conjugates (ADCs). MMAE is a synthetic derivative of dolastatin 10 and functions as a potent mitotic inhibitor by inhibiting tubulin polymerization. DBCO-PEG4-VC-PAB-MMAE is a click chemistry reagent, it contains a DBCO group that can undergo strain-promoted alkyne-azide cycloaddition (SPAAC) with molecules containing Azide groups.
More description
|
|
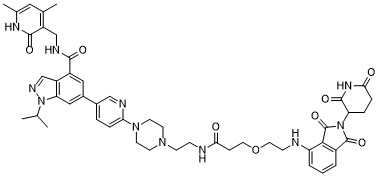
| DC70618 | MS177 Featured |
MS 177 (MS-177) is a potent and selective EZH2 degarder (PROTAC) based on EZH2 inhibitor C24 with CRBN ligand pomalidomide with DC50 of 0.2 uM in EOL-1 cells.MS177 effectively degraded cellular EZH2-PRC2, suppressed global H3K27me3 in leukaemia cells.MS177 exhibited half-maximal degradation concentration (DC50) values of 0.2 ± 0.1 μM and 1.5 ± 0.2 μM, and maximum degradation (Dmax) values of 82% and 68%, respectively, in EOL-1 and MV4;11 cells.MS177 efficiently suppresses EZH2-PRC2 functions, also efficiently induces Myc degradation in cancer cells, suppresses EZH2-PRC2 functions.MS177 efficiently induces leukaemia cell growth inhibition, apoptosis and cell cycle progression arrest, which is more effective than EZH2 inhibitors. MS177 (i.p. injection, 50-1 g/kg) represses AML growth without apparent toxicity in PDX models.
More description
|
|
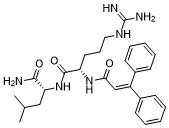
| DCC4404 | Rf3286 Featured |
Novel Highly Selective Neuropeptide FF1 Receptor Antagonist, Potently Preventing Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia
More description
|
|
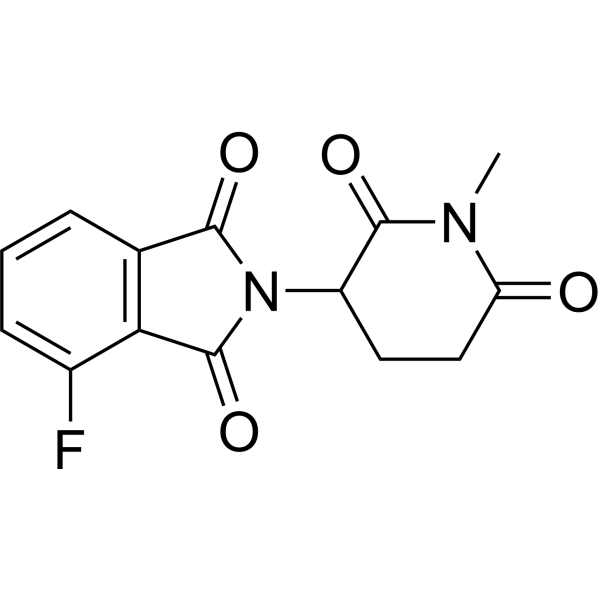
| DC67845 | N-Me-Thalidomide 4-fluoride Featured |
N-Me-Thalidomide 4-fluoride is a ligand for E3 ligase, used for the synthesis of Anti-inflammatory agent 70 .
More description
|
|
| DC67844 | CRBN ligand-880 Featured |
CRBN ligand-880 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase cereblon (CRBN) ligand used to recruit the cereblon protein. CRBN ligand-880 can be linked to a target protein ligand via a linker to form a PROTAC.
More description
|
|
| DC11387 | Erdafitinib Featured |
Erdafitinib (JNJ-42756493) is a potent and orally available FGFR family inhibitor; inhibits FGFR1-4 with IC50 values of 1.2, 2.5, 3.0 and 5.7nM, respectively.
More description
|
|
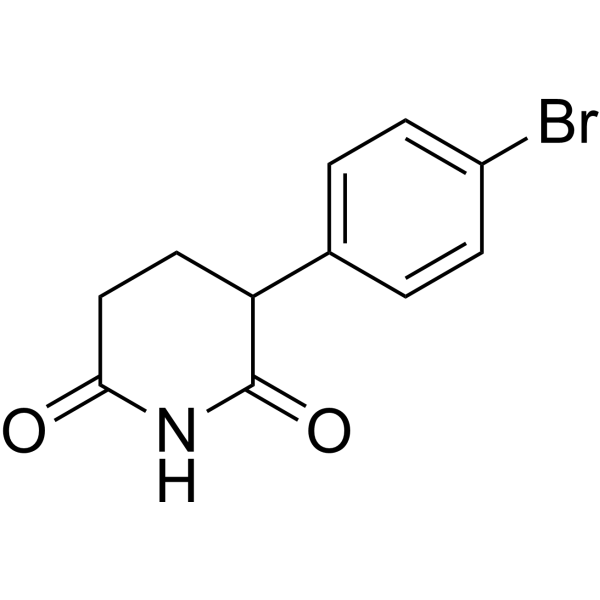
| DC67843 | 6-hydroxy-1-isopropyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-4-carboxylic acid Featured |
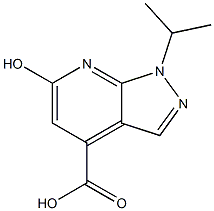
|
|
| DC67842 | Tert-butyl 4-(4-aMino-3-Methoxyphenyl)piperazine-1-carboxylate Featured |
piperazine-1-carboxylate.gif)
|
|
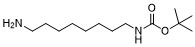
| DC60149 | 1-Boc-1,8-diaminooctane Featured |
tert-butyl (8-aminooctyl)carbamate can be used as a PROTAC linker in the synthesis of PROTACs. tert-butyl (8-aminooctyl)carbamate is an alkane chain with terminal amine and Boc-protected amino groups. Amine group is reactive with carboxylic acids, activated NHS esters, carbonyls (ketone, aldehyde) etc. The Boc group can be deprotected under mild acidic conditions to form the free amine.
More description
|
|
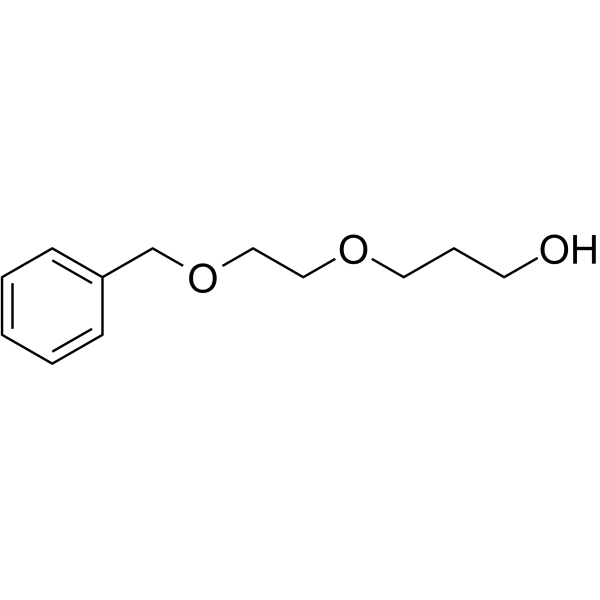
| DC44034 | Benzyl-PEG1-propanol Featured |
Benzyl-PEG1-propanol is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
More description
|
|
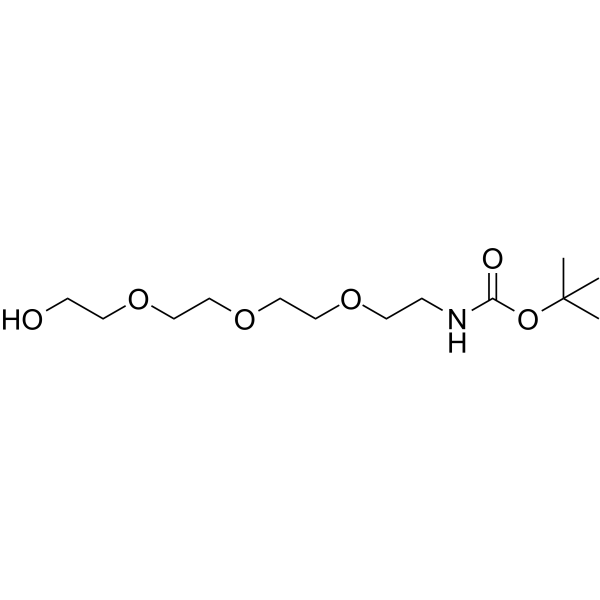
| DC67841 | Boc-NH-PEG4 Featured |
Boc-NH-PEG4 (PROTAC Linker 12) is a PEG-based PROTAC linker can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
More description
|
|
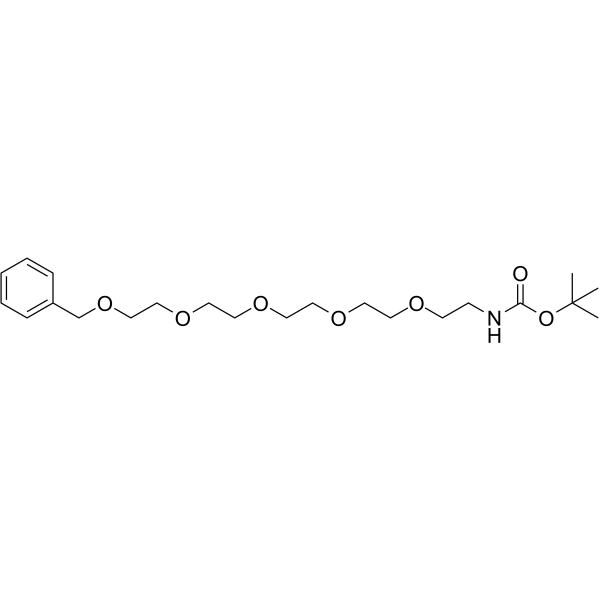
| DC44429 | Benzyl-PEG5-NHBoc Featured |
Benzyl-PEG5-NHBoc is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
More description
|
|
| DC67840 | tert-Butyl (6-hydroxyhexyl)carbamate Featured |
tert-Butyl (6-hydroxyhexyl)carbamate is a PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
More description
|
carbamate.gif)
|
| DC67839 | tert-Butyl N-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)carbamate (Standard) Featured |
tert-Butyl N-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)carbamate (Standard) is the analytical standard of tert-Butyl N-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)carbamate. This product is intended for research and analytical applications.
More description
|
carbamate (Standard).gif)
|
| DC67838 | 3-amino-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione hydrochloride Featured |
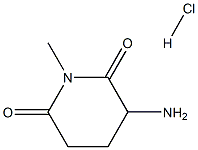
|
|
| DC67837 | (S)-3-Amino-piperidine-2,6-dione hydrochloride Featured |
-3-Amino-piperidine-2,6-dione hydrochloride.gif)
|
|
| DC67836 | (R)-3-Aminopyrrolidine-2,5-dione Featured |
(R)-3-Aminopyrrolidine-2,5-dione is a potential anticonvulsant agent and its derivatives have comparable in vivo efficacy.
More description
|
-3-Aminopyrrolidine-2,5-dione.gif)
|
| DC67835 | (S)-3-Aminopyrrolidine-2,5-dione Featured |
(S)-3-Aminopyrrolidine-2,5-dione is a potential anticonvulsant agent and its derivatives have comparable in vivo potency.
More description
|
-3-Aminopyrrolidine-2,5-dione.gif)
|
| DC67834 | 1H-Thieno[2,3-e]-1,4-diazepine-3-acetic acid, 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-6,7-diMethyl-2-oxo-, 1,1-diMethylethyl ester, (3S)- Featured |
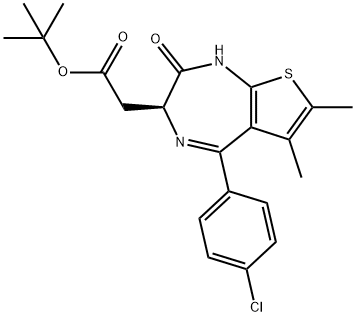
|
|
| DC67833 | I-BET762 carboxylic acid Featured |
I-BET762 carboxylic acid (Molibresib carboxylic acid) is an I-BET762-based warhead ligand for conjugation reactions of PROTAC targeting on BET. I-BET762 carboxylic acid (Molibresib carboxylic acid) is a BRD4 inhibitor with a pIC50 of 5.1.
More description
|
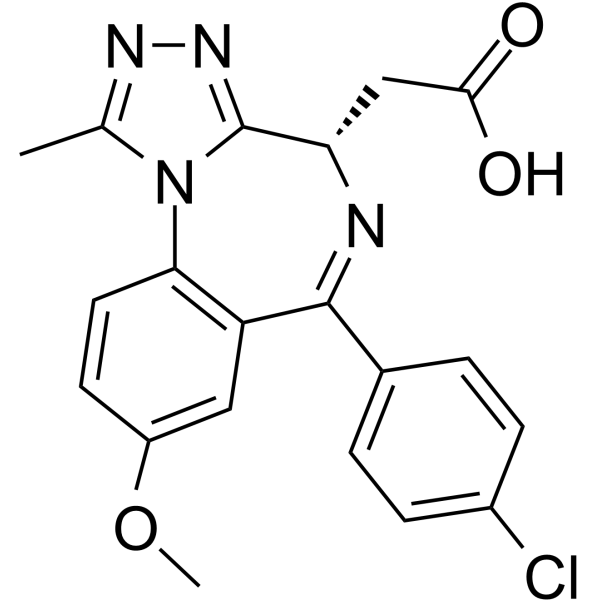
|
| DC67832 | (S,S,S)-AHPC-Boc Featured |
(S,S,S)-AHPC-Boc is the isomer of (S,R,S)-AHPC-Boc (HY-123109), and can be used as an experimental control. (S,R,S)-AHPC-Boc (VH032-Boc) is a ligand used in the recruitment of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) protein.
More description
|
-AHPC-Boc.gif)
|
| DC10656 | (+)-JQ1 carboxylic acid Featured |
(+)-JQ1 carboxylic acid is the carboxylic acid form of (+)-JQ1 for derivative synthesis.
More description
|

|
| DC67831 | 2-(aminomethyl)-5-(4-methylthiazol-5-yl)phenol hydrochloride Featured |
-5-(4-methylthiazol-5-yl)phenol hydrochloride.gif)
|
|
| DC67830 | CRBN ligand-798 Featured |
CRBN ligand-798 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase cereblon (CRBN) ligand used to recruit the cereblon protein. CRBN ligand-798 can be linked to a target protein ligand via a linker to form a PROTAC.
More description
|
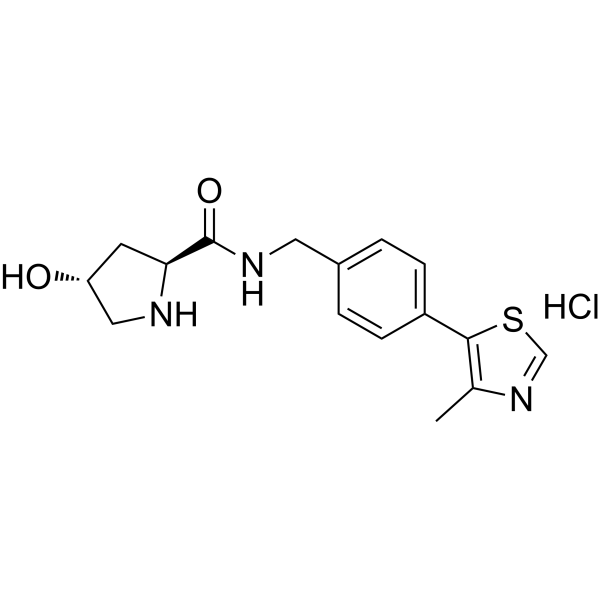
|
| DC65111 | CPD101077-B HCl Featured |
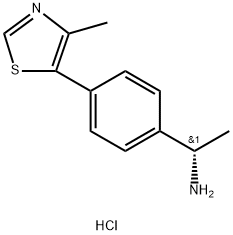
|
|
| DC65174 | CPD1584-B3 HCl Featured |
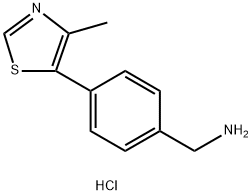
|
|
| DC67829 | 1-(Boc-L-tert-leucinyl)-(4S)-4-hydroxy-D-proline Featured |
-(4S)-4-hydroxy-D-proline.gif)
|
|
| DC67828 | CRBN ligand-878 Featured |
CRBN ligand-878 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase cereblon (CRBN) ligand used to recruit the cereblon protein. CRBN ligand-878 can be linked to a target protein ligand via a linker to form a PROTAC.
More description
|
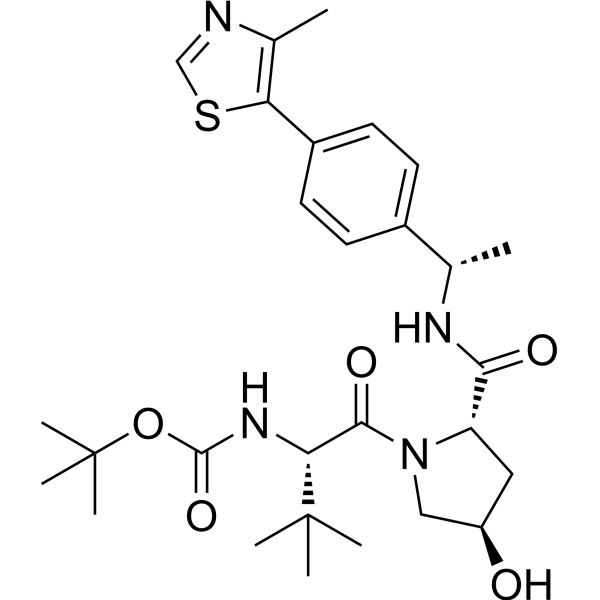
|
| DC22335 | E3 ligase Ligand 1A Featured |
E3 ligase Ligand 1A is a ligand of E3 ligase, used in PROTAC technology; E3 ligase Ligand 1A can be used in the research of cancer.
(S,R,S)-AHPC-Me (VHL ligand 2) is the (S,R,S)-AHPC-based VHL ligand used in the recruitment of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)
More description
|

|
| DC11578 | VHL Ligand 3 Featured |
A VHL ligand for PROTAC..
More description
|

|